Abstract
Introduction
Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography allow studying white matter fiber bundles in the human brain in vivo. Electrophysiological studies and postmortem dissections permit improving our knowledge about the short association fibers connecting the pre- and postcentral gyri. The aim of this study was first to extract and analyze the features of these short fiber bundles and secondly to analyze their asymmetry according to the subjects' handedness.
Methods
Ten right-handed and ten left-handed healthy subjects were included. White matter fiber bundles were extracted using a streamline tractography approach, with two seed regions of interest (ROI) taken from a parcellation of the pre- and postcentral gyri. This parcellation was achieved using T1 magnetic resonance images (MRI) and semi-automatically generated three ROIs within each gyrus. MRI tracks were reconstructed between all pairs of ROIs connecting the adjacent pre- and postcentral gyri. A quantitative analysis was performed on the number of tracks connecting each ROI pair. A statistical analysis studied the repartition of these MRI tracks in the right and left hemispheres and as a function of the subjects' handedness.
Results
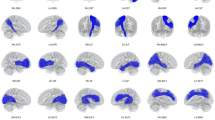
The quantitative analysis showed an increased density of MRI tracks in the middle part of the central area in each hemisphere of the 20 subjects. The statistical analysis showed significantly more MRI tracks for the left hemisphere, when we consider the whole population, and this difference was presumably driven by the left-handers.
Conclusion
These results raise questions about the functional role of these MRI tracks and their relation with laterality.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zilles K, Amunts K (2010) Centenary of Brodmann's map—conception and fate. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:139–145
Geyer S, Schleicher A, Zilles K (1997) The somatosensory cortex of human: cytoarchitecture and regional distributions of receptor-binding sites. NeuroImage 6:27–45
Zilles K, Schlaug G, Matelli M, Luppino G, Schleicher A, Qu M, Dabringhaus A, Seitz R, Roland PE (1995) Mapping of human and macaque sensorimotor areas by integrating architectonic, transmitter receptor, MRI and PET data. J Anat 187(Pt 3):515–537
White LE, Andrews TJ, Hulette C, Richards A, Groelle M, Paydarfar J, Purves D (1997) Structure of the human sensorimotor system. I: morphology and cytoarchitecture of the central sulcus. Cereb Cortex 7:18–30
Boling W, Olivier A, Fabinyi G (2002) Historical contributions to the modern understanding of function in the central area. Neurosurgery 50:1296–309, discussion
Mori S, van Zijl P (2007) Human white matter atlas. Am J Psychiatry 164:1005
Catani M, Dell'acqua F, Vergani F, Malik F, Hodge H, Roy P, Valabregue R, Thiebaut de Schotten M (2012) Short frontal lobe connections of the human brain. Cortex 48:273–291
Anwander A, Tittgemeyer M, von Cramon DY, Friederici AD, Knosche TR (2007) Connectivity-based parcellation of Broca's area. Cereb Cortex 17:816–825
Gonzalez-Darder JM, Gonzalez-Lopez P, Talamantes F, Quilis V, Cortes V, Garcia-March G, Roldan P (2010) Multimodal navigation in the functional microsurgical resection of intrinsic brain tumors located in eloquent motor areas: role of tractography. Neurosurg Focus 28:E5
Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN (2007) Cerebral white matter—historical evolution of facts and notions concerning the organization of the fiber pathways of the brain. J Hist Neurosci 16:237–267
Broca P (1888) Mémoires sur le cerveau de l'homme et des primates. Reinwald, Paris, pp 739–804
Boling W, Olivier A, Bittar RG, Reutens D (1999) Localization of hand motor activation in Broca's pli de passage moyen. J Neurosurg 91:903–910
Boling WW, Olivier A (2004) Localization of hand sensory function to the pli de passage moyen of Broca. J Neurosurg 101:278–283
Yousry TA, Schmid UD, Alkadhi H, Schmidt D, Peraud A, Buettner A, Winkler P (1997) Localization of the motor hand area to a knob on the precentral gyrus. A new landmark. Brain 120(Pt 1):141–157
Boling W, Parsons M, Kraszpulski M, Cantrell C, Puce A (2008) Whole-hand sensorimotor area: cortical stimulation localization and correlation with functional magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 108:491–500
Lawes IN, Barrick TR, Murugam V, Spierings N, Evans DR, Song M, Clark CA (2008) Atlas-based segmentation of white matter tracts of the human brain using diffusion tensor tractography and comparison with classical dissection. NeuroImage 39:62–79
Catani M, Thiebaut de Schotten M (2008) A diffusion tensor imaging tractography atlas for virtual in vivo dissections. Cortex 44:1105–1132
Thiebaut de Schotten M, Ffytche DH, Bizzi A, Dell'acqua F, Allin M, Walshe M, Murray R, Williams SC, Murphy DG, Catani M (2010) Atlasing location, asymmetry and inter-subject variability of white matter tracts in the human brain with MR diffusion tractography. Neuroimage
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Oishi K, Faria AV, Jiang H, Li X, Akhter K, Rosa-Neto P, Pike GB, Evans A, Toga AW, Woods R, Mazziotta JC, Miller MI, van Zijl PC, Mori S (2010) Atlas-guided tract reconstruction for automated and comprehensive examination of the white matter anatomy. NeuroImage 52:1289–1301
Kumar A, Juhasz C, Asano E, Sundaram SK, Makki MI, Chugani DC, Chugani HT (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging study of the cortical origin and course of the corticospinal tract in healthy children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1963–1970
Huang H, Zhang J, Jiang H, Wakana S, Poetscher L, Miller MI, van Zijl PC, Hillis AE, Wytik R, Mori S (2005) DTI tractography based parcellation of white matter: application to the mid-sagittal morphology of corpus callosum. NeuroImage 26:195–205
Bernal B, Altman N (2010) The connectivity of the superior longitudinal fasciculus: a tractography DTI study. Magn Reson Imaging 28:217–225
Oishi K, Zilles K, Amunts K, Faria A, Jiang H, Li X, Akhter K, Hua K, Woods R, Toga AW, Pike GB, Rosa-Neto P, Evans A, Zhang J, Huang H, Miller MI, van Zijl PC, Mazziotta J, Mori S (2008) Human brain white matter atlas: identification and assignment of common anatomical structures in superficial white matter. NeuroImage 43:447–457
Conturo TE, Lori NF, Cull TS, Akbudak E, Snyder AZ, Shimony JS, McKinstry RC, Burton H, Raichle ME (1999) Tracking neuronal fiber pathways in the living human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:10422–10427
Koch G, Cercignani M, Pecchioli C, Versace V, Oliveri M, Caltagirone C, Rothwell J, Bozzali M (2010) In vivo definition of parieto-motor connections involved in planning of grasping movements. NeuroImage 51:300–312
Dellatolas G, De Agostini M, Jallon P, Poncet M, Rey M, Lellouch J (1988) Mesure de la préférence manuelle par autoquestionnaire dans la population française adulte. Rev Psychol aplliquée 38:117–136
Annett M (1992) Five tests of hand skill. Cortex 28:583–600
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Wiest-Daessle N, Prima S, Morrissey SP, Barillot C (2007) Validation of a new optimisation algorithm for registration tasks in medical imaging. In 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. pp 41-44 2007
Coupe P, Yger P, Prima S, Hellier P, Kervrann C, Barillot C (2008) An optimized blockwise nonlocal means denoising filter for 3-D magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 27:425–441
Mangin JF, Coulon O, Frouin V (1998) Robust brain segmentation using histogram scale-space analysis and mathematical morphology. MICCAI 1230-1241
Le Goualher G, Barillot C, Bizais Y (1997) Modeling cortical sulci with active ribbons. Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 11:1295–1315
Ono M, Kubik S, Abernathey C (1990) Atlas of the cerebral sulci. Georg Thieme Verlag
Mechouche A, Morandi X, Golbreich C, Gibaud B (2009) A hybrid system using symbolic and numeric knowledge for the semantic annotation of sulco-gyral anatomy in brain MRI images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28:1165–1178
Fillard P, Pennec X, Arsigny V, Ayache N (2007) Clinical DT-MRI estimation, smoothing, and fiber tracking with log-Euclidean metrics. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 26:1472–1482
Fillard P, Souplet JC, Toussaint N (2009) Medical image navigation and research tool by INRIA (MedINRIA 1.9) Tutorial v2.0
Weinstein D, Kindlmann G, Lundberg E (1999) Tensorlines: Advection–diffusion based propagation through diffusion tensor fields. IEEE Visualization pp 249-253
R Development Core Team (2011) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienne
Shinoura N, Suzuki Y, Yamada R, Kodama T, Takahashi M, Yagi K (2005) Fibers connecting the primary motor and sensory areas play a role in grasp stability of the hand. NeuroImage 25:936–941
Hlustik P, Solodkin A, Gullapalli RP, Noll DC, Small SL (2001) Somatotopy in human primary motor and somatosensory hand representations revisited. Cereb Cortex 11:312–321
Amunts K, Schlaug G, Schleicher A, Steinmetz H, Dabringhaus A, Roland PE, Zilles K (1996) Asymmetry in the human motor cortex and handedness. NeuroImage 4:216–222
Amunts K, Jancke L, Mohlberg H, Steinmetz H, Zilles K (2000) Interhemispheric asymmetry of the human motor cortex related to handedness and gender. Neuropsychologia 38:304–312
Imfeld A, Oechslin MS, Meyer M, Loenneker T, Jancke L (2009) White matter plasticity in the corticospinal tract of musicians: a diffusion tensor imaging study. NeuroImage 46:600–607
Kertesz A, Geschwind N (1971) Patterns of pyramidal decussation and their relationship to handedness. Arch Neurol 24:326–332
Kertesz A, Polk M, Black S, Howell J (1992) Anatomical asymmetries and functional laterality. Brain 115:589–605
Geschwind N (1972) Cerebral dominance and anatomic asymmetry. N Engl J Med 287:194–195
Hagmann P, Cammoun L, Martuzzi R, Maeder P, Clarke S, Thiran JP, Meuli R (2006) Hand preference and sex shape the architecture of language networks. Hum Brain Mapp 27:828–835
Powell HW, Parker GJ, Alexander DC, Symms MR, Boulby PA, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Barker GJ, Noppeney U, Koepp MJ, Duncan JS (2006) Hemispheric asymmetries in language-related pathways: a combined functional MRI and tractography study. NeuroImage 32:388–399
Buchel C, Raedler T, Sommer M, Sach M, Weiller C, Koch MA (2004) White matter asymmetry in the human brain: a diffusion tensor MRI study. Cereb Cortex 14:945–951
Ellmore TM, Beauchamp MS, Breier JI, Slater JD, Kalamangalam GP, O'Neill TJ, Disano MA, Tandon N (2010) Temporal lobe white matter asymmetry and language laterality in epilepsy patients. NeuroImage 49:2033–2044
Vernooij MW, Smits M, Wielopolski PA, Houston GC, Krestin GP, van der Lugt A (2007) Fiber density asymmetry of the arcuate fasciculus in relation to functional hemispheric language lateralization in both right- and left-handed healthy subjects: a combined fMRI and DTI study. NeuroImage 35:1064–1076
Szaflarski JP, Binder JR, Possing ET, McKiernan KA, Ward BD, Hammeke TA (2002) Language lateralization in left-handed and ambidextrous people: fMRI data. Neurology 59:238–244
Pujol J, Lopez-Sala A, Deus J, Cardoner N, Sebastian-Galles N, Conesa G, Capdevila A (2002) The lateral asymmetry of the human brain studied by volumetric magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 17:670–679
Sommer IEC (2010) Sex differences in handedness, brain asymmetry, and language lateralization. Cambridge, Massachusetts, pp 277-312
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to warmly thank Alexandre Abadie for his assistance in setting up the data processing chain, Camille Maumet for her assistance in the asymmetry study and Jean-Christophe Gentric for his review of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magro, E., Moreau, T., Seizeur, R. et al. Characterization of short white matter fiber bundles in the central area from diffusion tensor MRI. Neuroradiology 54, 1275–1285 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1073-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1073-1