Abstract
Rationale
A substantial number of patients do not respond sufficiently to antidepressant drugs and are therefore often co-medicated with lithium as an augmentation strategy. However, the neurochemical rationale behind this strategy needs to be further clarified.
Objectives
We examined the effect of chronic citalopram and subchronic lithium, alone or in combination, on (a) serum levels of citalopram and lithium, (b) animal behaviour and (c) hippocampal serotonin (5-HT) and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) levels. Furthermore, we examined the serum level of citalopram and hippocampal 5-HT following one acute citalopram injection.
Methods
Microdialysis in the freely moving animals was used to determine hippocampal 5-HT and 5-HIAA. The animal behaviour was examined in the open field and forced swim test.
Results
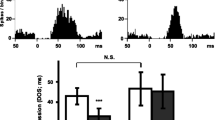
We found that chronic administration of citalopram (20 mg/kg/24 h s.c.) significantly increased the 5-HT baseline relative to vehicle-treated rats. Addition of subchronic lithium (60 mmol/kg chow pellet p.o.) to chronic citalopram therapy further elevated the 5-HT levels. Moreover, we found acute citalopram (5 mg/kg s.c.) to increase the 5-HT level. The immobility time in the FST and the locomotion in the OF were unaffected by any treatments.
Conclusions
The present results support the assumption that increases in hippocampal 5-HT neurotransmission may be important in the augmentatory effect of lithium.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai F, Li X, Clay M, Lindstrom T, Skolnick P (2001) Intra- and interstrain differences in models of "behavioral despair". Pharmacol Biochem Behav 70:187–192
Baptista TJ, Hernandez L, Burguera JL, Burguera M, Hoebel BG (1990) Chronic lithium administration enhances serotonin release in the lateral hypothalamus but not in the hippocampus in rats. A microdialysis study. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 82:31–41
Bauer M, Dopfmer S (1999) Lithium augmentation in treatment-resistant depression: meta-analysis of placebo-controlled studies. J Clin Psychopharmacol 19:427–434
Baumann P, Nil R, Souche A, Montaldi S, Baettig D, Lambert S, Uehlinger C, Kasas A, Amey M, Jonzier-Perey M (1996) A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of citalopram with and without lithium in the treatment of therapy-resistant depressive patients: a clinical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacogenetic investigation. J Clin Psychopharmacol 16:307–314
Bel N, Artigas F (1992) Fluvoxamine preferentially increases extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in the raphe nuclei: an in vivo microdialysis study. Eur J Pharmacol 229:101–103
Bel N, Artigas F (1993) Chronic treatment with fluvoxamine increases extracellular serotonin in frontal cortex but not in raphe nuclei. Synapse 15:243–245
Broderick P, Lynch V (1982) Behavioral and biochemical changes induced by lithium and l-tryptophan in muricidal rats. Neuropharmacology 21:671–679
Cappeliez P, White N, Duhamel JR (1982) Effect of serotonin depletion induced by p-chloroamphetamine on changes in rats' activity levels-produced by lithium. Neuropsychobiology 8:129–134
Collard KJ, Roberts MH (1975) Proceedings: the effects of chronic lithium administration on the metabolism of l-tryptophan in the rat forebrain. Br J Pharmacol 55:268P
Connor TJ, Kelly JP, Leonard BE (1997) Forced swim test-induced neurochemical, endocrine, and immune changes in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 58:961–967
Connor TJ, Kelliher P, Shen Y, Harkin A, Kelly JP, Leonard BE (2000) Effect of subchronic antidepressant treatments on behavioral, neurochemical, and endocrine changes in the forced-swim test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:591–597
Corrodi H, Fuxe K, Hokfelt T, Schou M (1967) The effect of lithium on cerebral monoamine neurons. Psychopharmacology 11:345–353
De Montigny C (1994) Lithium addition in treatment-resistant depression. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 9:S231–S235
Detke MJ, Johnson J, Lucki I (1997) Acute and chronic antidepressant drug treatment in the rat forced swimming test model of depression. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 5:107–112
Dufour H, Bouchacourt M, Thermoz P, Viala A, Phak Rop P, Gouezo F, Durand A, Hopfner Petersen HE (1987) Citalopram—a highly selective 5-HT uptake inhibitor—in the treatment of depressed patients. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 2:225–237
Fuller RW (1994) Uptake inhibitors increase extracellular serotonin concentration measured by brain microdialysis. Life Sci 55:163–167
Gorka Z, Wojtasik E, Kwiatek H, Maj J (1979) Action of serotonin mimetics in the behavioral despair test in rats. Commun Psychopharmacol 3:133–136
Grahame-Smith DG, Green AR (1974) The role of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine in the hyperactivity produced in rats by lithium and monoamine oxidase inhibition. Br J Pharmacol 52:19–26
Grof P (1998) Has the effectiveness of lithium changed? Impact of the variety of lithium's effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 19:183–188
Grove WM, Andreasen NC (1982) Simultaneous tests of many hypotheses in exploratory research. J Nerv Ment Dis 170:3–8
Haddjeri N, Szabo ST, De Montigny C, Blier P (2000) Increased tonic activation of rat forebrain 5-HT(1A) receptors by lithium addition to antidepressant treatments. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:346–356
Hascoet M, Bourin M, Khimake S (1994) Additive effect of lithium and clonidine with 5-HT1A agonists in the forced swimming test. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 18:381–396
Ho AK, Loh HH, Craves F, Hitzemann RJ, Gershon S (1970) The effect of prolonged lithium treatment on the synthesis rate and turnover of monoamines in brain regions of rats. Eur J Pharmacol 10:72–78
Hyttel J (1994) Pharmacological characterization of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Int Clin Psychopharmacol 9[Suppl 1]:19–26
Invernizzi R, Bramante M, Samanin R (1994) Chronic treatment with citalopram facilitates the effect of a challenge dose on cortical serotonin output: role of presynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 260:243–246
Iwata H, Okamoto H, Kuramoto I (1974) Effect of lithium on serum tryptophan and brain serotonin in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 24:235–240
Jensen J, Thomsen K, Olesen OV (1976) Current determination of lithium-induced minimum sodium requirement in rats. Psychopharmacology 45:295–299
Jordan S, Kramer GL, Zukas PK, Petty F (1994) Previous stress increases in vivo biogenic amine response to swim stress. Neurochem Res 19:1521–1525
Karoum F, Korpi ER, Chuang LW, Linnoila M, Wyatt RJ (1986) The effects of desipramine, zimelidine, electroconvulsive treatment and lithium on rat brain biogenic amines: a comparison with peripheral changes. Eur J Pharmacol 121:377–385
Katona CL (1988) Lithium augmentation in refractory depression. Psychiatr Dev 6:153–171
Kofman O, Patishi Y (1999) Interactions of lithium and drugs that affect signal transduction on behaviour in rats. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 9:385–397
Lopez-Rubalcava C, Lucki I (2000) Strain differences in the behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs in the rat forced swimming test. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:191–199
Maes M, Meltzer HY (1995) The serotonin hypothesis of major depression. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 933–944
Maj J, Rogoz Z, Skuza G (1982) Fluvoxamine, a new antidepressant drug, fails to show antiserotonin activity. Eur J Pharmacol 81:287–292
Mandell AJ, Knapp S (1980) Asymmetry and mood, emergent properties of serotonin regulation: a mechanism of action of lithium. In: Cooper T, Gershon S, Kline NS, Schou M (eds) Lithium controversies and unresolved issues. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 789–814
Massot O, Rousselle JC, Fillion MP, Januel D, Plantefol M, Fillion G (1999) 5-HT1B receptors: a novel target for lithium. Possible involvement in mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:530–541
McEwen BS (1999) Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:105–122
Mongeau R, Blier P, De Montigny C (1997) The serotonergic and noradrenergic systems of the hippocampus: their interactions and the effects of antidepressant treatments. Brain Res Rev 23:145–195
Mork A (1998) Effects of lithium treatment on extracellular serotonin levels in the dorsal hippocampus and wet-dog shakes in the rat. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 8:267–272
Muraki I, Inoue T, Hashimoto S, Izumi T, Ito K, Koyama T (2001) Effect of subchronic lithium treatment on citalopram-induced increases in extracellular concentrations of serotonin in the medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurochem 76:490–497
Nixon MK, Hascoet M, Bourin M, Colombel MC (1994) Additive effects of lithium and antidepressants in the forced swimming test: further evidence for involvement of the serotoninergic system. Psychopharmacology 115:59–64
Öhman R, Spigset O (1993) Serotonin syndrome induced by fluvoxamine-lithium interaction. Pharmacopsychiatry 26:263–264
Okamoto Y, Motohasi N, Hayakawa H, Muraoka M, Yamawaki S (1996) Addition of lithium to chronic antidepressant treatment potentiates presynaptic serotonergic function without changes in serotonergic receptors in the rat cerebral cortex. Neuropsychobiology 33:17–20
Otero LM, Rubio MC (1986) Time-related response of central serotonergic function to lithium administration. Gen Pharmacol 17:333–337
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York
Porsolt RD (1979) Animal model of depression. Biomedicine 30:139–140
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978) Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47:379–391
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Blavet N, Deniel M, Jalfre M (1979) Immobility induced by forced swimming in rats: effects of agents which modify central catecholamine and serotonin activity. Eur J Pharmacol 57:201–210
Price LH, Heninger GR (1994) Lithium in the treatment of mood disorders. N Engl J Med 331:591–598
Price LH, Charney DS, Delgado PL, Heninger GR (1990) Lithium and serotonin function: implications for the serotonin hypothesis of depression. Psychopharmacology 100:3–12
Rouillon F, Gorwood P (1998) The use of lithium to augment antidepressant medication. J Clin Psychiatry 59:S532–539
Sanchez C, Meier E (1997) Behavioral profiles of SSRIs in animal models of depression, anxiety and aggression. Are they all alike? Psychopharmacology 129:197–205
Satoh H, Mori J, Shimomura K, Ono T, Kikuchi H (1984) Effect of zimeldine, a new antidepressant, on the forced swimming test in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 35:471–473
Schou M (1991) Clinical aspects of lithium in psychiatry. In: Birch NJ (ed) Lithium and the cell: pharmacology and biochemistry. Academic Press, London, pp 1–6
Sharp T, Bramwell SR, Lambert P, Grahame Smith DG (1991) Effect of short- and long-term administration of lithium on the release of endogenous 5-HT in the hippocampus of the rat in vivo and in vitro. Neuropharmacology 30:977–984
Sheard MH, Aghajanian GK (1970) Neuronally activated metabolism of brain serotonin: effect of lithium. Life Sci 9:285–290
Smith DF (1975) Biogenic amines and the effect of short term lithium administration on open field activity in rats. Psychopharmacology 41:295–300
Sternbach H (1991) The serotonin syndrome. Am J Psychiatry 148:705–713
Thase ME, Howland RH, Friedman ES (1998) Treating antidepressant nonresponders with augmentation strategies: an overview. J Clin Psychiatry 59[Suppl 5]:5–12
van Praag HM, Korf J, Dols LCW, Schut T (1972) A pilot study of the predictive value of probenecid test in application of 5-hydroxytryptophan as antidepressant. Psychopharmacology 25:14–21
Waldmeier PC (1990) Mechanisms of action of lithium in affective disorders: a status report. Pharmacol Toxicol 66[Suppl 3]:121–132
Wegener G, Linnet K, Rosenberg R, Mork A (2000) The effect of acute citalopram on extracellular 5-HT levels is not augmented by lithium: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res 871:338–342
West HL, Mark GP, Hoebel BG (1991) Effects of conditioned taste aversion on extracellular serotonin in the lateral hypothalamus and hippocampus of freely moving rats. Brain Res 556:95–100
Willner P (1984) The validity of animal models of depression. Psychopharmacology 83:1–16
Willner P (1994) Animal models of depression. In: den Boer JA (ed) Handbook of depression and anxiety: a biological approach. Cambridge University Press, pp 291–316
Worrall EP, Moody JP, Peet M, Dick P, Smith A, Chambers C, Adams M, Naylor GJ (1979) Controlled studies of the acute antidepressant effects of lithium. Br J Psychiatry 135:255–262
Zall H, Therman PG, Myers JM (1968) Lithium carbonate: a clinical study. Am J Psychiatry 125:549–555
Zullino D, Baumann P (2001) Lithium augmentation in depressive patients not responding to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Pharmacopsychiatry 34:119–127
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from The Novo Nordisk Foundation (2000.12.07), Fonden til forskning af Sindslidelser (2001), Psykiatrisk Forskningsfond (5129.1), Fonden til Laegevidenskabens fremme (01217), Hede Nielsen Fonden (HNP-2001), Einar Geert-Jørgensen & hustrus Legat (1008529) and Max Wørzners mindelegat (58.884). We thank Karen Byrialsen and Uffe Villadsen for constructive comments and Bodil Schmidt for skillful technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wegener, G., Bandpey, Z., Heiberg, I.L. et al. Increased extracellular serotonin level in rat hippocampus induced by chronic citalopram is augmented by subchronic lithium: neurochemical and behavioural studies in the rat. Psychopharmacology 166, 188–194 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1341-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1341-6