Abstract
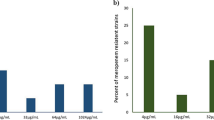
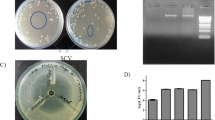
Multi drug resistant (MDR) pathogens pose a serious threat to public health since they can easily render most potent drugs ineffective. Efflux pump inhibitors (EPI) can be used to counter the MDR phenotypes arising due to increased efflux. In the present study, a series of dithiazole thione derivatives were synthesized and checked for its antibacterial and efflux pump inhibitory (EPI) activity. Among 10 dithiazole thione derivatives, real-time efflux studies revealed that seven compounds were potent EPIs relative to CCCP. Zebrafish toxicity studies identified four non-toxic putative EPIs. Both DTT3 and DTT9 perturbed membrane potential and DTT6 was haemolytic. Among DTT6 and DTT10, the latter was less toxic as evidenced by histopathology studies. Since DTT10 was non-haemolytic, did not affect the membrane potential, and was least toxic, it was chosen further for in vivo study, wherein DTT10 potentiated effect of ciprofloxacin against clinical strain of MRSA and reduced bacterial burden in muscle and skin tissue of infected zebrafish by ~ 1.7 and 2.5 log fold respectively. Gene expression profiling of major efflux transport proteins by qPCR revealed that clinical isolate of MRSA, in the absence of antibiotic, upregulated NorA, NorB and MepA pump, whereas it downregulates NorC and MgrA relative to wild-type strain of Staphylococcus aureus. In vitro studies with NorA mutant strains and substrate profiling revealed that at higher concentrations DTT10 is likely to function as a competitive inhibitor of NorA efflux protein in S. aureus, whereas at lower concentrations it might inhibit ciprofloxacin efflux through NorB and MepA as implied by docking studies. A novel non-toxic, non-haemolytic dithiazole thione derivative (DTT10) was identified as a potent competitive inhibitor of NorA efflux pump in S. aureus using in silico, in vitro and in vivo studies. This study also underscores the importance of using zebrafish infection model to screen and evaluate putative EPI for mitigating MDR strains of S. aureus.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson DH, Krikstopaityte V, Coote PJ (2015) Enhanced efficacy of putative efflux pump inhibitor/antibiotic combination treatments versus MDR strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Galleria mellonella in vivo infection model. J Antimicrob Chemother 70(8):2271–8. doi:10.1093/jac/dkv111
Andrews JM (2001) Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J Antimicrob Chemother 48(Suppl 1):5–16
Appelbaum PC (2006) The emergence of vancomycin-intermediate and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Infect 12(Suppl 1):16–23. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01344.x
Argentine JA, James AA (1995) Characterization of a salivary gland-specific esterase in the vector mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 25(5):621–30
Asaithampi G, Lowrence RC, Himesh MVS, Ulaganathan V, Raman T, Venkatabalasubramanian S, Kabilan K, Nagarajan S, Subramaniapillai SG (2016) Identification of benzochromene derivatives as a highly specific NorA efflux pump inhibitor to mitigate the drug resistant strains of S. aureus. RSC Adv 6 (36):30258–30267. doi:10.1039/C6RA01981A
Astashkina A, Mann B, Grainger DW (2012) A critical evaluation of in vitro cell culture models for high-throughput drug screening and toxicity. Pharmacol Ther 134(1):82–106. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.01.001S0163-7258(12)00002-2
Blair JM, Webber MA, Baylay AJ, Ogbolu DO, Piddock LJ (2015) Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 13(1):42–51. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3380
Blanchard C, Barnett P, Perlmutter J, Dunman PM (2014) Identification of Acinetobacter baumannii serum-associated antibiotic efflux pump inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(11):6360–70, doi:10.1128/AAC.03535-14
Brenwald NP, Gill MJ, Wise R (1998) Prevalence of a putative efflux mechanism among fluoroquinolone-resistant clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42(8):2032–5
Costa SS, Falcao C, Viveiros M, Machado D, Martins M, Melo-Cristino J, Amaral L, Couto T (2011) Exploring the contribution of efflux on the resistance to fluoroquinolones in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus
Ding Y, Onodera Y, Lee JC, Hooper DC (2008) NorB, an efflux pump in Staphylococcus aureus strain MW2, contributes to bacterial fitness in abscesses. J Bacteriol 190(21):7123–9. doi:10.1128/JB.00655-08
Dong Y, Zhao X, Kreiswirth BN, Drlica K (2000) Mutant prevention concentration as a measure of antibiotic potency: studies with clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44(9):2581–4
Edman P (1949) A method for the determination of amino acid sequence in peptides. ADTTh Biochem 22(3):475
Evangelista Sde S, de Oliveira AC (2015) Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a global problem. Rev Bras Enferm 68(1):128–35. doi:10.1590/0034-7167.2015680119pS0034-71672015000100136, 136-43
Fontaine F, Hequet A, Voisin-Chiret AS, Bouillon A, Lesnard A, Cresteil T, Jolivalt C, Rault S (2014) First identification of boronic species as novel potential inhibitors of the Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump. J Med Chem 57(6):2536–48. doi:10.1021/jm401808n
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, Sanschagrin PC, Mainz DT (2006) Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49(21):6177–96. doi:10.1021/jm051256o
Gupta A, Mishra P, Kashaw SK, Jatav V (2008) Synthesis, anticonvulsant, antimicrobial and analgesic activity of novel 1,2,4-dithiazoles. Indian J Pharm Sci 70(4):535–8. doi:10.4103/0250-474X.44614
Hequet A, BuDTThak ON, Jeanty M, Guinchard X, Le Pihive E, Maigre L, Bouhours P, Schneider D, Maurin M, Paris JM, Denis JN, Jolivalt C (2014) 1-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethanamine derivatives as potent Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors. ChemMedChem 9(7):1534–45. doi:10.1002/cmdc.201400042
Huet AA, Raygada JL, Mendiratta K, Seo SM, Kaatz GW (2008) Multidrug efflux pump overexpression in Staphylococcus aureus after single and multiple in vitro exposures to biocides and dyes. Microbiology 154(Pt 10):3144–53. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2008/021188-0154/10/3144
Kalia NP, Mahajan P, Mehra R, Nargotra A, Sharma JP, Koul S, Khan IA (2012) Capsaicin, a novel inhibitor of the NorA efflux pump, reduces the intracellular invasion of Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 67(10):2401–8. doi:10.1093/jac/dks232
Kollef MH (2007) Limitations of vancomycin in the management of resistant staphylococcal infections. Clin Infect Dis 45(Suppl 3):S191–5. doi:10.1086/519470
Kosmidis C, Schindler BD, Jacinto PL, Patel D, Bains K, Seo SM, Kaatz GW (2012) Expression of multidrug resistance efflux pump genes in clinical and environmental isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Antimicrob Agents 40(3):204–9. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.04.014S0924-8579(12)00184-7
Kumar A, Khan IA, Koul S, Koul JL, Taneja SC, Ali I, Ali F, Sharma S, Mirza ZM, Kumar M, Sangwan PL, Gupta P, Thota N, Qazi GN (2008) Novel structural analogues of piperine as inhibitors of the NorA efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 61(6):1270–6. doi:10.1093/jac/dkn088
Lawson AJ, Meloy CR (1973) Derivatives of 5-amino-1,2,4-dithiazole-3-thione. 5(4):465-470
Lin B, Chen S, Cao Z, Lin Y, Mo D, Zhang H, Gu J, Dong M, Liu Z, Xu A (2007) Acute phase response in zebrafish upon Aeromonas salmonicida and Staphylococcus aureus infection: striking similarities and obvious differences with mammals. Mol Immunol 44(4):295–301. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2006.03.001
Ling LL, Schneider T, Peoples AJ, Spoering AL, Engels I, Conlon BP, Mueller A, Schaberle TF, Hughes DE, Epstein S, Jones M, Lazarides L, Steadman VA, Cohen DR, Felix CR, Fetterman KA, Millett WP, Nitti AG, Zullo AM, Chen C, Lewis K (2015) A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance. Nature 517(7535):455–9. doi:10.1038/nature14098
Louw GE, Warren RM, Gey van Pittius NC, Leon R, Jimenez A, Hernandez-Pando R, McEvoy CR, Grobbelaar M, Murray M, van Helden PD, Victor TC (2011) Rifampicin reduces susceptibility to ofloxacin in rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis through efflux. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 184(2):269–76. doi:10.1164/DTTcm.201011-1924OC
Christena LR, Subramaniam S, Vidhyalakshmi M, Mahadevan V, Sivasubramanian A, Nagarajan S (2015a) Dual role of pinostrobin-a flavonoid nutraceutical as an efflux pump inhibitor and antibiofilm agent to mitigate food borne pathogens. Rsc Advances 5(76):61881–61887. doi:10.1039/C5RA07165H
Christena LR, Mangalagowri V, Pradheeba P, Ahmed KBA, Shalini BIS, Vidyalakshmi M, Anbazhagana V, Subramanian NS (2015b) Copper nanoparticles as an efflux pump inhibitor to tackle drug resistant bacteria. Rsc Advances 5(17):12899–12909. doi:10.1039/C4RA15382K
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–75
Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, Harbarth S, Hindler JF, Kahlmeter G, Olsson-Liljequist B, Paterson DL, Rice LB, Stelling J, Struelens MJ, Vatopoulos A, Weber JT, Monnet DL (2012) Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect 18(3):268–81. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.xS1198-743X(14)61632-3
Maiti R, Van Domselaar GH, Zhang H, Wishart DS (2004) SuperPose: a simple server for sophisticated structural superposition. Nucleic Acids ReseaDTTh 32(Web Server issue):W590–W594. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh477
Martins M, Viveiros M, Couto I, Costa SS, Pacheco T, Fanning S, Pages JM, Amaral L (2011) Identification of efflux pump-mediated multidrug-resistant bacteria by the ethidium bromide-agar cartwheel method. In vivo (Athens, Greece) 25(2):171–8
Mathers AJ, Peirano G, Pitout JD (2015) The role of epidemic resistance plasmids and international high-risk clones in the spread of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Clin Microbiol Rev 28(3):565–91. doi:10.1128/CMR.00116-1428/3/565
McAleese F, Petersen P, Ruzin A, Dunman PM, Murphy E, Projan SJ, Bradford PA (2005) A novel MATE family efflux pump contributes to the reduced susceptibility of laboratory-derived Staphylococcus aureus mutants to tigecycline. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(5):1865–71. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.5.1865-1871.2005
McHugh CG, Riley LW (2004) Risk factors and costs associated with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 25(5):425–30. doi:10.1086/502417
Merli M, Lucidi C, Di Gregorio V, Falcone M, Giannelli V, Lattanzi B, Giusto M, Ceccarelli G, FaDTTomeni A, Riggio O, Venditti M (2015) The spread of multi drug resistant infections is leading to an increase in the empirical antibiotic treatment failure in cirrhosis: a prospective survey. PLoS One 10(5):e0127448. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0127448PONE-D-14-38195
Mohammad H, Reddy PV, Monteleone D, Mayhoub AS, Cushman M, Hammac GK, Seleem MN (2015) Antibacterial characterization of novel synthetic thiazole compounds against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. PLoS One 10(6):e0130385. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0130385PONE-D-15-05317
Munita JM, Bayer AS, Arias CA (2015) Evolving resistance among gram-positive pathogens. Clin Infect Dis 61(Suppl 2):S48–57. doi:10.1093/cid/civ523
Neely MN, Pfeifer JD, Caparon M (2002) Streptococcus-zebrafish model of bacterial pathogenesis. Infect Immun 70(7):3904–14
Nelson MU, Bizzarro MJ, Baltimore RS, Dembry LM, Gallagher PG (2015) Clinical and molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a neonatal intensive care unit in the decade following implementation of an active detection and isolation program. J Clin Microbiol 53(8):2492–501. doi:10.1128/JCM.00470-15
Neyfakh AA, Borsch CM, Kaatz GW (1993) Fluoroquinolone resistance protein NorA of Staphylococcus aureus is a multidrug efflux transporter. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37(1):128–9
Nikaido H (2009) Multidrug resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem 78:119–46. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.082907.145923
Nishino K, Nikaido E, Yamaguchi A (2009) Regulation and physiological function of multidrug efflux pumps in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794(5):834–43. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.02.002S1570-9639(09)00026-0
Niven GW, Mulholland F (1998) Cell membrane integrity and lysis in Lactococcus lactis: the detection of a population of permeable cells in post-logarithmic phase cultures. J Appl Microbiol 84(1):90–6
Pfeifer HJ, Greenblatt DK, Koch-Wester J (1976) Clinical toxicity of reserpine in hospitalized patients: a report from the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program. Am J Med Sci 271(3):269–76
Piddock LJ (2006) Multidrug-resistance efflux pumps—not just for resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 4(8):629–36
Piddock LJ (2014) Understanding the basis of antibiotic resistance: a platform for drug discovery. Microbiology 160(Pt 11):2366–73. doi:10.1099/mic.0.082412-0
Rio DC (2015) Denaturation and electrophoresis of RNA with formaldehyde. Cold Spring Harb Protoc . doi:10.1101/pdb.prot080994
Sabatini S, Gosetto F, Iraci N, Barreca ML, Massari S, Sancineto L, Manfroni G, Tabarrini O, Dimovska M, Kaatz GW, Cecchetti V (2013) Re-evolution of the 2-phenylquinolines: ligand-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a potent new class of Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump inhibitors to combat antimicrobial resistance. J Med Chem 56(12):4975–89. doi:10.1021/jm400262a
Sannasiddappa TH, Hood GA, Hanson KJ, Costabile A, Gibson GR, Clarke SR (2015) Staphylococcus aureus MnhF mediates cholate efflux and facilitates survival under human colonic conditions. Infect Immun 83(6):2350–7. doi:10.1128/IAI.00238-15
Sarkissian EJ, Gans I, Gunderson MA, Myers SH, Spiegel DA, Flynn JM (2015) Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus musculoskeletal infections: emerging trends over the past decade. J Pediatr Orthop. doi:10.1097/BPO.0000000000000439
Sastry GM, Adzhigirey M, Day T, Annabhimoju R, Sherman W (2013) Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J Comput Aided Mol Des 27(3):221–34. doi:10.1007/s10822-013-9644-8
Sato T, Yokota S, Okubo T, Ishihara K, Ueno H, Muramatsu Y, Fujii N, Tamura Y (2013) Contribution of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump to high-level fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli isolated from dogs and humans. J Vet Med Sci 75(4):407–14
Schindler BD, Jacinto P, Kaatz GW (2013) Inhibition of drug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: current status of potentiating existing antibiotics. Future Microbiol 8(4):491–507. doi:10.2217/fmb.13.16
Schrödinger (2010). Maestro,V9.3 Schrödinger LLC, New York
Selter R, Considine WJ (1970) Basicity of isoperthiocyanic acid. J Org Chem 35(5):1665–1666
Silverman JA, Perlmutter NG, Shapiro HM (2003) Correlation of daptomycin bactericidal activity and membrane depolarization in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47(8):2538–44
Srivastava P, Singh A (2014) Potential effects of agricultural fungicide (Mancozeb) on fish Clarias batrachus. Res J Biol Sci 9:129–134
Sun J, Deng Z, Yan A (2014) Bacterial multidrug efflux pumps: mechanisms, physiology and pharmacological exploitations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 453(2):254–67. doi:10.1016/j.bbDTT.2014.05.090S0006-291X(14)00971-1
Thaden JT, Ericson JE, Cross H, Bergin SP, Messina JA, Fowler VG Jr, Benjamin DK Jr, Clark RH, Hornik CP, Smith PB (2015) Survival benefit of empirical therapy for Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections in infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000000850
Tillotson GS, Theriault N (2013) New and alternative approaches to tackling antibiotic resistance. F1000Prime Rep 5:51 doi:10.12703/P5-51
Tong SY, Davis JS, Eichenberger E, Holland TL, Fowler VG Jr (2015) Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev 28(3):603–61. doi:10.1128/CMR.00134-1428/3/603
Truong-Bolduc QC, Bolduc GR, Medeiros H, Vyas JM, Wang Y, Hooper DC (2015) Role of tet38 efflux pump in Staphylococcus aureus internalization and survival in epithelial cells. Infec Immun. doi:10.1128/IAI.00723-15
Truong-Bolduc QC, Hsing LC, Villet R, Bolduc GR, Estabrooks Z, Taguezem GF, Hooper DC (2012) Reduced aeration effects the expression of the NorB efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus by post translation modification of MgrA. J Bacteriol 1823-1834
Wang SH, Hines L, van Balen J, Mediavilla JR, Pan X, Hoet AE, Kreiswirth BN, Pancholi P, Stevenson KB (2015) Molecular and clinical characteristics of hospital and community onset methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with bloodstream infections. J Clin Microbiol 53(5):1599–608. doi:10.1128/JCM.03147-14
Westerfield M (1995) The zebrafish book: guide for the laboratory use of zebrafish (Danio rerio), 3rd edn. University of Oregon Press, Eugene
Wu S, Zhang Y (2008) MUSTER: improving protein sequence profile–profile alignments by using multiple sources of structure information. Proteins 72(2):547–556. doi:10.1002/prot.21945
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank TRR funding provided by management, SASTRA University to NS to carry out this work. TR would like to thank the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Government of India, (SERB/F/1266/2012-13, dated 31st May 2012) for financial support. DST-FIST funding (Grant No SR/FST/ETI-331/2013) provided by DST, Govt of India to SCBT, SASTRA University, is gratefully acknowledged. Infrastructure facility (CRF) established through R&M funds (Grant No R&M/0021/SCBT-007/2012-13) of SASTRA to carry out this work is gratefully acknowledged. R&M grant provided to Microbiology Department by Management SASTRA University is gratefully acknowledged. Research fellowship provided by UGC to L.R.C.Maulana Azad National Fellowship, UGC, New Delhi, India (MANF-2012-13-CHR-WES-13462), is gratefully acknowledged.
Author contribution:
CNS synthesized the compounds, SSG helped in purification and characterization of the compounds; NS designed study, LRC carried out the biological part of study, TR and UV designed in vivo and in silico part of study, AM carried out fish toxicity assays; AA helped in design and interpretation of gene expression data, NS, TR and UV wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work is supported by TRR research grant to NS by SASTRA University; DST SERB Funding to TR (SERB/F/1266/2012-13, dated 31st May 2012) and DST-FIST funding (Grant No SR/FST/ETI-331/2013).
Conflict of interest
Author 1 declares no conflict of interest, author 2 declares no conflict of interest, author 3 declares no conflict of interest, author 4 declares no conflict of interest, author 5 declares no conflict of interest, author 6 declares no conflict of interest, author 7 declares no conflict of interest, author 8 declares no conflict of interest and author 9 declares no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Supporting information (PDF 3517 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lowrence, R.C., Raman, T., Makala, H.V. et al. Dithiazole thione derivative as competitive NorA efflux pump inhibitor to curtail multi drug resistant clinical isolate of MRSA in a zebrafish infection model. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 9265–9281 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7759-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7759-2