Abstract
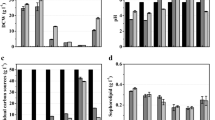
Candida sp. strain SY16 produces a glycolipid-type biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid (MEL-SY16), which can reduce the surface tension of a culture broth from 72 to 30 dyne cm−1 and highly emulsify hydrocarbons when cultured in soybean-oil-containing media. As such, laboratory-scale fermentation for MEL-SY16 production was performed using optimized conditions. In batch fermentation, MEL-SY16 was mainly produced during the stationary phase of growth, and the concentration of MEL-SY16 reached 37 g l−1 after 200 h. The effect of pH control on the production of MEL-SY16 was also examined in batch fermentation. The highest production yield of MEL-SY16 was when the pH was controlled at 4.0, and the production was significantly improved compared to batch fermentation without pH control. In fed-batch fermentation, glucose and soybean oil (1:1, w/w) were used in combination as the initial carbon sources for cell growth, and soybean oil was used as the feeding carbon source during the MEL production phase. The feeding of soybean oil resulted in the disappearance of any foam and a sharp increase in the MEL production until 200 h, at which point the concentration of MEL-SY16 was 95 g l−1. Among the investigated culture systems, the highest MEL-SY16 production and volumetric production rate were achieved with fed-batch fermentation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczak M, Bednarski W (2000) Influence of medium composition and aeration on the synthesis of biosurfactants produced by Candida antarctica. Biotechnol Lett 22:313–316
Alleman JE, Jones MN, Kamhawy SM, Keefe CW (1995) 4500-NH3 F. Phenate method. In: Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE (eds) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. APHA-AWWA-WEF, Washington DC, pp 4-80–4-81
Banat IM, Makkar RS, Cameotra SS (2000) Potential commercial applications of microbial surfactants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:495–508
Desai JD (1987) Microbial surfactants: evaluation, types, production and future applications. J Sci Ind Res 46:440–449
Georgiou G, Lin SC, Sharma MM (1992) Surface-active compounds from micro-organisms. Bio/Technology 10:60–65
Guerra-Santos LH, Käppeli O, Fiechter A (1984) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biosurfactant production in continuous culture with glucose as carbon source. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:301–305
Hommel R, Stüwer O, Stuber W, Haferburg D, Kleber HP (1987) Production of water-soluble surface-active exolipids by Torulopsis apicola. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26:199–205
Kawashima H, Nakahara T, Oogaki M, Tabuchi T (1983) Extracellular production of a mannosylerythritol lipid by a mutant of Candida sp. from n-alkanes and triacylglycerols. J Ferment Technol 61:143–149
Kim HS, Lee CH, Suh HH, Ahn KH, Oh HM, Kwon KS, Yang JW, Yoon BD (1997) A lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis C9 selected through the oil film-collapsing assay. J Microbiol Biotechnol 7:180–188
Kim HS, Yoon BD, Choung DH, Oh HM, Katsuragi T, Tani Y (1999) Characterization of a biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid produced from Candida sp. SY16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:713–721
Kim HS, Jeon JW, Lee HW, Park YI, Seo WT, Oh HM, Katsuragi T, Tani Y, Yoon BD (2002a) Extracellular production of a glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, from Candida antarctica. Biotechnol Lett 24:225–229
Kim HS, Jeon JW, Kim SB, Oh HM, Kwon TJ, Yoon BD (2002b) Surface and physico-chemical properties of a glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, from Candida antarctica. Biotechnol Lett 24:1637–1641
Kitamoto D, Fuzishiro T, Yanagishita H, Nakane T, Nakahara T (1992a) Production of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants by resting cells of Candida antarctica. Biotechnol Lett 14:305–310
Kitamoto D, Nakane T, Nakao N, Nakahara T, Tabuchi T (1992b) Intracellular accumulation of mannosylerythritol lipids as storage materials by Candida antarctica. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:768–772
Kitamoto D, Yanagishita H, Shinbo T, Nakane T, Kamisawa C, Nakahara T (1993) Surface active properties and antimicrobial activities of mannosylerythritol lipids as biosurfactants produced by Candida antarctica. J Biotechnol 29:91–96
Meesters PAEP, Huijberts GNM, Eggink G (1996) High-cell-density cultivation of the lipid accumulating yeast Cryptococcus curvatus using glycerol as a carbon source. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 45:575–579
Rau U, Nguyen LA, Schulz S, Wray V, Nimtz M, Roeper H, Koch H, Lang S (2004) Formation and analysis of mannosylerythritol lipids secreted by Pseudozyma aphidis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:551–559
Sekelsky AM, Shreve GS (1999) Kinetic model of biosurfactant-enhanced hexadecane biodegradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biotechnol Bioeng 63:401–409
Spoeckner S, Wray V, Nimtz M, Lang S (1999) Glycolipids of the smut fungus Ustilago maydis from cultivation on renewable resources. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:33–39
Stüwer O, Hommel R, Haferburg D, Kleber HP (1987) Production of crystalline surface-active glycolipids by a strain of Torulopsis apicola. J Biotechnol 6:259–269
Sugita T, Takashima M, Poonwan N, Mekha N, Malaithao K, Thungmuthasawat B, Prasarn S, Luangsook P, Kudo T (2003) The first isolation of ustilaginomycetous anamorphic yeasts, Pseudozyma species, from patients' blood and a description of two new species: P. parantarctica and P. thailandica. Microbiol Immunol 47:183–190
Woo SH, Park JM, Rittmann BE (2001) Evaluation of the interaction between biodegradation and sorption of phenanthrene in soil-slurry systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 73:12–24
Zhao X, Wakamatsu Y, Shibahara M, Nomura N, Geltinger C, Nakahara T, Murata T, Yokoyama K (1999) Mannosylerythritol lipid is a potent inducer of apoptosis and differentiation of mouse melanoma cells in culture. Cancer Res 59:482–486
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Korean Molecular and Cellular BioDiscovery Research Program and the MOST/KOSEF to the Environmental Biotechnology National Core Research Center (grant #: R15-2003-012-02001-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HS., Jeon, JW., Kim, BH. et al. Extracellular production of a glycolipid biosurfactant, mannosylerythritol lipid, by Candida sp. SY16 using fed-batch fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70, 391–396 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0092-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0092-9