Abstract
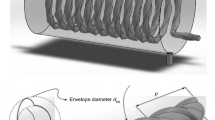
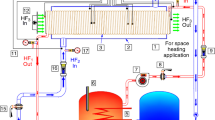
In this paper, a three fluid heat exchanger is analytically modeled in order to predict the effects of different design parameters on its thermal performances. The optimum values of these parameters relating to maximum heat transfer and minimum pressure drop are assessed using Taguchi based optimization technique. The present heat exchanger is an improvement of double tube heat exchanger, where a helical coil is inserted in the annular space occupied in between two straight tubes. It is different from other three fluid heat exchangers with respect to construction, flow arrangement and thermal communication point of view, where the hot water is flowing through the helical coil as the heating fluid and continuously transferring thermal energy to normal water and air, which are flowing, in outer annulus and innermost straight tube. The results of the analytical approach are compared and validated against literature and good conformity between them is observed. The temperature distributions of three different fluids along the length of the present heat exchanger are assessed analytically for different flow configurations. Three different non-dimensional design parameters i.e. curvature ratio, non dimensional coil pitch and coil side Reynolds number are selected and their effect on heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics i.e. coil side Nusselt number, effectiveness and friction factor respectively are assessed. It is found that, for tube size 0.0045 m, coil pitch 0.013 m, coil diameter 0.04253 m and hot water flow rate 5 liters per minute, present heat exchanger will perform optimum. It is also resulted that, volumetric flow rate of hot water is the most effective parameter affecting heat transfer with a contribution ratio of 66.82% and tube size is the most effective parameters affecting pressure drop with a contribution ratio of 71.07%.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Surface area, m2
- A i :
-
Surface area of innermost tube, m2
- B :
-
Diameter of innermost tube, m
- c p :
-
Specific heat, kJ/kg-K
- C :
-
Diameter of outermost tube, m
- C 1 :
-
Intercept
- C 2 :
-
Constant, 1/(Slope × Ac, i)
- C p :
-
Heat capacity, kJ/K
- CV:
-
Control volume
- d c :
-
Diameter of helical tube, m
- D c :
-
Coil diameter, m
- D e :
-
Equivalent diameter
- De :
-
Dean number
- f :
-
Friction factor
- h :
-
Convective heat transfer co-efficient, W/ m2.K
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity, W/m-K
- L :
-
Length, m
- ṁ :
-
Mass flow rate, kg/s
- N :
-
Number of turns
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- p :
-
Pitch of helical coil, m
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- Q˙:
-
Rate of heat transfer, W
- R :
-
Resistance
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- T :
-
Temperature, o C
- U :
-
Overall heat transfer co-efficient, W/m2.K
- V :
-
Velocity, m/s
- \( \overset{\infty }{V} \) :
-
Volume, m3
- \( \dot{V} \) :
-
Volumetric flow rate, m3/s
- ρ :
-
Density, kg/m3
- ɛ :
-
Effectiveness
- μ :
-
viscosity, N-s/m2
- δ :
-
Curvature ratio, dc, i/Dc
- λ :
-
Non-dimensional coil pitch, p/πDc
- 1 :
-
Inlet
- 2 :
-
Outlet
- a :
-
Air
- act :
-
Actual
- ann :
-
Annulus
- c :
-
Coil
- cr :
-
Critical
- cu :
-
Copper
- e :
-
Equivalent
- f :
-
Fluid
- h :
-
Hot water
- i :
-
Inner
- L :
-
Larger
- m :
-
mean
- max :
-
Maximum
- min :
-
Minimum
- n :
-
Normal water
- o :
-
Outer
- ov :
-
Overall
- S :
-
Smaller
- TS :
-
Test section
- w :
-
Wall
- n :
-
Velocity exponent
- DOE:
-
Design of experiments
- LPM:
-
Litre per minute
- NTU:
-
Numbers of transfer unit
- SNR:
-
Signal to noise ratio
References
Shokouhmand H, Salimpour MR, Akhavan-Behabadi MA (2008) Experimental investigation of shell and coiled tube heat exchangers using Wilson plots. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 35:84–92
Batmaz E, Sandeep KP (2005) Calculation of overall heat transfer coefficients in a triple tube heat exchangers. Heat Mass Transf 41:271–279
Rennie TJ, Raghavan VGS (2005) Experimental studies of a double-pipe helical heat exchanger. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 29:919–924
Pawar SS, Sunnapwar VK (2013) Experimental studies on heat transfer to Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids in helical coils with laminar and turbulent flow. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 44:792–804
Zhang H, Shao S, Xu H, Zou H, Tang M, Tian C (2016) Numerical investigation on fin-tube three-fluid heat exchanger for hybrid source HVAC & R systems. Appl Therm Eng 95:157–164
Pătrăşcioiu C, Rădulescu S (2015) Prediction of outlet temepratures in triple concentric-tube heat exchangers in laminar flow regime: case study. Heat Mass Transf 51:59–66
Boultif N, Vougriou C (2017) Steady and unsteady state thermal behavior of triple concentric-tube heat exchanger. Heat Mass Transf 53:849–863
Alimoradi A, Veysi F (2017) Optimal and critical values of geometrical parameters of shell and helically coiled tube heat exchangers. Case Stud Therm Eng 10:73–78
Omidi M, Farhadi M, Jafari M (2017) A comprehensive review on double pipe heat exchangers. Appl Therm Eng 110:1075–1090
Dizaji HS, Khalilarya S, Jafarmadar S, Hashemian M, Khezri M (2017) A comprehensive second law analysis for tube-in-tube helically coiled heat exchangers. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 76:118–125
Gomaa A, Halim MA, Elsaid AM (2017) Enhancement of cooling characteristics and optimization of a triple concentric-tube heat exchanger with inserted ribs. Int J Heat Therm Sci 120:106–120
Unal A (1998) Theoretical analysis of triple concentric-tube heat exchangers, part-1: mathematical modelling. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 25:949–958
Unal A (2001) Theoretical analysis of triple concentric-tube heat exchangers, part-2: case studies. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 28:243–256
Mohapatra T, Padhi BN, Sahoo SS (2017) Experimental investigation of convective heat transfer in an inserted coiled tube type three fluid heat exchanger. Appl Therm Eng 117:297–307
Sekulic DP, Shah RK (1995) Thermal design theory of three fluid heat exchangers. Adv Heat Tran 26:219–329
Jamshidi N, Farhadi M, Ganji DD, Sedighi K (2013) Experimental analysis of heat transfer enhancement in shell and helical tube heat exchangers. Appl Therm Eng 51:644–652
Rose JW (2004) Heat-transfer coefficients, Wilson plots and accuracy of thermal measurements. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 28:77–86
Gnielinski V (1976) New equation for heat and mass transfer in turbulent pipe and channel flow. Int Chem Eng 16:359–368
Seban RA, McLaughlin EF (1963) Heat transfer in tube coils with laminar and turbulent flow. Int J Heat Mass Transf 6:387–395
Rogers GFC, Mayhew YR (1964) Heat transfer and pressure loss in helically coiled tube with turbulent flow. Int J Heat Mass Transf 7:1207–1216
Kalb CE, Seader JD (1972) Heat and mass transfer phenomena for viscous flow in curved circular pipe. Int J Heat Mass Transf 15:801–817
Mishra P, Gupta SN (1979) Momentum transfer in curved pipes: Newtonian fluids. Ind Eng Chem Des Dev 18:130–137
Coates J, Pressburg BS (1959) Heat transfer to moving fluids. Chem Eng 28:67–72
Blasius H (1908) Grenzschichten in Flussigkeiten mit kleiner Reibung (German). Z Math Phys 56:1–37
Etghani MM, Baboli SAH (2017) Numerical investigation and optimization of heat transfer and exergy loss in shell and helical tube heat exchanger. Appl Therm Eng 121:294–301
Gunes S, Manay E, Senyigit E, Ozceyhan V (2011) A Taguchi approach for optimization of design parameters in a tube with coiled wire inserts. Appl Therm Eng 31:2568–2577
Jamshidi N, Farhadi M, Sedighi K, Ganji DD (2012) Optimization of design parameters for nanofluids flowing inside helical coils. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 35:84–92
www.me.ua.edu/me215/f07.woodbury/ExcelStuff/XSteam-v2a.xlsm. Accessed 3 Nov 2017
https://www.mne.psu.edu/cimbala/me433/Links/Table_A_9_CC_Properties_of_Air.pdf. Accessed 3 Nov 2017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Thermo physical properties of various fluid used.
-
For water: [28]
-
For air: [29]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohapatra, T., Padhi, B.N. & Sahoo, S.S. Analytical investigation and performance optimization of a three fluid heat exchanger with helical coil insertion for simultaneous space heating and water heating. Heat Mass Transfer 55, 1723–1740 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-018-02545-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-018-02545-2