Abstract
Rationale
Arcaine is a competitive antagonist of the polyamine binding site at the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor which induces state-dependent recall. However, no study has addressed the involvement of other neurotransmitter/neuromodulators in arcaine-induced state dependency.
Objectives
The current study investigates whether the opioid system is involved in arcaine-induced state-dependent memory retrieval of the inhibitory avoidance task (IA) in rats.
Results
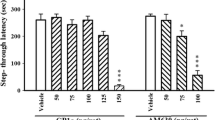
The systemic administration of arcaine (30 mg/kg, intraperitoneally (i.p.)) or morphine (5 mg/kg, i.p.) 0, 3, 6, or 9 h post-training, reduced step-down latencies at testing. Arcaine (30 mg/kg, i.p.) or morphine (5 mg/kg, i.p.) injection 30 min before testing reversed the performance deficit induced by administration of arcaine or morphine 0, 3 or 6, but not 9 h post-training. The reversal of arcaine-induced impairment of IA performance was completely transferred to morphine and vice versa. The association of low and ineffective doses of morphine and arcaine (10 and 1.5 mg/kg, respectively) were additive and caused state dependency. Naloxone (2 mg/kg, 3 min post-training, or 1 mg/kg, 1 h pre-test, i.p.) reversed the amnesia and the state dependency induced by morphine and arcaine.
Conclusion
These results suggest that state dependency induced by arcaine involves the opioid system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi S, Zarrindast MR, Nouri M, Haeri-Rohani A, Rezayof A (2007) N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the ventral tegmental area are involved in retrieval of inhibitory avoidance memory by nicotine. Neurobiol Learn Mem 88:352–358
Berger BD, Stein L (1969) Asymmetrical dissociation of learning between scopolamine and Wy 4036, a new benzodiazepine tranquilizer. Psychopharmacologia 14:351–358
Berlese DB, Sauzem PD, Carati MC, Guerra GP, Stiegemeier JA, Mello CF, Rubin MA (2005) Time-dependent modulation of inhibitory avoidance memory by spermidine in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 83:48–53
Bethus I, Tse D, Morris RG (2010) Dopamine and memory: modulation of the persistence of memory for novel hippocampal NMDA receptor-dependent paired associates. J Neurosci 30:1610–1618
Bodnar RJ (2009) Endogenous opiates and behavior: 2008. Peptides 30:2432–2479
Bruins Slot LA, Colpaert FC (1999) Opiate states of memory: receptor mechanisms. J Neurosci 19:10520–10529
Camera K, Mello CF, Ceretta AP, Rubin MA (2007) Systemic administration of polyaminergic agents modulate fear conditioning in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 192:457–464
Castellano C (1975) Effects of morphine and heroin on discrimination learning and consolidation in mice. Psychopharmacologia 42:235–242
Ceretta AP, Camera K, Mello CF, Rubin MA (2008) Arcaine and MK-801 make recall state-dependent in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 201:405–411
Cestari V, Castellano C (1997) MK-801 potentiates morphine-induced impairment of memory consolidation in mice: involvement of dopaminergic mechanisms. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 133:1–6
Girouard H, Wang G, Gallo EF, Anrather J, Zhou P, Pickel VM, Iadecola C (2009) NMDA receptor activation increases free radical production through nitric oxide and NOX2. J Neurosci 29:2545–2552
Gomes GM, Mello CF, Rosa MM, Bochi GV, Ferreira J, Barron S, Rubin MA (2010) Polyaminergic agents modulate contextual fear extinction in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93:589–595
Guerra GP, Mello CF, Sauzem PD, Berlese DB, Furian AF, Tabarelli Z, Rubin MA (2006) Nitric oxide is involved in the memory facilitation induced by spermidine in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 186:150–158
Harrod SB, Flint RW, Riccio DC (2001) MK-801 induced retrieval, but not acquisition, deficits for passive avoidance conditioning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 69:585–593
Hashimoto K, Mantione CR, Spada MR, Neumeyer JL, London ED (1994) Further characterization of [3H]ifenprodil binding in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 266:67–77
Izquierdo I (1979) Effect of naloxone and morphine on various forms of memory in the rat: possible role of engogenous opiate mechanisms in memory consolidation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 66:199–203
Izquierdo I, Dias RD (1983) Effect of ACTH, epinephrine, beta-endorphin, naloxone, and of the combination of naloxone or beta-endorphin with ACTH or epinephrine on memory consolidation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 8:81–87
Izquierdo I, Dias RD (1985) Influence on memory of posttraining or pre-test injections of ACTH, vasopressin, epinephrine, and beta-endorphin, and their interaction with naloxone. Psychoneuroendocrinology 10:165–172
Jackson A, Koek W, Colpaert FC (1992) NMDA antagonists make learning and recall state-dependent. Behav Pharmacol 3:415–421
Katche C, Bekinschtein P, Slipczuk L, Goldin A, Izquierdo IA, Cammarota M, Medina JH (2010) Delayed wave of c-Fos expression in the dorsal hippocampus involved specifically in persistence of long-term memory storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:349–354
Khalilzadeh A, Zarrindast MR, Djahanguiri B (2006) Effects of intracerebroventricular administration of ultra low doses of histaminergic drugs on morphine state-dependent memory of passive avoidance in mice. Behav Brain Res 166:184–187
Khavandgar S, Homayoun H, Torkaman-Boutorabi A, Zarrindast MR (2001) The effects of adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists on morphine state-dependent memory of passive avoidance. Neurobiol Learn Mem 78:390–405
Khavandgar S, Homayoun H, Zarrindast MR (2003) The effect of L-NAME and L-arginine on impairment of memory formation and state-dependent learning induced by morphine in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 167:291–296
Lourenco CF, Santos R, Barbosa RM, Gerhardt G, Cadenas E, Laranjinha J (2010) In vivo modulation of nitric oxide concentration dynamics upon glutamatergic neuronal activation in the hippocampus. Hippocampus (in press)
Miyamoto Y, Ozaki M, Yamamoto H (1988) Effects of adrenalectomy on pharmacokinetics and antinociceptive activity of morphine in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 46:379–386
Netto CA, Izquierdo I (1985) Posterior hypothalamic deafferentation abolishes the amnestic effect of electroconvulsive shock in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 10:159–163
Netto CA, Maltchik M (1991) Retrieval effects of beta-endorphin and naloxone, and the novelty-induced antinociception in the developing rat. Behav Neural Biol 55:366–379
Ngai SH, Berkowitz BA, Yang JC, Hempstead J, Spector S (1976) Pharmacokinetics of naloxone in rats and in man: basis for its potency and short duration of action. Anesthesiology 44:398–401
Nishimura M, Shiigi Y, Kaneto H (1990) State dependent and/or direct memory retrieval by morphine in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 100:27–30
Overton DA (1964) State-dependent or “dissociated” learning produced with pentobarbital. J Comp Physiol Psychol 57:3–12
Pellegrini-Giampietro DE (2003) An activity-dependent spermine-mediated mechanism that modulates glutamate transmission. Trends Neurosci 26:9–11
Pu S, Horvath TL, Diano S, Naftolin F, Kalra PS, Kalra SP (1997) Evidence showing that beta-endorphin regulates cyclic guanosine 3′, 5′-monophosphate (cGMP) efflux: anatomical and functional support for an interaction between opiates and nitric oxide. Endocrinology 138:1537–1543
Ransom RW, Stec NL (1988) Cooperative modulation of [3H]MK-801 binding to the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-ion channel complex by L-glutamate, glycine, and polyamines. J Neurochem 51:830–836
Rezayof A, Amini R, Rassouli Y, Zarrindast MR (2006) Influence of nitric oxide on morphine-induced amnesia and interactions with dopaminergic receptor agents. Physiol Behav 88:124–131
Rezayof A, Sharifi K, Zarrindast MR, Rassouli Y (2008) Modulation of ethanol state-dependent learning by dorsal hippocampal NMDA receptors in mice. Alcohol 42:667–674
Riccio DC, Millin PM, Bogart AR (2006) Reconsolidation: a brief history, a retrieval view, and some recent issues. Learn Mem 13:536–544
Rock DM, Macdonald RL (1995) Polyamine regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 35:463–482
Roesler R, Vianna MR, Schroder N, Ferreira MB, Quevedo J (2006) Aversive learning under different training conditions: effects of NMDA receptor blockade in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Neurochem Res 31:679–683
Rossato JI, Bevilaqua LR, Izquierdo I, Medina JH, Cammarota M (2009) Dopamine controls persistence of long-term memory storage. Science 325:1017–1020
Rubin MA, Boemo RL, Jurach A, Rojas DB, Zanolla GR, Obregon AD, Souza DO, Mello CF (2000) Intrahippocampal spermidine administration improves inhibitory avoidance performance in rats. Behav Pharmacol 11:57–61
Rubin MA, Stiegemeier JA, Volkweis MA, Oliveira DM, Fenili AC, Boemo RL, Jurach A, Mello CF (2001) Intra-amygdala spermidine administration improves inhibitory avoidance performance in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 423:35–39
Rubin MA, Berlese DB, Stiegemeier JA, Volkweis MA, Oliveira DM, dos Santos TL, Fenili AC, Mello CF (2004) Intra-amygdala administration of polyamines modulates fear conditioning in rats. J Neurosci 24:2328–2334
Scott RH, Sutton KG, Dolphin AC (1993) Interactions of polyamines with neuronal ion channels. Trends Neurosci 16:153–160
Shimada A, Spangler EL, London ED, Ingram DK (1994) Spermidine potentiates dizocilpine-induced impairment of learning performance by rats in a 14-unit T-maze. Eur J Pharmacol 263:293–300
Velloso NA, Dalmolin GD, Gomes GM, Rubin MA, Canas PM, Cunha RA, Mello CF (2009) Spermine improves recognition memory deficit in a rodent model of Huntington's disease. Neurobiol Learn Mem 92:574–580
Wang SH, Redondo RL, Morris RG (2010) Relevance of synaptic tagging and capture to the persistence of long-term potentiation and everyday spatial memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19537–19542
Williams K (1997) Interactions of polyamines with ion channels. Biochem J 325(Pt 2):289–297
Williams K, Romano C, Dichter MA, Molinoff PB (1991) Modulation of the NMDA receptor by polyamines. Life Sci 48:469–498
Yokoi I, Kabuto H, Habu H, Inada K, Toma J, Mori A (1994) Structure–activity relationships of arginine analogues on nitric oxide synthase activity in the rat brain. Neuropharmacology 33:1261–1265
Zarrindast MR, Rezayof A (2004) Morphine state-dependent learning: sensitization and interactions with dopamine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 497:197–204
Zarrindast MR, Jafari MR, Ahmadi S, Djahanguiri B (2004) Influence of central administration ATP-dependent K+ channel on morphine state-dependent memory of passive avoidance. Eur J Pharmacol 487:143–148
Zarrindast MR, Askari E, Khalilzadeh A, Nouraei N (2006a) Morphine state-dependent learning sensitization and interaction with nitric oxide. Pharmacology 78:66–71
Zarrindast MR, Bananej M, Khalilzadeh A, Fazli-Tabaei S, Haeri-Rohani A, Rezayof A (2006b) Influence of intracerebroventricular administration of dopaminergic drugs on morphine state-dependent memory in the step-down passive avoidance test. Neurobiol Learn Mem 86:286–292
Zarrindast MR, Jafari-Sabet M, Rezayat M, Djahanguiri B, Rezayof A (2006c) Involvement of NMDA receptors in morphine state-dependent learning in mice. Int J Neurosci 116:731–743
Zarrindast MR, Shendy MM, Ahmadi S (2007) Nitric oxide modulates state dependency induced by lithium in an inhibitory avoidance task in mice. Behav Pharmacol 18:289–295
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by CNPq and CAPES. All the experiments comply with the current laws of Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Table S1
Effect of treatments of experiment 1 on the training step-down latency (s) and on the behavior of rats in the open field immediately after the inhibitory avoidance testing session (DOC 46 kb)
Supplemental Table S2
Effect of treatments of experiment 1 on the training step-down latency (s) and on the behavior of rats in the open field immediately after the inhibitory avoidance testing session (DOC 48 kb)
Supplemental Table S3
Effect of treatments of experiment 2 on the training step-down latency (s) and on the behavior of rats in the open field immediately after the inhibitory avoidance testing session (DOC 36 kb)
Supplemental Table S4
Effect of treatments of experiment 3 on the training step-down latency (s) and on the behavior of rats in the open field immediately after the inhibitory avoidance testing session (DOC 46 kb)
Supplemental Table S5
Effect of treatments of experiment 4 on the training step-down latency (s) and on the behavior of rats in the open field immediately after the inhibitory avoidance testing session (DOC 45 kb)
Supplemental Table S6
Effect of arcaine (30 mg/kg) or vehicle (Sal) administration immediately post-training on the test step-down latency (s) of rats pseudo trained (without shock) (DOC 28 kb)
Supplemental Table S7
Effect of vehicle (Sal) administration immediately post-training and 30 min pre-test on the training and test step-down latency (s) (DOC 28 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mariani, R.K., Mello, C.F., Rosa, M.M. et al. Effect of naloxone and morphine on arcaine-induced state-dependent memory in rats. Psychopharmacology 215, 483–491 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2215-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2215-6