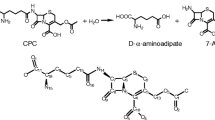
Abstract
Penicillin G acylase (PGA) was isolated from Providencia rettgeri PX04 (PrPGApx04) and utilized for the kinetically controlled synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics. Site-directed mutagenesis was performed to increase the process efficiency. Molecular docking was carried out to speculate the key mutant positions corresponding with synthetic activity, which resulted in the achievement of an efficient mutant, βF24G. It yielded higher conversions than the wild-type enzyme in the synthesis of amoxicillin (95 versus 17.2%) and cefadroxil (95.4 versus 43.2%). The reaction time for achieving the maximum conversion decreased from 14 to 16 h to 2–2.5 h. Furthermore, the secondary hydrolysis of produced antibiotics was hardly observed. Kinetic analysis showed that the (kcat/Km)AD value for the activated acyl donor D-hydroxyphenylglycine methyl ester (D-HPGME) increased up to 41 times. In contrast, the (kcat/Km)Ps values for the products amoxicillin and cefadroxil decreased 6.5 and 21 times, respectively. Consequently, the α value (kcat/Km)Ps/(kcat/Km)AD, which reflected the relative hydrolytic specificity of PGA for produced antibiotics with respect to the activated acyl donor, were only 0.028 and 0.043, respectively. The extremely low hydrolytic activity for the products of the βF24G mutant enabled greater product accumulation to occur during synthesis, which made it a promising enzyme for industrial applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkema WBL, Dijkhuis AJ, de Vries E, Janssen DB (2002) The role of hydrophobic active-site residues in substrate specificity and acyl transfer activity of penicillin acylase. Eur J Biochem 269(8):2093–2100. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02857.x
Alkema WBL, de Vries E, Floris R, Janssen DB (2003) Kinetics of enzyme acylation and deacylation in the penicillin acylase-catalyzed synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics. Eur J Biochem 270(18):3675–3683. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03728.x
Alkema WB, Hensgens CM, Snijder HJ, Keizer E, Dijkstra BW, Janssen DB (2004) Structural and kinetic studies on ligand binding in wild-type and active-site mutants of penicillin acylase. Protein Eng Des Sel 17(5):473–480. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzh057
Arroyo M, De la Mata I, Acebal C, Castillon MP (2003) Biotechnological applications of penicillin acylases: state-of-the-art. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60(5):507–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1113-6
Bečka S, Štěpánek V, Vyasarayani RW, Grulich M, Maršálek J, Plháčková K, Dobišová M, Marešová H, Plačková M, Valešová R (2014) Penicillin G acylase from Achromobacter sp. CCM 4824. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(23):1195–1203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6104-x
Cecchini DA, Pavesi R, Sanna S, Daly S, Xaiz R, Pregnolato M, Terreni M (2012) Efficient biocatalyst for large-scale synthesis of cephalosporins, obtained by combining immobilization and site-directed mutagenesis of penicillin acylase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(6):1491–1500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3817-y
Cheng T, Chen M, Zheng H, Wang J, Yang S, Jiang W (2006) Expression and purification of penicillin G acylase enzymes from four different micro-organisms, and a comparative evaluation of their synthesis/hydrolysis ratios for cephalexin. Protein Expr Purif 46(1):107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2005.07.016
Choi JH, Lee SY (2004) Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64(5):625–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1559-9
Deng S, Su E, Ma X, Yang S, Wei D (2015) Efficient enzymatic synthesis of ampicillin by mutant Alcaligenes faecalis penicillin G acylase. J Biotechnol 199:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.01.004
Deng S, Ma X, Sun M, Wei D, Su E (2016) Efficient enzymatic synthesis of ampicillin using mutant penicillin G acylase with bio-based solvent glycerol. Catal Commun 79:31–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2016.02.014
Fernandezlafuente R, Rosell CM, Guisán JM (1991) Enzyme reaction engineering: synthesis of antibiotics catalysed by stabilized penicillin G acylase in the presence of organic cosolvents. Enzym Microb Technol 13(11):898–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(91)90106-K
Gabor EM, Janssen DB (2004) Increasing the synthetic performance of penicillin acylase PAS2 by structure-inspired semi-random mutagenesis. Protein Eng Des Sel 17(7):571–579. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzh070
Grulich M, Stepanek V, Kyslik P (2013) Perspectives and industrial potential of PGA selectivity and promiscuity. Biotechnol Adv 31(8):1458–1472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.07.005
Hernández-Jústiz O, Terreni M, Pagani G, JL Garcı́A, Guisán JM, Fernández-Lafuente R (1999) Evaluation of different enzymes as catalysts for the production of β-lactam antibiotics following a kinetically controlled strategy. Enzym Microb Technol 25(3-5):336–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(99)00050-2
Jager SA, Shapovalova IV, Jekel PA, Alkema WB, Svedas VK, Janssen DB (2008) Saturation mutagenesis reveals the importance of residues αR145 and αF146 of penicillin acylase in the synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics. J Biotechnol 133(1):18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.08.039
Kameda Y, Kimura Y, Toyoura E, Omori T (1961) A method for isolating bacteria capable of producing 6-aminopenicillanic acid from benzylpenillin. Nature 191(4793):1122–1123. https://doi.org/10.1038/1911122a0
Koshland DE (1958) Application of a theory of enzyme specificity to protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 44(2):98–104. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.44.2.98
Maresova H, Plackova M, Grulich M, Kyslik P (2014) Current state and perspectives of penicillin G acylase-based biocatalyses. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(7):2867–2879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5492-7
Mcvey CE, Walsh MA, Dodson GG, Wilson KS, Brannigan JA (2001) Crystal structures of penicillin acylase enzyme-substrate complexes: structural insights into the catalytic mechanism. J Mol Biol 313(1):139–150. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.5043
Prieto MA, Diaz EGarcia JL (1996) Molecular characterization of the 4-hydroxyphenylacetate catabolic pathway of Escherichia coli W: engineering a mobile aromatic degradative cluster. J Bacteriol 178(1):111–120. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.178.1.111-120.1996
Sio CF, Quax WJ (2004) Improved β-lactam acylases and their use as industrial biocatalysts. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15(4):349–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2004.06.006
Srirangan K, Orr V, Akawi L, Westbrook A, Moo-Young M, Chou CP (2013) Biotechnological advances on penicillin G acylase: pharmaceutical implications, unique expression mechanism and production strategies. Biotechnol Adv 31(8):1319–1332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.05.006
Valle F, Balbás P, Merino E, Bolivar F (1991) The role of penicillin amidases in nature and in industry. Trends in Biochem Sci 16(1):36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0968-0004(91)90014-M
Volpato G, Rodrigues RC, Fernandez-Lafuente R (2010) Use of enzymes in the production of semi-synthetic penicillins and cephalosporins: drawbacks and perspectives. Curr Med Chem 17(32):3855–3873. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986710793205435
Wang J, Zhang Q, Huang H, Yuan Z, Ding D, Yang S, Jiang W (2007) Increasing synthetic performance of penicillin G acylase from Bacillus megaterium by site-directed mutagenesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74(5):1023–1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0752-4
Wegman MA, Janssen MHA, Van Rantwijk F, Sheldon RA (2001) Towards biocatalytic synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics. Adv Synthe Catal 343(6-7):559–576. https://doi.org/10.1002/1615-4169(200108)343:6/7<559::AID-ADSC559>3.0.CO;2-Z
Yang S, Huang H, Zhang R, Huang X, Li S, Yuan Z (2001) Expression and purification of extracellular penicillin G acylase in Bacillus subtilis. Protein Expr Purif 21(1):60–64. https://doi.org/10.1006/prep.2000.1339
Youshko MI, Chilov GG, Shcherbakova TA, Švedas VK (2002) Quantitative characterization of the nucleophile reactivity in penicillin acylase-catalyzed acyl transfer reactions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1599(1-2):134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1570-9639(02)00413-2
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21376119, 81673321) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu (BK20151541).
Funding
We also acknowledge the fund sponsored by the Program for Innovative Research Team in Universities of Jiangsu Province (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1588 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, X., Wang, L., Ye, J. et al. Efficient synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics with very low product hydrolysis by a mutant Providencia rettgeri penicillin G acylase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 1749–1758 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8692-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8692-8