Abstract.
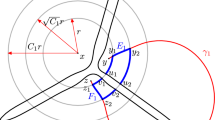
Any compact ? ∞ manifold with boundary admits a Riemann metric on its interior taking the form x −4 dx 2 +x −2 h′ near the boundary, where x is a boundary defining function and h′ is a smooth symmetric 2-cotensor restricting to be positive-definite, and hence a metric, h, on the boundary. The scattering theory associated to the Laplacian for such a ‘scattering metric’ was discussed by the first author and here it is shown, as conjectured, that the scattering matrix is a Fourier integral operator which quantizes the geodesic flow on the boundary, for the metric h, at time π. To prove this the Poisson operator, of the associated generalized boundary problem, is constructed as a Fourier integral operator associated to a singular Legendre manifold.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Oblatum 24-VII-1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melrose, R., Zworski, M. Scattering metrics and geodesic flow at infinity. Invent math 124, 389–436 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002220050058
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002220050058