Abstract
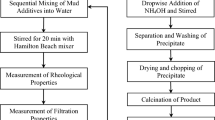
The success of drilling operations is heavily dependent on the drilling fluid. Drilling fluids cool down and lubricate the drill bit, remove cuttings, prevent formation damage, suspend cuttings and also cake off the permeable formation, thus retarding the passage of fluid into the formation. Typical micro or macro sized loss circulation materials (LCM) show limited success, especially in formations dominated by micropores, due to their relatively large sizes. Due to unique characteristics of nanoparticles such as their size and high surface area to volume ratio, they play an effective role in solving problems associated with the drilling fluid. In this study, we investigate the effect of adding Al2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles into the drilling mud. Al2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles were used in 20 and 60 nm of size and 0.05 wt% in concentration. Investigating the effects of temperature and pressure has shown that an increase in temperature can reduce the drilling mud rheological properties such as plastic viscosity, while an increase in pressure can enhance these properties. Also, the effects of pressure in high temperatures were less than those in low temperatures. Studying the effects of adding nanoparticles has shown that they can reduce the drilling mud rheological properties. Moreover, they can increase gel strength, reduce capillary suction time and decrease formation damage.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdo J, Haneef MD (2010) Nanoparticles: romising Solution to Overcome Stern Drilling Problems. NSTI- Nano Tech 3:635–638
Roddy CW, Ricky L, Chatterji J, Brenneis DC (2010) U.S. Patent, US 0025039 A1
Sharma MM, Zhang R, Chenevert ME, Ji L, Guo Q, Friedheim J (2012) A New Family of Nanoparticle Based Drilling Fluids// SPE 160045 San Antonio, Texas, USA, 8–10 October 2012
Akhtarmanesh S, Shahrabi M, Atashnezhad A (2001) Improvement of Wellbore Stability in Shale Using Nanoparticles. J Pet Sci Eng 112:190–195
Clenand AG, Doehler RW (1963) Industrial Application of Bentonite. Proceedings of the Tenth National Conference on Clays and Clay Minerals
Remillard SC (2010) Applications of Nanotechnology within the Oil and Gas Industry. Oil Gas Rev 8:1–108
Tungittiplakorn W (2005) Engineered Polymeric Nanoparticles for Bioremediation of Hydrophobic Contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 39(5):1354–1358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi, N., Mirzaee, M., Aghayari, R. et al. Investigating Created Properties of Nanoparticles Based Drilling Mud. Heat Mass Transfer 54, 1381–1393 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-017-2229-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-017-2229-7