Abstract
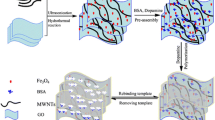
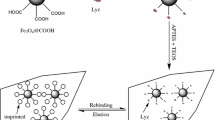
Novel magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes@Fe3O4 molecularly imprinted polymers (MWNTs@Fe3O4-MIPs) intended for bovine serum albumin (BSA) recognition were successfully developed. The MWNTs@Fe3O4-MIPs were characterized with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Scanning electron microscopy images showed that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles (diameter: 50–60 nm) were coated with a layer of MIPs with an average thickness of 25–30 nm. The magnetic material was easily dispersed and retrieved through the application of an external magnetic field. Adsorption experiments showed that the estimated maximum amount of BSA that could be adsorbed onto the MWNTs@Fe3O4-MIPs was 52.8 mg/g, and the time taken to reach equilibrium was about 40 min. Meanwhile, the MWNTs@Fe3O4-MIPs exhibited excellent selectivity towards (i.e., recognition of) BSA. The feasibility of the use of the MWNTs@Fe3O4-MIPs as a solid-phase extraction (SPE) sorbent was evaluated, and the results showed that the MWNTs@Fe3O4-MIPs were able to separate the template protein BSA from a binary protein solution. The proposed sorbent based on MWNTs@Fe3O4-MIPs for BSA separation exhibited satisfactory recoveries ranging from 92.0% to 97.3% in real samples. It was also successfully used for the purification of BSA from bovine calf serum.

Procedure for preparing magnetic protein imprinted polymers.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamayo FG, Turiel E, Martin-Esteban A (2007) Molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction and solid-phase microextraction: recent developments and future trends. J Chromatogr A 1152:32–40
Long Y, Xing XC, Han RF, Sun Y, Wang Y, Zhao Z, Mi HF (2008) Two-step purification of low-content cellular protein using protein-imprinted polymers. Anal Biochem 380:268–275
Baggiani C, Baravalle P, Giraudi G, Tozzi CJ (2007) Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction method for the high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of fungicide pyrimethanil in wine. J Chromatogr A 1141:158–164
Sontimuang C, Suedee R, Dickert F (2011) Interdigitated capacitive biosensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid detection of Hev b1 latex allergen. Anal Biochem 410:224–233
Pasetto P, Maddock SC, Resmini M (2005) Synthesis and characterisation of molecularly imprinted catalytic microgels for carbonate hydrolysis. Anal Chim Acta 542:66–75
Vlatakis G, Andersson LI, Muller R, Mosbach K (1993) Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 361:645–647
Wulff G (1995) Molecular imprinting in cross-linked materials with the aid of molecular templates-a way towards artificial antibodies. Chem Int Ed Engl 34:1812–1832
Gao DM, Zhang ZP, Wu MH, Xie C, Guan GJ, Wang DP (2007) A surface functional monomer-directing strategy for highly dense imprinting of TNT at surface of silica nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 129:7859–7866
Niu J, Liu ZH, Fu L, Shi F, Ma HW, Ozaki Y, Zhang X (2008) Surface-imprinted nanostructured layer-by-layer film for molecular recognition of theophylline derivatives. Langmuir 24:11988–11994
Zhai CX, Lu Q, Chen XM, Peng Y, Chen L, Du SH (2009) Molecularly imprinted layer-coated silica nanoparticles toward highly selective separation of active diosgenin from Dioscorea nipponica Makino. J Chromatogr A 1216:2254–2262
Xie CG, Liu BH, Wang ZY, Gao DM, Guan GJ, Zhang ZP (2008) Molecular imprinting at walls of silica nanotubes for TNT recognition. Anal Chem 80:437–443
Li HB, Li YL, Cheng J (2010) Molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded CdSe quantum dots for highly selective and sensitive optosensing of pyrethroids. Chem Mater 22:2451–2457
Tan CJ, Chua HG, Ker KH, Tong YW (2008) Preparation of bovine serum albumin surface-imprinted submicrometer particles with magnetic susceptibility through core–shell miniemulsion polymerization. Anal Chem 80:683–692
Li Y, Yin XF, Chen FR, Yang HH, Zhuang ZX, Wang XR (2006) Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanowires using a nanoporous alumina template. Macromolecules 39:4497–4499
Jia BP, Gao L, Sun J (2007) Self-assembly of magnetite beads along multiwalled carbon nanotubes via a simple hydrothermal process. Carbon 45:1476–1481
De Araújo ACV Jr, Alves S, Azevedo WM (2008) A new synthesis route to prepare polyaniline (PANI) nanotubes containing magnetic nanoparticles. Adv Sci Technol 54:325–330
Kong LR, Lu XF, Zhang WJ (2008) Facile synthesis of multifunctional multiwalled carbon nanotubes/Fe3O4 nanoparticles/polyaniline composite nanotubes. J Solid State Chem 181:628–636
Zhang W, Qin L, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2009) Novel surface modified molecularly imprinted polymer using acryloyl-β-cyclodextrin and acrylamide as monomers for selective recognition of lysozyme in aqueous solution. J Chromatogr A 1216:4560–4567
Hua ZD, Chen ZY, Li YZ, Zhao MP (2008) Thermosensitive and salt-sensitive molecularly imprinted hydrogel for bovine serum albumin. Langmuir 24:5773–5780
Zhao LP, Gao L (2004) Coating of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with thick layers of tin(IV) oxide. Carbon 42:1858–1861
Kan X, Zhao Y, Geng Z, Wang Z, Zhu JJ (2008) Composites of multiwalled carbon nanotubes and molecularly imprinted polymers for dopamine recognition. J Phys Chem C 112:4849–4854
Rachkov A, Minoura N (2000) Recognition of oxytocin and oxytocin-related peptides in aqueous media using a molecularly imprinted polymer synthesized by the epitope approach. J Chromatogr A 889:111–118
Zhang MS, Huang JR, Yu P, Chen X (2010) Preparation and characteristics of protein molecularly imprinted membranes on the surface of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Talanta 81:162–166
Lu XF, Yu YH, Chen L, Mao HP, Zhang WJ, Wei Y (2004) Preparation and characterization of polyaniline microwires containing CdS nanoparticles. Chem Commun 13:1522–1523
Liu HM, Liu CH, Yang XJ, Zeng SJ, Xiong YQ, Xu WJ (2008) Uniformly sized-β-cyclodextrin molecularly imprinted microspheres prepared by a novel surface imprinting technique for ursolic acid. Anal Chim Acta 628:87–94
Tang PP, Cai JB, Su QD (2010) Synthesis and adsorption study of BSA surface imprinted polymer on CdS quantum dots. Chinese J Chem Phys 23:195–200
Piletsky SA, Piletska EV, Bossi A, Karim K, Lowe P, Turner APF (2001) Substitution of antibodies and receptors with molecularly imprinted polymers in enzyme-linked and fluorescent assays. Biosens Bioelectron 16:701–707
Bossi A, Piletsky SA, Piletska EV, Righetti PG, Turner APF (2001) Surface-grafted molecularly imprinted polymers for protein recognition. Anal Chem 73:5281–5286
Acknowledgment
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21005030), the Research Foundation of Education Bureau of Hunan Province, China (No.10A099), and the Science and Technology Innovative Research Team in Higher Educational Institutions of Hunan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplemental material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 123 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Yang, X., Chen, X. et al. Novel magnetic bovine serum albumin imprinted polymers with a matrix of carbon nanotubes, and their application to protein separation. Anal Bioanal Chem 401, 2855–2863 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5373-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5373-9