Abstract
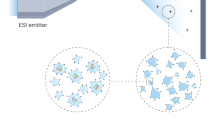
The advent of nano-electrospray ionization (nano-ESI) has considerably extended the usability of ESI in the analytical mass spectrometric laboratory. One of the remarkable features of nano-ESI is its extremely low sample consumption. Only a few microliters of analyte solution (10–5–10–8 M) are sufficient for molecular weight determination and structural investigations by MS/MS. But nano-ESI is more than just a minimized-flow ESI; the low solvent flow rate also affects the mechanism of ion formation. As a consequence, the area of ESI-MS applications is significantly enhanced. Oligosaccharides, glycosides as well as glycoproteins can be analyzed more easily than with normal ion spray. The same holds for the analysis of non-covalent complexes sprayed directly from aqueous solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 October 1999 / Revised: 2 December 1999 / Accepted: 11 December 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karas, M., Bahr, U. & Dülcks, T. Nano-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: addressing analytical problems beyond routine. Fresenius J Anal Chem 366, 669–676 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160051561
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160051561