Abstract
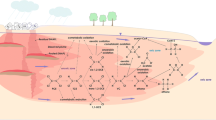
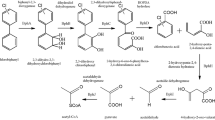
Chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds (CNAs) are persistent environmental pollutants that have been introduced into the environment due to the anthropogenic activities. Bacteria that utilize CNAs as the sole sources of carbon and energy have been isolated from different contaminated and non-contaminated sites. Microbial metabolism of CNAs has been studied, and several metabolic pathways for degradation of CNAs have been proposed. Detoxification and biotransformation of CNAs have also been studied in various fungi, actinomycetes and bacteria. Several physicochemical methods have been used for treatment of wastewater containing CNAs; however, these methods are not suitable for in situ bioremediation. This review describes the current scenario of the degradation of CNAs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora PK, Jain RK (2011a) Biotransformation of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol into 5-chloro-2-methylbenzoxazole by a marine Bacillus sp. strain MW-1. Biodegradation. doi:10.1007/s10532-011-9512-y
Arora PK, Jain RK (2011b) Pathway for degradation of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol by Arthrobacter sp. SJCon. Curr Microbiol 63:568–573
Arora PK, Kumar M, Chauhan A, Raghava GP, Jain RK (2009) OxDBase: a database of oxygenases involved in biodegradation. BMC Res Notes 2:67
Arora PK, Srivastava A, Singh VP (2010) Application of monooxygenases in dehalogenation, desulphurization, denitrification and hydroxylation of aromatic compounds. J Bioremed Biodegrad 1:110
Betts JJ, James SP, Thorpe WV (1955) The metabolism of pentachloronitrobenzene and 2,3,4,6-tetrachloronitrobenzene and the formation of mercapturic acids in the rabbit. Biochem J 61:611–617
Beunink J, Rehm HJ (1990) Coupled reductive and oxidative degradation of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol by a co-immobilized mixed culture system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34:108–115
Bhushan B, Samanta SK, Chauhan A, Chakraborti AK, Jain RK (2000) Chemotaxis and biodegradation of 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol by Ralstonia sp. SJ98. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275:129–133
Bruhn C, Bayly RC, Knackmuss HJ (1988) The in vivo construction of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol assimilatory bacteria. Arch Microbiol 150:171–177
Capek A, Simek A, Leiner J, Weichet J (1970) Antimicrobial agents. VII. Microbial degradation of the antifungal agent 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol (Nitrofungin). Folia Microbiol (Praha) 15:350–353
Chacke CI, Lockwood JL, Zabik M (1966) Chlorinated hydrocarbon pesticides: degradation by microbes. Science 154:893–895
Chauhan A, Chakraborti AK, Jain RK (2000) Plasmid-encoded degradation of p-nitrophenol and 4-nitrocatechol by Arthrobacter protophormiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:733–740
de Vos RH, ten Noever de Brauw MC, Olthof PDA (1974) Residues of pentachloronitrobenzene and related compounds in greenhouse soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 11:567–571
Field JA, Sierra-Alvarez R (2008) Microbial degradation of chlorinated benzenes. Biodegradation 19:463–480
Gharbani P, Khosravi M, Tabatabaii SM, Zare K, Dastmalchi S, Mehrizad A (2010) Degradation of trace aqueous 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol occurring in pharmaceutical industrial wastewater by ozone. Int J Environ Sci Technol 7:377–384
Ghosh A, Khurana M, Chauhan A, Takeo M, Chakraborti AK, Jain RK (2010) Degradation of 4-nitrophenol, 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol, and 2,4-dinitrophenol by Rhodococcus imtechensis strain RKJ300. Environ Sci Technol 44:1069–1077
Gonzalez LF, Sarria V, Sanchez OF (2010) Degradation of chlorophenols by sequential biological-advanced oxidative process using Trametes pubescens and TiO2/U. Bioresour Technol 101:3493–3499
Holliger C, Wohlfarth G, Diekert G (1998) Reductive dechlorination in the energy metabolism of anaerobic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:383–398
Jechorek M, Wendlandt KD, Beck M (2003) Cometabolic degradation of chlorinated aromatic compounds. J Biotechnol 102:93–98
Ju KS, Parales RE (2009) Application of nitroarene dioxygenases in the design of novel strains that degrade chloronitrobenzenes. Microb Biotechnol 2:241–252
Ju KS, Parales RE (2010) Nitroaromatic compounds, from synthesis to biodegradation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 74:250–272
Kanaly RA, Kim IS, Hur HG (2005) Biotransformation of 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol, a main product of the insecticide fenitrothion, by Aspergillus niger. J Agric Food Chem 53:6426–6431
Karn SK, Chakrabarti SK, Reddy MS (2011) Degradation of pentachlorophenol by Kocuria sp. CL2 isolated from secondary sludge of pulp and paper mill. Biodegradation 22:63–69
Katsivela E, Wray V, Pieper DH, Wittich RM (1999) Initial reactions in the biodegradation of 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene by a newly isolated bacterium, strain LW1. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1405–1412
Klecka GM, Maier WJ (1988) Kinetics of microbial growth on mixtures of pentachlorophenol and chlorinated aromatic compounds. Biotechnol Bioeng 31:328–335
Kogel W, Müller WF, Coulston F, Korte F (1979) Biotransformation of pentachloronitrobenzene-14C in rhesus monkeys after single and chronic oral administration. Chemosphere 8:97–105
Korde VM, Phelps TJ, Bienkowski PR, White DC (1993) Biodegradation of chlorinated aliphatics and aromatic compounds in total-recycle expanded-bed biofilm reactors. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 39:631–641
Kuhlmann A, Hegemann W (1997) Degradation of monochloronitrobenzenes by Pseudomonas acidovorans CA50. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 25:298–305
Larsen GL, Huwe JK, Bakke JE (1998) Intermediary metabolism of pentachloronitrobenzene in the control and germ-free rat and rat with cannulated bile ducts. Xenobiotica 28:973–984
Lenke H, Knackmuss HJ (1996) Initial hydrogenation and extensive reduction of substituted 2,4-dinitrophenols. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:784–790
Li Q, Minami M, Hanaoka, Yamamura Y (1999) Acute immunotoxicity of p-chloronitrobenzene in mice: II. Effect of p-chloronitrobenzene on the immunophenotype of murine splenocytes determined by flow cytometry. Toxicology 137:35–45
Li B, Xu X, Zhu L (2009) Ozonation of chloronitrobenzenes in aqueous solution: kinetics and mechanism. J Chem Tech Biotechnol 84:167–175
Li BZ, Xu XY, Zhu L (2010) Catalytic ozonation-biological coupled processes for the treatment of industrial wastewater containing refractory chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds. J Zhejiang Univ-Sc B 11:177–189
Li R, Zheng JW, Ni B, Chen K, Yang XJ, Li SP, Jiang JD (2011) Biodegradation of pentachloronitrobenzene by Labrys portucalensis pcnb-21 isolated from polluted soil. Pedosphere 21:31–36
Lievremont D, SeigleMurandi F, BenoitGuyod JL, Steiman R (1996) Biotransformation and biosorption of pentachloronitrobenzene by fungal mycelia. Mycol Res 100:948–954
Lievremont D, SeigleMurandi F, BenoitGuyod JL (1998) Removal of PCNB from aqueous solution by a fungal adsorption process. Water Res 32:3601–3606
Liu H, Wang SJ, Zhou NY (2005) A new isolate of Pseudomonas stutzeri that degrades 2-chloronitrobenzene. Biotechnol Lett 27:275–278
Liu L, Jiang CY, Liu XY, Wu JF, Han JG, Liu SJ (2007a) Plant–microbe association for rhizoremediation of chloronitroaromatic pollutants with Comamonas sp. strain CNB-1. Environ Microbiol 9:465–473
Liu L, Wu JF, Ma YF, Wang SY, Zhao GP, Liu SJ (2007b) A novel deaminase involved in chloronitrobenzene and nitrobenzene degradation with Comamonas sp. strain CNB-1. J Bacteriol 189:2677–2682
Liu H, Wang SJ, Zhang JJ, Dai H, Tang H, Zhou NY (2011) Patchwork assembly of nag-like nitroarene dioxygenase genes and the 3-chlorocatechol degradation cluster for evolution of the 2-chloronitrobenzene catabolism pathway in Pseudomonas stutzeri ZWLR2-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4547–4552
Livingston AG (1993) A novel membrane bioreactor for detoxifying industrial wastewater: II. Biodegradation of 3-chloronitrobenzene in an industrially produced wastewater. Biotechnol Bioeng 41:927–936
Ma YF, Wu JF, Wang SY, Jiang CY, Zhang Y, Qi SW, Liu L, Zhao GP, Liu SJ (2007) Nucleotide sequence of plasmid pCNB1 from Comamonas strain CNB-1 reveals novel genetic organization and evolution for 4-chloronitrobenzene degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4477–4483
Mohn WW, Tiedje JM (1992) Microbial reductive dehalogenation. Microbiol Rev 56:482–507
Murphy SE, Drotar AM, Fall AR (1982) Biotransformation of the fungicide pentachloronitrobenzene by Tetrahymena thermophila. Chemosphere 11:33–39
Murthy BKN, Kaufman DD (1978) Degradation of pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) in anaerobic soils. J Agric Food Chem 26:1151–1156
Nair RS, Johannsen FR, Levinskas GJ, Terrill JB (1986) Assessment of toxicity of o-nitrochlorobenzene in rats following a 4-week inhalation exposure. Fundam Appl Toxicol 7:609–614
Nakanishi T, Oku H (1969) Metabolism and accumulation of pentachloronitrobenzene by phytopathogenic fungi in relation to selective toxicity. Phytopathology 59:1761–1762
Niu GL, Zhang JJ, Zhao S, Liu H, Boon N, Zhou NY (2009) Bioaugmentation of a 4-chloronitrobenzene contaminated soil with Pseudomonas putida ZWL73. Environ Pollut 157:763–771
Pandey J, Heipieper HJ, Chauhan A, Arora PK, Prakash D, Takeo M, Jain RK (2011) Reductive dehalogenation mediated initiation of aerobic degradation of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol (2C4NP) by Burkholderia sp. strain SJ98. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:597–607
Park HS, Lim SJ, Chang YK, Livingston AG, Kim HS (1999) Degradation of chloronitrobenzenes by a coculture of Pseudomonas putida and a Rhodococcus sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1083–1091
Prakash D, Kumar R, Jain RK, Tiwary BN (2011) Novel pathway for the degradation of 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid by Acinetobacter sp. strain RKJ12. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6606–6613
Priya MH, Madras G (2006) Kinetics of photocatalytic degradation of phenols with multiple substituent groups. J Photochem Photobiol 179:256–262
Renner G (1980) Metabolic studies on pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) in rats. Xenobiotica 10:537–550
Renner G (1981) Biotransformation of the fungicides hexachlorobenzene and pentachloronitrobenzene. Xenobiotica 11:435–446
Renner G, Nguyen PT (1984) Mechanisms of the reductive denitration of pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) and the reductive dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene (HCB). Xenobiotica 14:705–710
Renner G, Ruckdeschel G (1983) Effects of pentachloronitrobenzene and some of its known and possible metabolites on fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:765–768
Rieger PG, Preuss A, Sinnwell V, Francke W, Lenke H, Knackmuss HJ (1994) H2 additions as initial steps of aerobic degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (picric acid), abstr. Q-120, p. 409. In: Abstracts of the 94th General Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology 1994. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Sabbioni G, Jones CR, Sepai O, Liu YY, Yan H (2007) Urinary metabolites and health effects in workers exposed chronically to chloronitrobenzene. Biomarkers 12:1–20
Sahasrabudhe SR, Modi VV (1987) Microbial degradation of chlorinated aromatic compounds. Microbiol Sci 4:300–303
Saritha P, Aparna C, Himabindu V, Anjaneyulu Y (2007) Comparison of various advanced oxidation processes for the degradation of 4-chloro-2 nitrophenol. J Hazard Mater 149:609–614
Schenzle A, Lenke H, Spain JC, Knackmuss HJ (1999) Chemoselective nitro group reduction and reductive dechlorination initiate degradation of 2-chloro-5-nitrophenol by Ralstonia eutropha JMP134. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2317–2323
Shen JM, Chen ZL, Xu ZZ, Li XY, Xu BB, Qi F (2008) Kinetics and mechanism of degradation of p-chloronitrobenzene in water by ozonation. J Hazard Mater 152:1325–1331
Smith AG, Francis JE (1983) Evidence for the active renal secretion of S-pentachlorophenyl-N-acetyl-L-cysteine by female rats. Biochem Pharmacol 2:3797–3801
Spain JC (1995a) Bacterial degradation of nitroaromatic compounds under aerobic conditions. Environ Sci Res 49:19–35232
Spain JC (1995b) Biodegradation of nitroaromatic compounds. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:523–555
Susarla S, Masunaga S, Yonezawa Y (1996) Transformations of chloronitrobenzenes in anaerobic sediment. Chemosphere 32:967–977
Symons ZC, Bruce NC (2006) Bacterial pathways for degradation of nitroaromatics. Nat Prod Rep 23:845–850
Tabak HH, Chambers CW, Kabler PW (1964) Microbial metabolism of aromatic compounds. I. Decomposition of phenolic compounds and aromatic hydrocarbons by phenol-adapted bacteria. J Bacteriol 87:910–919
Takagi K, Iwasaki A, Kamei I, Satsuma K, Yoshioka Y, Harada N (2009) Aerobic mineralization of hexachlorobenzene by newly isolated pentachloronitrobenzene-degrading Nocardioides sp. strain PD653. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4452–4458
Tas DO, Pavlostathis SG (2005) Microbial reductive transformation of pentachloronitrobenzene under methanogenic conditions. Environ Sci Technol 39:8264–8272
Tas DO, Pavlostathis SG (2007) Temperature and pH effect on the microbial reductive transformation of pentachloronitrobenzene. J Agric Food Chem 55:5390–5398
Tas DO, Pavlostathis SG (2008) Effect of nitrate reduction on the microbial reductive transformation of pentachloronitrobenzene. Environ Sci Technol 42:3234–3240
Tas DO, Pavlostathis SG (2010) Microbial transformation of pentachloronitrobenzene under nitrate reducing conditions. Biodegradation 21:691–702
Thiele J, Muller R, Lingens F (1988) Enzymatic dehalogenation of chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1199–1202
Torres RM, Grosset C, Steiman R, Alary J (1996) Liquid chromatography study of degradation and metabolism of pentachloronitrobenzene by four soil micromycetes. Chemosphere 33:683–692
Travlos GS, Mahler J, Ragan HA, Chou BJ, Bucher JR (1996) Thirteen-week inhalation toxicity of 2- and 4-chloronitrobenzene in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol 30:75–92
van der Meer JR (1997) Evolution of novel metabolic pathways for the degradation of chloroaromatic compounds. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 7:159–178
Vilhunen S, Sillanpaa M (2010) Recent developments in photochemical and chemical AOPs in water treatment: a mini review. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 9:323–330
Volskay VT, Grady CPL (1990) Respiration inhibition kinetic-analysis. Water Res 24:863–874
Wu JF, Sun CW, Jiang CY, Liu ZP, Liu SJ (2005) A novel 2-aminophenol 1,6-dioxygenase involved in the degradation of p-chloronitrobenzene by Comamonas strain CNB-1: purification, properties, genetic cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol 183:1–8
Wu JF, Jiang CY, Wang BJ, Ma YF, Liu ZP, Liu SJ (2006) Novel partial reductive pathway for 4-chloronitrobenzene and nitrobenzene degradation in Comamonas sp. strain CNB-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1759–1765
Wu HZ, Wei CH, Wang YQ, He QC, Liang SZ (2009) Degradation of o-chloronitrobenzene as the sole carbon and nitrogen sources by Pseudomonas putida OCNB-1. J Environ Sci-China 21:89–95
Xiao Y, Wu JF, Liu H, Wang SJ, Liu SJ, Zhou NY (2006) Characterization of genes involved in the initial reactions of 4-chloronitrobenzene degradation in Pseudomonas putida ZWL73. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:166–171
Yamamoto K, Nishimura M, Kato D, Takeo M, Negoro S (2011) Identification and characterization of another 4-nitrophenol degradation gene cluster, nps, in Rhodococcus sp. strain PN1. J Biosci Bioeng 111:687–694
Yin Y, Zhou NY (2010) Characterization of MnpC, a hydroquinone dioxygenase likely involved in the meta-nitrophenol degradation by Cupriavidus necator JMP134. Curr Microbiol 61:471–476
Zhao JS, Ward OP (1999) Microbial degradation of nitrobenzene and mono-nitrophenol by bacteria enriched from municipal activated sludge. Can J Microbiol 45:427–432
Zhen D, Liu H, Wang SJ, Zhang JJ, Zhao F, Zhou NY (2006) Plasmid-mediated degradation of 4-chloronitrobenzene by newly isolated Pseudomonas putida strain ZWL73. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:797–803
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the University Grants Commission, New Delhi under Dr. D. S. Kothari Postdoctoral Fellowship Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, P.K., Sasikala, C. & Ramana, C.V. Degradation of chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 2265–2277 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3927-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3927-1