Abstract
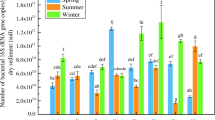
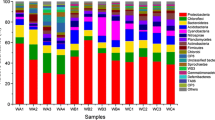
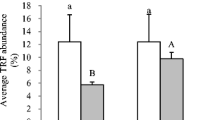
Constructed wetlands offer an effective means for treatment of wastewater from a variety of sources. An understanding of the microbial ecology controlling nitrogen, carbon and sulfur cycles in constructed wetlands has been identified as the greatest gap for optimizing performance of these promising treatment systems. It is suspected that operational factors such as plant types and hydraulic operation influence the subsurface wetland environment, especially redox, and that the observed variation in effluent quality is due to shifts in the microbial populations and/or their activity. This study investigated the biofilm associated sulfate reducing bacteria and ammonia oxidizing bacteria (using the dsrB and amoA genes, respectively) by examining a variety of surfaces within a model wetland (gravel, thick roots, fine roots, effluent), and the changes in activity (gene abundance) of these functional groups as influenced by plant species and season. Molecular techniques were used including quantitative PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE), both with and without propidium monoazide (PMA) treatment. PMA treatment is a method for excluding from further analysis those cells with compromised membranes. Rigorous statistical analysis showed an interaction between the abundance of these two functional groups with the type of plant and season (p < 0.05). The richness of the sulfate reducing bacterial community, as indicated by DGGE profiles, increased in planted vs. unplanted microcosms. For ammonia oxidizing bacteria, season had the greatest impact on gene abundance and diversity (higher in summer than in winter). Overall, the primary influence of plant presence is believed to be related to root oxygen loss and its effect on rhizosphere redox.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal A, Lal B (2009) Rapid detection and quantification of bisulfite reductase genes in oil field samples using real-time PCR. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 69:301–312
Aho K, Roberts DW, Weaver T (2008) Using geometric and non-geometric internal evaluators to compare eight vegetation classification methods. J Veg Sci 19:549–562
Allen WC, Hook PB, Biederman JA, Stein OR (2002) Temperature and wetland plant species effects on wastewater treatment and root zone oxidation. J Enviro Qual 31:1010–1016
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in-situ detection of individual microbial-cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Bahr M, Crump BC, Klepac-Ceraj V, Teske A, Sogin ML, Hobbie JE (2005) Molecular characterization of sulfate-reducing bacteria in a New England salt marsh. Environ Microbiol 7:1175–1185
Bais HP, Weir TL, Perry LG, Gilroy S, Vivanco JM (2006) The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interations with plants and other organisms. Ann Rev Plant Biol 57:233–266
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate — a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B-Methodol 57:289–300
Boon N, De Windt W, Verstraete W, Top EM (2002) Evaluation of nested PCR-DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) with group-specific 16S rRNA primers for the analysis of bacterial communities from different wastewater treatment plants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:101–112
Borden D, Stein O, Hook P (2001) Seasonal effects of supplemental organic carbon on sulfate reduction and zinc sulfide precipitation in constructed wetland microcosms. Intern Ecol Eng Soc Meet Lincoln University, New Zealand, In, pp 296–300
Brix H (1994) Functions of macrophytes in constructed wetlands. Water Sci Technol 29:71–78
Brix H (1997) Do macrophytes play a role in constructed treatment wetlands? Water Sci Technol 35:11–17
Brune A, Frenzel P, Cypionka H (2000) Life at the oxic–anoxic interface: microbial activities and adaptations. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:691–710
Burgmann H, Meier S, Bunge M, Widmer F, Zeyer J (2005) Effects of model root exudates on structure and activity of a soil diazotroph community. Environ Microbiol 7:1711–1724
Burr MD, Clark SJ, Spear CR, Camper AK (2006) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis can rapidly display the bacterial diversity contained in 16S rDNA clone libraries. Microb Ecol 51:479–486
Calheiros CSC, Teixeira A, Pires C, Franco AF, Duque AF, Crsipim LFC, Moura SC, Castro PML (2010) Bacterial dynamics in horizontal flow constructed wetlands with different plants for high salinity industrial wastewater polishing. Water Res 44:5032–5038
Chain P, Lamerdin J, Larimer F, Regala W, Lao V, Land M et al (2003) Complete genome sequence of the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium and obligate chemolithoautotroph Nitrosomonas europaea. J Bacteriol 185:2759–2773
Cooper P, Griffin P (1999) A review of the design and performance of vertical-flow and hybrid reed bed treatment systems. Water Sci Technol 40:1–9
Cypionka H (2000) Oxygen respiration by Desulfovibrio species. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:827–848
Dang HY, Li J, Chen RP, Wang L, Guo LZ, Zhang ZN, Klotz MG (2010) Diversity, abundance, and spatial distribution of sediment ammonia-oxidizing betaproteobacteria in response to environmental gradients and coastal eutrophication in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4691–4702
Devereux R, Hines ME, Stahl DA (1996) S cycling: characterization of natural communities of sulfate-reducing bacteria by 16S rRNA sequence comparisons. Microb Ecol 32:283–292
Faulwetter JL, Gagnon V, Sundberg C, Chazarenc F, Burr MD, Brisson J et al (2009) Microbial processes influencing performance of treatment wetlands: a review. Ecol Eng 35:987–1004
Ferris MJ, Muyzer G, Ward DM (1996) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of 16S rRNA-defined populations inhabiting a hot spring microbial mat community. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:340–346
Fogel G, Collins C, Li J, Brunk C (1999) Prokaryotic genome size and SSU rDNA copy number: estimation of microbial relative abundance from a mixed population. Microb Ecol 38:93–113
Fortin D, Goulet R, Roy M (2000) Seasonal cycling of Fe and S in a constructed wetland: the role of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Geomicrobiol J 17:221–235
Fromin N, Hamelin J, Tarnawski S, Roesti D, Jourdain-Miserez K, Forestier N et al (2002) Statistical analysis of denaturing gel electrophoresis (DGE) fingerprinting patterns. Environ Microbiol 4:634–643
Gagnon V, Chazarenc F, Comeau Y, Brisson J (2007) Influence of macrophyte species on microbial density and activity in constructed wetlands. Water Sci Technol 56:249–254
Geets J, Borrernans B, Diels L, Springael D, Vangronsveld J, van der Lelie D, Vanbroekhoven K (2006) DsrB gene-based DGGE for community and diversity surveys of sulfate-reducing bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 66:194–205
Geets J, de Cooman M, Wittebolle L, Heylen K, Vanparys B, De Vos P et al (2007) Real-time PCR assay for the simultaneous quantification of nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria in activated sludge. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:211–221
Girvan MS, Bullimore J, Pretty JN, Osborn AM, Ball AS (2003) Soil type is the primary determinant of the composition of the total and active bacterial communities in arable soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1800–1809
Gregori G, Citterio S, Ghiani A, Labra M, Sgorbati S, Brown S, Denis M (2001) Resolution of viable and membrane-compromised bacteria in freshwater and marine waters based on analytical flow cytometry and nucleic acid double staining. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4662–4670
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:95–108
Hallin S, Jones CM, Schloter M, Philippot L (2009) Relationship between N-cycling communities and ecosystem functioning in a 50-year-old fertilization experiment. ISME J 3:597–605
Hammer M, Hammer MJ (2001) Water and wastewater technology. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA
Hatano K, Frederick DJ, Moore JA (1994) Microbial ecology of constructed wetlands used for treating pulp-mill waste-water. Water Sci Technol 29:233–239
Hsu S, Maynard J (1999) The use of sulfur isotopes to monitor the effectiveness of constructed wetlands in controlling acid mine drainage. Environ Eng Policy 1:223–233
Iasur-Kruh L, Hadar Y, Milstein D, Gasith A, Minz D (2010) Microbial population and activity in wetland microcosms constructed for improving treated municipal wastewater. Microb Ecol 59:700–709
Ibekwe AM, Papiernik SK, Gan J, Yates SR, Yang CH, Crowley DE (2001) Impact of fumigants on soil microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3245–3257
Ibekwe AM, Grieve CM, Lyon SR (2003) Characterization of microbial communities and composition in constructed dairy wetland wastewater effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5060–5069
Johnson K, Martin C, Moshiri G, McCrory W (1999) Performance of a constructed wetland leachate treatment system at the Chunchula landfill, Mobile County, Alabama. In: Mulamoottil F, McBean E, Rovers F (eds) Constructed wetlands for the treatment of landfill leachates. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA, pp 57–70
Josephson KL, Gerba CP, Pepper IL (1993) Polymerase chain reaction detection of non-viable bacterial pathogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3513–3515
Kalin M, Fyson A, Wheeler WN (2006) The chemistry of conventional and alternative treatment systems for the neutralization of acid mine drainage. Sci Total Environ 366:395–408
Kirk JL, Beaudette LA, Hart M, Moutoglis P, Khironomos JN, Lee H, Trevors JT (2004) Methods of studying soil microbial diversity. J Microbiol Methods 58:169–188
Klein M, Friedrich M, Roger A, Hugenholtz P, Fishbain S, Abicht H et al (2001) Multiple lateral transfers of dissimilatory sulfite reductase genes between major lineages of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes. J Bacteriol 183:6028–6035
Konopka A (2009) What is microbial community ecology? ISME J 3:1223–1230
Kowalchuk GA, Stienstra AW, Heilig GHJ, Stephen JR, Woldendorp JW (2000) Molecular analysis of ammonia-oxidising bacteria in soil of successional grasslands of the Drentsche A (The Netherlands). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31:207–215
Kowalchuk GA, Buma DS, de Boer W, Klinkhamer PGL, van Veen JA (2002) Effects of above-ground plant species composition and diversity on the diversity of soil-borne microorganisms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Intern J Gen Mol Microbiol 81:509–520
Kuschk P, Wiessner A, Kappelmeyer U, Weissbrodt E, Kastner M, Stottmeister U (2003) Annual cycle of nitrogen removal by a pilot-scale subsurface horizontal flow in a constructed wetland under moderate climate. Water Res 37:4236–4242
Leloup J, Fossing H, Kohls K, Holmkvist L, Borowski C, Jorgensen BB (2009) Sulfate-reducing bacteria in marine sediment (Aarhus Bay, Denmark): abundance and diversity related to geochemical zonation. Environ Microbiol 11:1278–1291
Luo J-F, Lin W-T, Guo Y (2010) Method to detect only viable cells in microbial ecology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:377–384
McCune B, Grace JB (2002) Analysis of ecological communities. MjM Software Design, Gleneden Beach, OR, USA
Minz D, Flax J, Green S, Muyzer G, Cohen Y, Wagner M et al (1999) Diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in oxic and anoxic regions of a microbial mat characterized by comparative analysis of dissimilatory sulfite reductase genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4666–4671
Molle P, Prost-Boucle S, Lienard A (2008) Potential for total nitrogen removal by combining vertical flow and horizontal flow constructed wetlands: a full scale experiment study. Ecol Eng 34:23–29
Munch C, Neu T, Kuschk P, Roske I (2007) Ecological considerations—the root surface as the definitive detail for microbial transformation processes in constructed wetlands—a biofilm characteristic. Water Sci Technol 56:271–276
Murray AE, Hollibaugh JT, Orrego C (1996) Phylogenetic compositions of bacterioplankton from two California estuaries compared by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of 16S rDNA fragments. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2676–2680
Muyzer G, Dewaal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S ribosomal-RNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nocker A, Camper AK (2009) Novel approaches toward preferential detection of viable cells using nucleic acid amplification techniques. FEMS Microbiol Lett 291:137–142
Nocker A, Cheung CY, Camper AK (2006) Comparison of propidium monoazide with ethidium monoazide for differentiation of live vs. dead bacteria by selective removal of DNA from dead cells. J Microbiol Methods 67:310–320
Nocker A, Sossa-Fernandez P, Burr MD, Camper AK (2007) Use of propidium monoazide for live/dead distinction in microbial ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5111–5117
Okano Y, Hristova KR, Leutenegger CM, Jackson LE, Denison RF, Gebreyesus B et al (2004) Application of real-time PCR to study effects of ammonium on population size of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1008–1016
Painter H (1986) Nitrification in the treatment of sewage and waste-waters. In: Prosser J (ed) Nitrification. Information Printing, Oxford, UK, pp 185–211
Paredes D, Kuschk P, Koser H (2007) Influence of plants and organic matter on the nitrogen removal in laboratory-scale model subsurface flow constructed wetlands inoculated with anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Eng Life Sci 7:565–576
Park H-D, Wells GF, Bae H, Criddle CS, Francis CA (2006) Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in wastewater treatment plant bioreactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5643–5647
Pathak B, Kazama F, Tanaka Y, Mori K, Sumino T (2007) Quantification of anammox populations enriched in an immobilized microbial consortium with low levels of ammonium nitrogen and at low temperature. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1173–1179
Rencher AC (1998) Multivariate statistical inference and applications. Wiley
Roberts DW (2009) labdsv: Ordination and multivariate analysis for ecology. In: R package version 1.3-3, http://ecology.msu.montana.edu/labdsv/R
Roberts DW (2010) optpart: Optimal partitioning of similarity relations. In: R package version 2.0-1, http://CRAN.R-project.org/package==optpart
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Rousseeuw PJ (1987) Silhouettes — a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster-analysis. J Comput Appl Math 20:53–65
Saleh-Lakha S, Miller M, Campbell RG, Schneider K, Elahimanesh P, Hart MM, Trevors JT (2005) Microbial gene expression in soil: methods, applications and challenges. J Microbiol Methods 63:1–19
Scheid D, Stubner S (2001) Structure and diversity of Gram-negative sulfate-reducing bacteria on rice roots. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 36:175–183
Scholz M, Lee B (2005) Constructed wetlands: a review. Intern J Environ Stud 62:421–447
Sigalevich P, Baev MV, Teske A, Cohen Y (2000) Sulfate reduction and possible aerobic metabolism of the sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio oxyclinae in a chemostat coculture with Marinobacter sp strain MB under exposure to increasing oxygen concentrations. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5013–5018
Sims A, Gajaraj S, Hu Z (2012) Seasonal population changes of ammonia-oxidizing organisms and their relationship to water quality in a constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 40:100–107
Sims A, Horton J, Gajaraj S, McIntosh S, Miles RJ, Mueller R, Reed R, Hu Z (2012) Temporal and spatial distributions of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria and their ratio as an indicator of oligotrophic conditions in natural wetlands. Water Res 46:4121–4129
Smalla K, Wieland G, Buchner A, Zock A, Parzy J, Kaiser S et al (2001) Bulk and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities studied by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis: plant-dependent enrichment and seasonal shifts revealed. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4742–4751
Song Y, Fitch M, Burken J, Nass L, Chilukiri S, Gale N, Ross C (2001) Lead and zinc removal by laboratory-scale constructed wetlands. Water Environ Res 73:37–44
Song ZW, Zheng ZP, Li J, Sun XF, Han XY, Wang W, Xu M (2006) Seasonal and annual performance of a full-scale constructed wetland system for sewage treatment in China. Ecol Eng 26:272–282
Stein OR, Hook PB (2005) Temperature, plants, and oxygen: how does season affect constructed wetland performance? J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 40:1331–1342
Stein OR, Borden-Stewart DJ, Hook PB, Jones WL (2007) Seasonal influence on sulfate reduction and zinc sequestration in subsurface treatment wetlands. Water Res 41:3440–3448
Stewart P, Franklin M (2008) Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:199–210
Stottmeister U, Wieβner KP, Kappelmeyer U, Kastner BO, Muller RA, Moormann H (2003) Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Adv 22:93–117
Sundberg C, Stendahl JSK, Tonderski K, Lindgren PE (2007) Overland flow systems for treatment of landfill leachates — potential nitrification and structure of the ammonia-oxidising bacterial community during a growing season. Soil Biol Biochem 39:127–138
Sundblad K (1998) Sweden. In: Vymazal J, Brix H, Cooper PF, Green MB, Haberl R (eds) Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment in Europe. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands, pp 251–259
Taylor CR, Stein OR, Hook PB, Zabinski CA (2008) In: Comparing 19 plant species’ seasonal effects on COD removal in model treatment wetlands. 11th Intern Conf Wetl Syst Water Pollut Control. Indore, India, pp 132–138
Taylor CR (2009) Selecting plant species to optimize wastewater treatment in constructed wetlands. MSc thesis, Mont State Univ
Taylor C, Hook P, Stein O, Zabinski C (2011) Seasonal effects of 19 plant species on COD removal in subsurface treatment wetland microcosms. Ecol Eng 37:703–710
Van der Gucht K, Sabbe K, De Meester L, Vloemans N, Zwart G, Gillis M, Vyverman W (2001) Contrasting bacterioplankton community composition and seasonal dynamics in two neighbouring hypertrophic freshwater lakes. Environ Microbiol 3:680–690
van der Wielen PWJJ, Voost S, van der Kooij D (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in groundwater treatment and drinking water distribution systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4687–4695
Varma M, Field R, Stinson M, Rukovets B, Wymer L, Haugland R (2009) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of total and propidium monoazide-resistant fecal indicator bacteria in wastewater. Water Res 43:4790–4801
Vladar P, Rusznyak A, Marialigeti K, Borsodi AK (2008) Diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria inhabiting the rhizosphere of Phragmites australis in Lake Velencei (Hungary) revealed by a combined cultivation-based and molecular approach. Microb Ecol 56:64–75
Wagner M, Roger AJ, Flax JL, Brusseau GA, Stahl DA (1998) Phylogeny of dissimilatory sulfite reductases supports an early origin of sulfate respiration. J Bacteriol 180:2975–2982
Wang R, Baldy V, Perissol C, Korboulewsky (2012) Influence of plants on microbial activity in a vertical-downflow wetland system treating waste activated sludge with high organic matter concentrations. J Environ Mgt 95:S158–S164
Whitmire SL, Hamilton SK (2005) Rapid removal of nitrate and sulfate in freshwater wetland sediments. J Environ Qual 34:2062–2071
Wiessner A, Kuschk P, Jechorek M, Seidel H, Kastner M (2008) Sulphur transformation and deposition in the rhizosphere of Juncus effusus in a laboratory-scale constructed wetland. Environ Pollut 155:125–131
Yin J, Jiang LY, Wen Y, Yao ZL, Zhou Q (2009) Treatment of polluted landscape lake water and community analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in constructed wetland. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 44:722–731
Zhu T, Sikora FJ (1995) Ammonium and nitrate removal in vegetated and unvegetated gravel bed microcosm wetlands. Water Sci Technol 32:219–228
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by: USDA-NRI Competitive Grants Program, Award 2004-35102-14832, the Montana Board of Research and Commercialization Technology (MBRCT), Grant Agreement #09-26, and the Society of Wetland Scientists through the Student Research Grant Program. We would like to thank Bennett Hisey and Rachel Van Kempen-Fryling for their assistance in preparation and production of DGGE gels for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faulwetter, J.L., Burr, M.D., Parker, A.E. et al. Influence of Season and Plant Species on the Abundance and Diversity of Sulfate Reducing Bacteria and Ammonia Oxidizing Bacteria in Constructed Wetland Microcosms. Microb Ecol 65, 111–127 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0114-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0114-y