Abstract
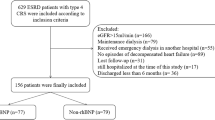
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a biomarker of cardiovascular disease that is common in adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, in children with CKD, the range and predictive power of BNP concentrations are not known. We aimed to determine the effect of HD on BNP, as well as the prognostic impact of BNP, in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) children undergoing hemodialysis (HD). Thirty-five children with chronic renal failure (16 boys age 12.1 ± 3.7 years) on maintenance HD were included. BNP level was measured, and Doppler echocardiography was performed 30 min before (pre-HD BNP) and 30 min after (post-HD BNP) HD in each patient. An adverse event was defined as all-cause death and heart failure hospitalization. The median pre-HD BNP, the post-HD BNP, and the change in BNP were, respectively, 240 pg/ml (72 to 3346), 318 pg/ml (79 to 3788), and 9 pg/ml (−442 to 1889). Pre-HD BNP concentration was negatively correlated with left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (r = −0.41, P = 0.018). During a mean follow-up of 39 ± 14 months, 6 patients died, and 3 were hospitalized for heart failure. Using univariate analysis, BNP before and after HD as well as Doppler tissue imaging velocities had a strong graded relationship with adverse events. Cox proportional hazards model demonstrated that pre-HD body weight (P = 0.008), pre-HD BNP (P = 0.011), and post-HD BNP (P = 0.038) remained independent predictors of adverse outcome. Even in case of ESRD, BNP still strongly correlated with LV systolic and diastolic dysfunction and was associated with mortality in HD children.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alibay Y, Schmitt C, Beauchet A, Dubourg O, Alexandre JA, Boileau C et al (2005) Non-radioimmunometric NT-ProBNP and BNP assays: impact of diluent, age, gender, BMI. Ann Biol Clin 63:43–49
Apple FS, Murakami MM, Pearce LA, Herzog CH (2004) Multi-biomarker risk stratification of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and cardiac troponin T and I in end-stage renal disease for all-cause death. Clin Chem 50:2279–2285
Ariceta G, Brooks ER, Langman CB (2005) Assessing cardiovascular risk in children with chronic kidney disease. B-type natriuretic peptide: a potential new marker. Pediatr Nephrol 20:1701–1707
Auerbach SR, Richmond ME, Lamour JM, Blume ED, Addonizio LJ, Shaddy RE et al (2010) BNP levels predict outcome in pediatric heart failure patients: post hoc analysis of the Pediatric Carvedilol Trial. Circ Heart Fail 3:606–611
Bargnoux AS, Klouche K, Fareh J, Barazer I, Villard-Saussine S, Dupuy AM et al (2008) Prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (proBNP), BNP and N-terminal-proBNP circulating levels in chronic hemodialysis patients. Correlation with ventricular function, fluid removal and effect of hemodiafiltration. Clin Chem Lab Med 46:1019–1024
Cantinotti M, Storti S, Parri MS, Prontera C, Murzi B, Clerico A (2010) Reference intervals for brain natriuretic peptide in healthy newborns and infants measured with an automated immunoassay platform. Clin Chem Lab Med 48:697–700
Cataliotti A, Malatino LS, Jougasaki M, Zoccali C, Castellino P, Giacone G et al (2001) Circulating natriuretic peptide concentrations in patients with end-stage renal disease: role of brain natriuretic peptide as a biomarker for ventricular remodeling. Mayo Clin Proc 76:1111–1119
Civilibal M, Caliskan S, Oflaz H, Sever L, Candan C, Canpolat N et al (2009) Left ventricular function by ‘conventional’ and ‘tissue Doppler’ echocardiography in pediatric dialysis patients. Nephrology 14:636–642
Codognotto M, Piccoli A, Zaninotto M, Mion M, Plebani M, Vertolli U et al (2007) Renal dysfunction is a confounder for plasma natriuretic peptides in detecting heart dysfunction in uremic and idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathies. Clin Chem 53:2097–3104
Hedyig J, Podracka L, Potocekova D (2010) Elevated brain natriuretic peptide is associated with abnormal heart geometry in children with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Blood Press Res 33:87–93
Hickman PE, McGill DA, Talaulikar G, Hiremagalur B, Bromley J, Rahman A et al (2009) Prognostic efficacy of cardiac biomarkers for mortality in dialysis patients. Intern Med J 39:812–818
Ichihashi K, Sato A, Shiraishi H, Momoi M (2011) Tissue Doppler combined with pulsed-wave Doppler echocardiography for evaluating ventricular diastolic function in normal children. Echocardiography 28:93–96
Ishizaka Y, Yamamoto Y, Fukunaga T, Yokota N, Kida O, Kitamura K et al (1994) Plasma concentration of human brain natriuretic peptide in patients on hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 24:46–72
Ito S, Murai S, Takada N, Ozasa A, Hanada M, Sugiyama M et al (2006) Relationship between Doppler transmitral flow velocity pattern and plasma atrial and brain natriuretic peptide concentrations in anuric patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Int Heart J 47:401–408
Koch A, Singer H (2003) Normal values of B-type natriuretic peptide in infants, children, and adolescents. Heart 89:875–878
Koch A, Zink S, Singer H (2006) B-type natriuretic peptide in paediatric patients with congenital heart disease. Eur Heart J 27:861–866
Law YM, Keller BB, Feingold BM, Boyle (2005) Usefulness of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide to identify ventricular dysfunction in pediatric and adult patients with congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol 95:474–478
Law YM, Hoyer AW, Reller MD, Silberbach M (2009) Accuracy of plasma B-type natriuretic peptide to diagnose significant cardiovascular disease in children: the Better Not Pout Children! Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:1467–1475
Lee SW, Song JH, Kim GA, Lim HJ, Kim MJ (2003) Plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration on assessment of hydration status in hemodialysis patient. Am J Kidney Dis 416:1257–1266
Lee JA, Kim DH, Yoo SJ, Oh DJ, Yu SH, Kang ET (2006) Association between serum n-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide concentration and left ventricular dysfunction and extracellular water in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Perit Dial Int 26:360–365
Levin RE, Gardner DG, Samson WK (1998) Natriuretic peptides. N Engl J Med 339:321–328
Liu H, Zhang YZ, Gao M, Liu BC (2010) Elevation of B-type natriuretic peptide is a sensitive marker of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with maintenance haemodialysis. Biomarkers 15:533–537
McCullough PA, Duc P, Omland T, McCord J, Nowak RM, Hollander JE et al (2003) B-type natriuretic peptide and renal function in the diagnosis of heart failure: an analysis from the Breathing Not Properly multinational study. Am J Kidney Dis 41:571–579
McMahon CJ, Nagueh SF, Eapen RS, Dreyer WJ, Finkelshtyn I, Cao X et al (2004) Echocardiographic predictors of adverse clinical events in children with dilated cardiomyopathy: a prospective clinical study. Heart 90:908–915
McMahon CJ, Nagueh SF, Pignatelli RH, Denfield SW, Dreyer WJ, Price JF et al (2004) Characterization of left ventricular diastolic function by tissue Doppler imaging and clinical status in children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 109:1756–1762
Mir TS, Marohn S, Läer S, Eiselt M, Grollmus O, Weil J (2002) Plasma concentrations of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in control children from the neonatal to adolescent period and in children with congestive heart failure. Pediatrics 110:e76
Mir TS, Flato M, Falkenberg J, Haddad M, Budden R, Weil J et al (2006) Plasma concentrations of N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide in healthy children, adolescents, and young adults: effect of age and gender. Pediatr Cardiol 27:73–77
Mitsnefes MM (2008) Cardiovascular complications of pediatric chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 23:27–39
Naganuma T, Sugimura K, Wada S, Yasumoto R, Sugimura T, Masuda C et al (2002) The prognostic role of brain natriuretic peptides in hemodialysis patients. Am J Nephrol 22:437–444
Nishikimi T, Futoo Y, Tamano K, Takahashi M, Suzuki T, Minami J et al (2001) Plasma brain natriuretic peptide levels in chronic hemodialysis patients: influence of coronary artery disease. Am J kidney Dis 37:1201–1208
Ouali S, Abroug S, Neffeti E, Taamalah S, Hammas S, Ben Khalfallah A et al (2010) Effects of acute decrease in preload on echocardiographic indices of systolic and diastolic function of the left ventricle in children with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Comparative study before and after hemodialysis. Ann Cardiol Angiol 59:14–19
Price JF, Thomas AK, Grenier M, Eidem BW, O’Brian Smith E, Denfield SW et al (2006) B-type natriuretic peptide predicts adverse cardiovascular events in pediatric outpatients with chronic left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Circulation 114:1063–1069
Redfield MM, Rodeheffer RJ, Jacobsen SJ, Mahoney DW, Bailey KR, Burnett JC (2002) Plasma brain natriuretic peptide concentration: impact of age and gender. J Am Coll Cardiol 40:976–982
Safley DM, Awad A, Sullivan RA, Sandberg KR, Mourad I, Boulware M et al (2005) Changes in B-type natriuretic peptide levels in hemodialysis and the effect of depressed left ventricular function. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 12:117–124
Saygılı A, Yıldırım SV, Cengiz N, Uslu Y, Tokel K, Saatci U (2005) Assessment of left ventricular diastolic function by Doppler tissue imaging in children with end-stage renal disease. Acta Paediatr 94:1055–1059
Schiller NB, Shah PM, Crawford M, DeMaria A, Devereux R, Feigenbaum H et al (1989) Recommendations for quantitation of the left ventricle by two-dimensional echocardiography. American Society of Echocardiography Committee on Standards, Subcommittee on Quantitation of Two-Dimensional Echocardiograms. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2:358–367
Sugimoto M, Manabe H, Nakau K, Furuya A, Okushima K, Fujiyasu H et al (2010) The role of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure in children. Correlation with the heart failure score and comparison with B-type natriuretic peptide. Circ J 74:998–1005
Sun L, Sun Y, Zhao X, Xu C, Chen D, Li L et al (2008) Predictive role of BNP and NT-proBNP in hemodialysis patients. Nephron Clin Pract 110:c178–c184
Suresh M, Farrington K (2005) Natriuretic peptides and the dialysis patient. Semin Dial 18:409–419
Tafreshi RI, Human N, Otukesh H, Nikavar A (2011) Evaluation of combined left ventricular function using the myocardial performance index in children with chronic kidney disease. Echocardiography 28:97–103
Tagore R, Ling LH, Yang H, Daw HY, Chan YH, Sethi SK (2008) Natriuretic peptides in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:1644–1651
Taskesen M, Taskesen T, Katar S, Karadede A, Tas MA (2009) Elevated plasma levels of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in children with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Tohoku J Exp Med 217:295–298
Tei C, Ling LH, Hodge DO et al (1995) New index of combined systolic and diastolic myocardial performance: a simple and reproducible measure of cardiac function: a study in normals and dilated cardiomyopathy. J Cardiol 26:357–366
Uçar T, Tutar E, Yalçinkaya F, Cakar N, Ozçakar ZB, Atalay S et al (2008) Global left-ventricular function by tissue Doppler imaging in pediatric dialysis patients. Pediatr Nephrol 23:779–785
Wahl HG, Graf S, Renz H, Fassbinder W (2004) Elimination of the cardiac natriuretic peptides B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal proBNP by hemodialysis. Clin Chem 50:1071–1074
Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Leip EP, Benjamin EJ, Wilson PW et al (2002) Impact of age and sex on plasma natriuretic peptide levels in healthy adults. Am J Cardiol 90:254–258
Westerlind A, Wahlander H, Lindstedt G, Lumberg PA, Holmgren D (2004) Clinical signs of heart failure are associated with increased levels of natriuretic peptides types B and A in children with congenital heart defects or cardiomyopathy. Acta Paediatr 93:340–345
Wiley CL, Switzer SP, Berg RL, Glurich I, Dart RA (2010) Association of B-type natriuretic peptide levels with estimated glomerular filtration rate and congestive heart failure. Clin Med Res 8:7–12
Yang AY, Lai KN (2008) Use of cardiac biomarkers in end stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1643–1652
Yang JW, Kim MS, Kim JS, Myoung J, Han ST, Kim BR et al (2008) Relationship between serum brain natriuretic peptide and heart function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Korean J Intern Med 23:191–200
Yokota N, Yamamoto Y, Aburaya M, Kitamura K, Eto T, Kangawa K et al (1991) Increased secretion of brain natriuretic peptide and atrial natriuretic peptide, but not sufficient to induce natriuresis in rats with nephrotic syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 174:128–135
Zoccali C, Mallamaci F, Benedetto FA, Tripepi G, Parlongo S, Cataliotti A et al (2001) Cardiac natriuretic peptides are related to left ventricular mass and function and predict mortality in dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1508–1515
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouali, S., Bougmiza, I., Abroug, S. et al. Relationship of Brain Natriuretic Peptide Concentrations to Left Ventricular Function and Adverse Outcomes in Children With End-Stage Renal Disease Undergoing Hemodialysis. Pediatr Cardiol 32, 568–577 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-011-9909-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-011-9909-8