Abstract
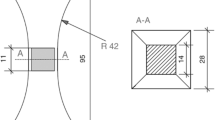
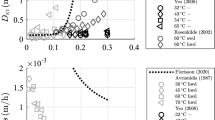
Elastic material properties are one of the most important material characteristics in mechanical modelling. Wood with distinctively different properties in the longitudinal, radial and tangential directions exhibits a strong moisture-dependent material characteristic in the elastic range. In order to characterise beech wood as an orthotropic material, all of the independent elastic properties were determined at different moisture conditions. These characteristic properties have never been determined before as a function of moisture content yet are vital to the field of wood modelling. All elastic parameters, except for some Poisson’s ratios, show a decrease in stiffness with increasing moisture content. In comparison to available literature references at a moisture content of ω ≈ 12%, the identified values were of the same order of magnitude. The determined material properties can be used to investigate the mechanical behaviour of beech wood structures including different moisture conditions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcan M, Hashin Z, Voloshin A (1978) A method to produce uniform plane-stress states with applications to fiber-reinforced materials. Exp Mech 18(4):141–146
Bodig J, Jayne BA (1993) Mechanics of wood and wood composites. Krieger Publishing Company, New York
Bucur V (1995) Acoustics of wood. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Bucur V, Archer RR (1984) Elastic constants for wood by an ultrasonic method. Wood Sci Technol 18:255–265
Dahl KB, Malo KA (2009a) Linear shear properties of spruce softwood. Wood Sci Technol 43(5–6):499–525
Dahl KB, Malo KA (2009b) Nonlinear shear properties of spruce softwood:experimental results. Wood Sci Technol 69(13):2144–2151
DIN V 65352 (1987) Verfahren zur statistischen Auswertung der Prüfergebnisse bei der Qualifikations- und Abnahmeprüfung von Faserverbundwerkstoffen. DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V
Diot S, Guines D, Gavrus A, Ragneau E (2008) Minimization of friction influence on the evaluation of rheological parameters from compression test—application to a forging steel behavior identification. J Eng Mater T ASME 131(1):10
Dumail JF, Oloffson K, Salmén L (2000) An analysis of rolling shear of spruce wood by the Iosipescu method. Holzforschung 54:420–426
Garab J, Keunecke D, Hering S, Szalai J, Niemz P (2010) Measurement of standard and off-axis elastic moduli and Poisson’s ratios of spruce and yew wood in the transverse plane. Wood Sci Technol 44(3):451–464
Grimsel M (1999) Mechanisches Verhalten von Holz. Dissertation, Dresden, p 89
Guitard D, Amri FE (1987) Tridimensional elastic behavior predicting models for hardwood and softwood (in French). Ann Sci Forest 44:335–358
Hearmon RFS, Barkas WW (1941) The effect of grain direction on the Young’s moduli and rigidity moduli of beech and Sitka spruce. In: Proceedings of the physical society
Hörig H (1933) Zur Elastizität des Fichtenholzes. Z Tech Phys 12:369–379
Hörig H (1935) Anwendung der Elastizitätstheorie anisotroper Körper auf Messungen an Holz. Arch Appl Mech 6(1):8–14
Iosipescu N (1967) New accurate procedure for single shear testing of metals. J Mater 2:537
Keunecke D, Sonderegger W, Pereteanu K, Lüthi T, Niemz P (2007) Determination of Young’s and shear moduli of common yew and Norway spruce by means of ultrasonic waves. Wood Sci Technol 41(4):309–327
Keunecke D, Hering S, Niemz P (2008) Three-dimensional elastic behaviour of common yew and Norway spruce. Wood Sci Technol 42(8):633–647
Keylwerth R (1951) Die anisotrope Elastizität des Holzes und der Lagenhölzer. Verlag des Vereins Deutscher Ingenieure—VDI-Forschungsheft 430
Kollmann F (1951) Technologie des Holzes und der Holzwerkstoffe. Springer, Berlin
Neuhaus FH (1981) Elastizitätszahlen von Fichtenholz in Abhängigkeit von der Holzfeuchtigkeit. Dissertation, Bochum, p 162
Neuhaus FH (1983) Über das elastische Verhalten von Fichtenhoiz in Abhängigkeit von der Holzfeuchtigkeit. Holz Roh Werkst 41:21–25
Neumann AJ (1998) Ermittlung und Bewertung der elastischen Materialkennwerte von Vollholz in Abhängigkeit der Feuchte und der Anisotropie. Master Thesis, Dresden, p 87
Niemz P (1993) Physik des Holzes und der Holzwerkstoffe. DRW-Verlag Weinbrenner GmbH & Co
Niemz P, Caduff D (2008) Research into determination of the Poisson ratio of spruce wood. Holz Roh Werkst 66(1):1–4
Pozgaj A, Chovanec D, Kuriatko S, Babiak M (1993) Štruktúra a vlastnosti dreva (Wood structure and properties). Príroda, Bratislava
Stamer J (1935) Elastizitätsuntersuchungen an Hölzern. Arch Appl Mech 6(1):1–8
Stamer J, Sieglerschmidt H (1933) Elastische Formänderung der Hölzer. Zeitschrift des Vereins Deutscher Ingenieure 77(19):503–505
van Mier JGM (1997) Fracture processes of concrete: assessment of material parameters for fracture models. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wommelsdorf O (1966) Dehnungs- und Querdehnungszahlen von Hölzern. Dissertation, Hannover, p 100
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the State Secretariat for Education and Research of Switzerland (SER) and supported by the European Cooperation in the field of Scientific and Technical Research (COST, Action E53).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hering, S., Keunecke, D. & Niemz, P. Moisture-dependent orthotropic elasticity of beech wood. Wood Sci Technol 46, 927–938 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-011-0449-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-011-0449-4