Abstract
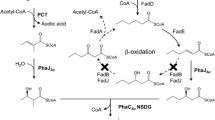
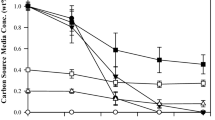
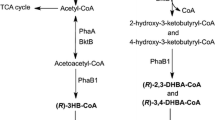
Medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates (mcl-PHA) consisting of 3-hydroxyhexanoate (HHx), 3-hydroxyoctanoate (HO), 3-hydroxydecanoate, 3-hydroxydodecanoate, and high-content 3-hydroxytetradecanoate (HTD) was produced by knockout mutant Pseudomonas putida KT2442 termed P. putida KTOY06. When grown on 6 to14 g/L single-carbon-source tetradecanoic acid, P. putida KTOY06, which β-oxidation pathway was weakened by deleting genes of 3-ketoacyl-coenzyme A (CoA) thiolase (fadA) and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (fadB), for the first time, produced several mcl-PHA including 31 to 49 mol% HTD as a major monomer. HHx contents in these mcl-PHAs remained approximately constant at less than 3 mol%. In addition, large amounts of oligo-HTD were detected in cells, indicating the limited ability of P. putida KTOY06 in polymerizing long-chain-length 3-hydroxyalkanoates. The mcl-PHA containing high HTD monomer contents was found to have both higher crystallinity and improved tensile strength compared with that of typical mcl-PHA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashby RD, Foglia TA, Solaiman DK, Liu C, Nunez A, Eggink G (2000) Viscoelastic properties of linseed oil-based medium chain length poly(hydroxyalkanoate) films: effects of epoxidation and curing. Int J Biol Macromol 28:355–361
Atkins TW, Peacock SJ (1996) The incorporation and release of bovine serum albumin from poly-hydroxybutyrate–hydroxyvalerate microcapsules. J Microencapsul 13:709–717
Braunegg G, Sonnleitner B, Lafferty RM (1978) A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of poly-b-hydroxybutyric acid in microbial biomass. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 6:29–37
Chen GQ, Wu Q (2005) The application of polyhydroxyalkanoates as tissue engineering materials. Biomaterials 26:6565–6578
Chen GQ, Xu J, Wu Q, Zhang ZM, Ho KP (2001a) Synthesis of copolyesters consisting of medium-chain-length β-hydroxyalkanoates by Pseudomonas stutzeri 1317. React Funct Polym 48:107–112
Chen GQ, Zhang G, Park SJ, Lee SY (2001b) Industrial scale production of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:50–55
Curley JM, Hazer B, Lenz RW, Fuller RC (1996) Production of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) containing aromatic substituents by Pseudomonas oleovorans. Macromolecules 29:1762–1766
de Roo G, Kellerhals MB, Ren Q, Witholt B, Kessler B (2002) Production of chiral R-3-hydroxyalkanoic acids and R-3-hydroxyalkanoic acid methylesters via hydrolytic degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesized by pseudomonads. Biotechnol Bioeng 77:717–722
Fiedler S, Steinbüchel A, Rehm, B (2002) The role of the fatty acid β-oxidation multienzyme complex from Pseudomonas oleovorans in polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis: molecular characterization of the fadBA operon from P. oleovorans and of the enoyl-CoA hydratase genes phaJ from Pseudomonas oleovorans and Pseudomonas putida. Arch Microbiol 178:149–160
Fritzsche K, Lenz RW, Fuller RC (1990) An unusual bacterial polyester with a phenyl pendant group. Makromol Chem 191:1957–1965
Gross RA, DeMello C, Lenz RW (1989) Biosynthesis and characterization of poly (β-hydroxyalkanoates) produced by Pseudomonas oleovorans. Macromolecules 22:1106–1115
Gursel I, Hasirci V (1995) Properties and drug release behavior of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid) and various poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate) copolymer microcapsules. J Microencapsul 12:185–193
Hartmann R, Hany R, Geiger T, Egli T, Witholt B, Zinn M (2004) Tailored biosynthesis of olefinic medium-chain-length poly[(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoates] in Pseudomonas putida GPo1 with improved thermal properties. Macromolecules 37:6780–6785
Hoffmann N, Rehm BH (2004) Regulation of polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis in Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 237:1–7
Holmes PA (1985) Application of PHB—a microbially produced biodegradable thermoplastic. Phys Technol 16:32–36
Jung K, Hany R, Rentsch D, Storni T, Egli T, Witholt B (2000) Characterization of new bacterial copolyesters containing 3-hydroxy-oxoalkanoates and acetoxy-3-hydroxyalkanoates. Macromolecules 33:8571–8575
Kellerhals MB, Kessler B, Witholt B (2000) Renewable long-chain fatty acids for production of biodegradable medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates (mcl-PHAs) at laboratory and pilot plant scales. Macromolecules 33:4690–4698
Kim DY, Kim YB, Rhee YH (1998) Bacterial poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) bearing carbon–carbon triple bonds. Macromolecules 31:4760–4763
Kim YB, Kim DY, Rhee YH (1999) PHAs produced by Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas oleovorans grown with n-alkanoic acids containing aromatic groups. Macromolecules 32:6058–6064
Lageveen RG, Huisman GW, Preusting H, Ketelaar P, Eggink G, Witholt B (1988) Formation of polyesters by Pseudomonas oleovorans: effect of substrates on formation and poly-(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoates. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2924–2932
Luo RC, Chen JY, Zhang L, Chen JC, Chen GQ (2006) Polyhydroxyalkanoates copolyesters produced by Ralstonia eutropha PHB-4 harboring a low-substrate-specificity PHA synthase PhaC2Ps from Pseudomonas stutzeri 1317. Biochem Eng J 31:218–225
Nakamura S, Kunioka M, Doi Y (1991) Biosynthesis and characterization of bacterial poly(3hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxy- propionate). Macromol Rep 28:15–24
Noda I, Satkowski MM, Dowrey AE, Marcott C (2004) Polymer alloys of Nodax copolymers and poly(lactic acid). Macromol Biosci 15:269–275
Noda I, Green PR, Satkowski MM, Schechtman LA (2005) Preparation and properties of a novel class of polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymers. Biomacromolecules 6:580–586
Ouyang SP, Liu Q, Fang L, Chen GQ (2007) Construction of pha-operon-defined knockout mutants of Pseudomonas putida KT2442 and their applications in poly(hydroxyalkanoate) production. Macromol Biosci 7:227–233
Preusting H, Nijenhuis A, Witholt B (1990) Physical characteristics of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) and poly (3-hydroxyalkenoates) produced by Pseudomonas oleovorans. Macromolecules 23:4220–4224
Schäfer A, Tauch A, Jäger, W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Pühler A (1994) Small mobilizble multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 145:69–73
Sim SJ, Snell KD, Hogan SA, Stubbe J, Rha CK, Sinskey A (1997) PHA synthase activity controls the molecular weight and polydispersity of polyhydroxybutyrate in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 15:63–67
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in gram negative bacteria. Bio/Technology 1:784–791
Steinbüchel A, Valentin HE (1995) Diversity of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoic acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett 128:219–228
Sun ZY, Ramsay JA, Guay M, Ramsay, BA (2006) Automated feeding strategies for high-cell-density fed-batch cultivation of Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:423–431
Sun Z, Ramsay JA, Guay M, Ramsay BA (2007) Carbon-limited fed-batch production of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates from nonanoic acid by Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:69–77
Taguchi S, Doi Y (2004) Evolution of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production system by “enzyme evolution”: successful case studies of directed evolution. Macromol Biosci 4:145–156
Weinel C, Nelson KE, Tummler B (2002) Global features of the Pseudomonas putida KT2440 genome sequence. Environ Microbiol 4:809–818
Witholt B, Kessler B (1999) Perspectives of medium chain length poly(hydroxyalkanoates), a versatile set of bacterial bioplastics. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10:279–285
Xu SL, Luo RC, Wu LP, Xu KT, Chen GQ (2006) Blending and characterizations of microbial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) with dendrimers. J Appl Polym Sci 102:3782–3790
Zheng Z, Bei FF, Deng Y, Tian HL, Chen GQ (2005) Effects of crystallization of polyhydroxyalkanoate blend on surface physicochemical properties and resulting biocompatibility for chondrocytes. Biomaterials 26:3537–3548
Zinn M, Witholt B, Egli T (2001) Occurrence, synthesis and medical application of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoate. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 53:5–21
Acknowledgments
The strain P. putida KTOY06 was kindly donated by Dr. Ouyang SP. We are grateful to Li Ka Shing Foundation and State High Tech Project 863 Grant no. 2006AA02Z242 for financial support. We also like to thank Mr. Luo RC and Wu LP in the Multidisciplinary Research Center of Shantou University for their DSC and MRI studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Chen, GQ. Production and characterization of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate with high 3-hydroxytetradecanoate monomer content by fadB and fadA knockout mutant of Pseudomonas putida KT2442. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76, 1153–1159 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1092-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1092-8