Abstract
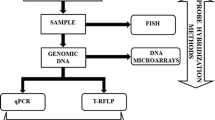
Molecular biological methods for mixed culture analysis outshine conventional culture-based techniques in terms of better sensitivity and reliability. The majority of these methods exploit the 16S rRNA sequences of the community DNA, which often fall short for the analysis of closely related microorganisms. This research details the development and validation of a comprehensive methodology to differentiate and quantitatively characterize two Pseudomonas species in a mixed culture. A bioinformatics tool based on whole-genome polymorphism comparison was used to identify marker sequences to differentiate the two bacteria using quantitative real-time PCR. The quantification of the two species was achieved through a correlation of the genomic DNA versus cell number (genomic DNA purification) and threshold cycle number versus genomic DNA (real-time PCR). Several factors including the limitation of genomic DNA purification, effects of substrate concentrations and growth phase on cellular DNA, and choice of simplex or duplex reaction for real-time PCR were considered and evaluated. The developed method was experimentally validated against synthetically constructed consortia.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åkerlund T, Nordstörm K, Bernander R (1995) Analysis of cell size and DNA content in exponentially growing and stationary-phase batch cultures of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177:6791–6797
Bastein P, Procop GW, Reischl U (2008) Quantitative real-time PCR is not more sensitive than “conventional” PCR. J Clin Microbiol 46:1897–1900
Broadaway SC, Barton SA, Pyle BH (2003) Rapid staining and enumeration of small numbers of total bacteria in water by solid-phase laser cytometry. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4272–4273
Brousseau R, Hill JE, Préfontaine G, Goh S-H, Harel J, Hemmingsen SM (2001) Streptococcus suis serotypes characterized by analysis of chaperonin 60 gene sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4828–4833
Cannone JJ, Subramanian S, Schnare MN, Collett JR, D'Souza LM, Du Y, Feng B, Lin N, Madabusi LV, Müller KM, Pande N, Shang Z, Yu N, Gutell RR (2002) The comparative RNA web (CRW) site: an online database of comparative sequence and structure information for ribosomal, intron, and other RNAs. BMC Bioinforma 3:15
Cladera AM, del Sepúlveda-Torres LC, Valens-Vadell M, Meyer J-M, Lalucat J, Garíca-Valdés E (2006) A detailed phenotypic and genotypic description of Pseudomonas strain OX1. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:422–430
Coşkuner G (2002) A new molecular technique for the identification of micro-organisms in biological treatment plants: fluorescent in situ hybridization. Turk J Biol 26:57–63
Crosby LD, Criddle CS (2003) Understanding bias in microbial community analysis techniques due to rrn operon copy number heterogeneity. Biotechniques 34:790–794
Cupples AM (2008) Real-time PCR quantification of Dehalococcoides populations: methods and applications. J Microbiol Methods 72:1–11
Delcher AL, Phillippy A, Carlton J, Salzberg SL (2002) Fast algorithms for large-scale genome alignment and comparison. Nucleic Acids Res 30:2478–2483
Díaz-Ramírez IJ, Escalante-Espinosa E, Favela-Torres E, Guítterrez-Rojas M, Ramírez-Saad H (2008) Design of defined mixed cultures for biodegradation of specific crude oil fractions, using population dynamics analysis by DGGE. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 62:21–30
Erlandson K, Batt CA (1997) Strain-specific differentiation of lactococci in mixed starter culture populations using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA-derived probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2702–2707
Fang C, Radosevich M, Fuhrmann JJ (2001) Characterization of rhizosphere microbial community structure in five similar grass species using FAME and BIOLOG analyses. Soil Biol Biochem 33:679–682
Forney LJ, Zhou X, Brown CJ (2004) Molecular microbial ecology: land of the one-eyed king. Curr Opin Microbiol 7:210–220
Fox GE, Wisotzkey JD, Jurtshuk P Jr (1992) How close is close: 16S rRNA sequence identity may not be sufficient to guarantee species identity. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:166–170
Franklin RB, Taylor DB, Mill AL (1999) Characterization of microbial communities using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). J Microbiol Methods 35:225–235
Friedrich U, Lenke J (2006) Improved enumeration of lactic acid bacteria in mesophilic dairy starter cultures by using multiplex quantitative real-time PCR and flow cytometry–fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4163–4171
Gamo M, Shoji T (1999) A method of profiling microbial communities based on a most-probable-number assay that uses BIOLOG plates and multiple sole carbon sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4419–4425
Grattepanche F, Lacroix C, Audet P, Lapointe G (2005) Quantification by real-time PCR of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris in milk fermented by a mixed culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:414–421
Hamer G (1997) Microbial consortia for multiple pollutant biodegradation. Pure Appl Chem 69:2343–2356
Hamilton MS, Schremmer R (2002) High frequency of competitive inhibition in the Roche Cobas AMPLICOR multiplex PCR for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol 40:4393
Hiibel SR, Pereyra LP, Inman LY, Tischer A, Reisman D, Reardon KF, Pruden A (2008) Microbial community analysis of two field-scale sulfate-reducing bioreactors treating mine drainage. Environ Microbiol 10:2087–2097
Hill JE, Penny LS, Crowell KG, Goh SH, Hemmingsen SM (2004) cpnDB: a chaperonin sequence database. Genome Res 14:1669–1675
Hjort K, Bernander R (1999) Changes in cell size and DNA content in Sulfolobus cultures during dilution and temperature shift experiments. J Bacteriol 181:5669–5675
Hu H-Y, Lim B-R, Goto N, Fujie K (2001) Analytical precision and repeatability of respiratory quinones for quantitative study of microbial community structure in environmental samples. J Microbiol Methods 47:17–24
Klappenbach JA, Saxman PR, Cole JR, Schmidt TM (2001) rrndb: the ribosomal RNA operon copy number database. Nucleic Acids Res 29:181–184
Kösters K, Reischl U, Schmetz J, Riffelmann M, König CHWV (2002) Real-time lightcycler PCR for detection and discrimination of Bordtella pertussis and Bordtella parapertussis. J Clin Microbiol 40:1719–1722
Lee S, Fuhrman JA (1990) DNA hybridization to compare species compositions of natural bacterioplankton assemblages. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:739–746
Lee H-W, Lee S-Y, Lee J-W, Park J-B, Choi E-S, Park YK (2002) Molecular characterization of microbial community in nitrate-removing activated sludge. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 41:85–94
Lee C, Lee S, Shin SG, Hwang S (2008) Real-time PCR determination of rRNA gene copy number: absolute and relative quantification assays with Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:371–376
Lisle JT, Hamilton MA, Willse AR, McFeters GA (2004) Comparison of fluorescence microscopy and solid-phase cytometry methods for counting bacteria in water. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5343–5348
Livak KJ (1999) Allelic discrimination using fluorogenic probes and the 5′ nuclease assay. Genet Anal Biomol Eng 14:143–149
McGuigan FEA, Ralston SH (2002) Single nucleotide polymorphism detection: allelic discrimination using Taqman. Psychiatr Genet 12:133–136
Merwe TVD, Wolfaardt F, Riedel K-H (2003) Analysis of functional diversity of the microbial communities in a paper-mill water system. Water SA 29:31–34
Müller S, Babel W (2003) Analysis of bacterial DNA patterns—an approach for controlling biotechnological processes. J Microbiol Methods 55:851–858
Nagarajan K (2011) Formulation of microbial cocktails for biodegradation of BTEX. Dissertation, National University of Singapore
Nakatsu CH (2007) Soil microbial community analysis using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:562–571
Oslen GJ, Lane DJ, Giovannoni SJ, Pace NR (1986) Microbial ecology and evolution: ribosomal RNA approach. Annu Rev Microbiol 40:337–365
Providenti MA, Lee H, Trevors JT (1993) Selected factors limiting the microbial degradation of recalcitrant compounds. J Ind Microbiol 12:379–395
Reardon KF, Mosteller DC, Rogers JB, DuTeau NM, Kim K-H (2002) Biodegradtaion kinetics of aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures by pure and mixed bacterial cultures. Environ Health Perpect 110:1005–1011
Rogers JB, DuTeau NM, Reardon KF (2000) Use of 16S-rRNA to investigate microbial population dynamics during biodegradation of toluene and phenol by a binary culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 70:436–445
Schmidt JK, Konig B, Reichl U (2007) Characterization of a three bacteria mixed culture in a chemostat: evaluation and application of a quantitative terminal-restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis for absolute and species specific cell enumeration. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:738–756
Shim H, Hwang B, Lee S-S, Kong S-H (2005) Kinetics of BTEX biodegradation by a coculture of Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas fluorescens under hypoxic conditions. Biodegradation 16:319–327
Smalla K, Wachtendorf U, Heuer H, Liu W-T, Forney L (1998) Analysis of BIOLOG GN substrate utilization patterns by microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1220–1225
Smits THM, Devenoges C, Szynalski K, Maillard J, Holliger C (2004) Development of a real-time PCR method for quantification of the three genera Dehalobacter, Dehalococcoides and Desulfitobacterium in microbial communities. J Microbiol Methods 57:369–378
Soto K, Collantes G, Zahar M, Kuznar J (2005) Simultaneous enumeration of Phaedactylum tricornutum (MLB 292) and bacteria growing in mixed communities. Lat Am J Aquat Res 33:143–149
Stoner DL, Browning CK, Bulmer DK, Ward TE, MacDonell MT (1996) Direct 5S rRNA assay for monitoring mixed-culture bioprocess. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1969–1976
Szymanski M, Barciszewska MZ, Erdmann VA, Barciszewski J (2002) 5S ribosomal database. Nucleic Acids Res 30:176–178
Thies JE (2007) Soil microbial community analysis using terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:579–591
Tourva TP (2003) Copy number of ribosomal operons in prokaryotes and its effect on phylogenetic analysis. Microbiology 72:437–452
Valasek MA, Repa JY (2005) The power of real-time PCR. Adv Physiol Educ 29:151–159
Van Ert MN, Easterday WR, Simonson TS, U’Ren JM, Pearson T, Kenefic LJ, Busch JD, Huynh LY, Dukerich M, Trim CB, Beaudry J, Welty-Bernard A, Read T, Fraser CM, Ravel J, Keim P (2007) Strain-specific single-nucleotide polymorphism assays for the Bacillus anthracis Ames strain. J Clin Microbiol 45:47–53
Van Hamme JD, Odumeru JA, Ward OP (2000) Community dynamics of a mixed-bacterial culture growing on petroleum hydrocarbons in batch culture. Can J Microbiol 46:441–450
Wang GCY, Wang Y (1997) Frequency of formation of chimeric molecules as a consequence of PCR coamplification of 16S rRNA genes from mixed bacterial genomes. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4645–4650
Watanabe K, Nelson JS, Harayama S, Kasai H (2001) ICB database: the gyrB database for identification and classification of bacteria. Nucleic Acid Res 29:344–345
Werker AG, Becker J, Huitema C (2003) Assessment of activated sludge microbial community analysis in full-scale biological wastewater treatment plants using patterns of fatty acid isopropyl esters (FAPEs). Water Res 37:2162–2172
Wilen B-M, Onuki M, Hermannson M, Lumley D, Mino T (2008) Microbial community structure in activated sludge floc analysed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and its relation to floc stability. Wat Res 42:2300–2308
Winderl C, Anneser B, Griebler C, Meckenstock RU, Lueders T (2008) Depth-resolved quantification of anaerobic toluene degraders and aquifer microbial community patterns in distinct redox zones of a tar oil contaminant plume. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:792–801
Yu C-P, Ahuja R, Sayler G, Chu K-H (2005) Quantitative molecular assay for finger printing microbial communities of wastewater and estrogen-degrading consortia. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1433–1444
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagarajan, K., Loh, KC. & Swarup, S. Bioinformatics and molecular biology for the quantification of closely related bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 6489–6502 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4943-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4943-5