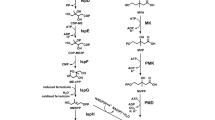
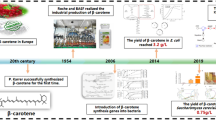
Abstract
Lycopene is a dark red carotenoid belonging to C40 terpenoids and is widely found in a variety of plants, especially ripe red fruits and vegetables. Lycopene has been shown to reduce the risk of prostate cancer, other cancers, and cardiovascular disease. It is one of the most widely used carotenoids in the healthcare product market. Currently, commercially available lycopene is mainly extracted from tomatoes. However, production of lycopene from plants is costly and environmentally unfriendly. To date, there have been many reports on the biosynthesis of lycopene by microorganisms, providing another route for lycopene production. This review discusses the lycopene biosynthetic pathway and natural and engineered lycopene-accumulating microorganisms, as well as their production of lycopene. The effects of different metabolic engineering strategies on lycopene accumulation are also considered. Furthermore, this work presents perspectives concerning the microbial production of lycopene, especially trends to construct microbial cell factories for lycopene production.
Key points
• Recent achievements in the lycopene biosynthesis in microorganisms.
• Review of lycopene biosynthetic metabolism engineering strategy.
• Discuss the current challenges and prospects of using microorganisms to produce lycopene.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alper H, Fischer C, Nevoigt E, Stephanopoulos G (2005a) Tuning genetic control through promoter engineering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(36):12678–12683. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504604102
Alper H, Jin Y, Moxley JF, Stephanopoulos G (2005b) Identifying gene targets for the metabolic engineering of lycopene biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 7(3):155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2004.12.003
Alper H, Miyaoku K, Stephanopoulos G (2005c) Construction of lycopene-overproducing E. coli strains by combining systematic and combinatorial gene knockout targets. Nat Biotechnol 23(5):612–616. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1083
Arathi BP, Raghavendra-Rao Sowmya P, Vijay K, Baskaran V, Lakshminarayana R (2015) Metabolomics of carotenoids: the challenges and prospects-a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 45(1):105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.06.003
Bahieldin A, Gadalla NO, Al-Garni SM, Almehdar H, Noor S, Hassan SM, Shokry AM, Sabir JS, Murata N (2014) Efficient production of lycopene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by expression of synthetic crt genes from a plasmid harboring the ADH2 promoter. Plasmid 72:18–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plasmid.2014.03.001
Bai C, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Hu Y, Xiang S, Miao J, Lou C, Zhang L (2015) Exploiting a precise design of universal synthetic modular regulatory elements to unlock the microbial natural products in Streptomyces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(39):12181–12186. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1511027112
Bhataya A, Schmidt-Dannert C, Lee PC (2009) Metabolic engineering of Pichia pastoris X-33 for lycopene production. Process Biochem 44(10):1095–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2009.05.012
Blazeck J, Hill A, Liu L, Knight R, Miller J, Pan A, Otoupal P, Alper HS (2014) Harnessing Yarrowia lipolytica lipogenesis to create a platform for lipid and biofuel production. Nat Commun 5(3131):3131. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4131
Caseiro M, Ascenso A, Costa A, Creagh-Flynn J, Johnson M, Simoes S (2020) Lycopene in human health. LWT Food Sci Technol 127:109323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109323
Chasse GA, Mak ML, Deretey E, Farkas I, Torday LL, Papp JG, Sarma DSR, Agarwal A, Chakravarthi S, Agarwal S, Rao AV (2001) An ab initio computational study on selected lycopene isomers. J Mol Struct THEOCHEM 571(1):27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-1280(01)00424-9
Chen Y, Shen H, Cui Y, Chen S, Weng Z, Zhao M, Liu J (2013) Chromosomal evolution of Escherichia coli for the efficient production of lycopene. BMC Biotechnol 13(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-13-6
Chen Y, Xiao W, Wang Y, Liu H, Li X, Yuan Y (2016) Lycopene overproduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through combining pathway engineering with host engineering. Microb Cell Fact 15(1):113. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0509-4
Chen R, Yang S, Zhang L, Zhou YJ (2020) Advanced strategies for production of natural products in yeast. iScience 23(3):100879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.100879
Choudhari SM, Ananthanarayan L, Singhal RS (2008) Use of metabolic stimulators and inhibitors for enhanced production of β-carotene and lycopene by Blakeslea trispora NRRL 2895 and 2896. Bioresour Technol 99(8):3166–3173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.05.051
Cui M, Wang Z, Hu X, Wang X (2019) Effects of lipopolysaccharide structure on lycopene production in Escherichia coli. Enzym Microb Technol 124:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.01.009
Ernst H (2002) Recent advances in industrial carotenoid synthesis. Pure Appl Chem 74(8):1369–1382. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200274081369
Farmer WR, Liao JC (2000) Improving lycopene production in Escherichia coli by engineering metabolic control. Nat Biotechnol 18(5):533–537. https://doi.org/10.1038/75398
Fazeli MR, Tofighi H, Madadkar-Sobhani A, Shahverdi AR, Nejad-Sattari T, Mirzaie S, Jamalifar H (2009) Nicotine inhibition of lycopene cyclase enhances accumulation of carotenoid intermediates by Dunaliella salina CCAP 19/18. Eur J Phycol 44:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1080/09670260802578526
Feng L, Qiang W, Yu X, Kwame F (2019) Effects of exogenous lipids and cold acclimation on lycopene production and fatty acid composition in Blakeslea trispora. AMB Express 9:162. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0891-5
Gong M, Bassi A (2016) Carotenoids from microalgae: a review of recent developments. Biotechnol Adv 34(8):1396–1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.10.005
Grabowska MG, Wawrzyniak D, Rolle K, Chomczy Ski P, Oziewicz S, Jurga S, Barciszewski J (2019) Let food be your medicine: nutraceutical properties of lycopene. Food Funct 1(6):39–312. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo00580c
Hernandez-Almanza A, Montanez-Saenz J, Martinez-Avila C, Rodriguez-Herrera R, Aguilar CN (2014) Carotenoid production by Rhodotorula glutinis YB-252 in solid-state fermentation. Food Biosci 7:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2014.04.001
Hernández-Almanza A, Montañez J, Martínez G, Aguilar-Jiménez A, Contreras-Esquivel JC, Aguilar CN (2016) Lycopene: progress in microbial production. Trends Food Sci Technol 56:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2016.08.013
Hernandez-Arranz S, Perez-Gil J, Marshall-Sabey D, Rodriguez-Concepcion M (2019) Engineering Pseudomonas putida for isoprenoid production by manipulating endogenous and shunt pathways supplying precursors. Microb Cell Factories 18:152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1204-z
Hong J, Park S, Kim S, Kim S, Hahn J (2019) Efficient production of lycopene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by enzyme engineering and increasing membrane flexibility and NAPDH production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(1):211–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9449-8
Huang L, Pu Y, Yang X, Zhu X, Cai J, Xu Z (2015) Engineering of global regulator cAMP receptor protein (CRP) in Escherichia coli for improved lycopene production. J Biotechnol 199:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.02.006
Ishikawa E, Abe H (2004) Lycopene accumulation and cyclic carotenoid deficiency in heterotrophic Chlorella treated with nicotine. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 31(12):585–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-004-0179-9
Jin Y, Stephanopoulos G (2007) Multi-dimensional gene target search for improving lycopene biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 9(4):337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2007.03.003
Jung H, Im D, Lim JH, Jung GY, Oh M (2019) Metabolic perturbations in mutants of glucose transporters and their applications in metabolite production in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Factories 18(1701):170. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1224-8
Kang W, Ma T, Liu M, Qu J, Liu Z, Zhang H, Shi B, Fu S, Ma J, Lai LTF, He S, Qu J, Wing-Ngor Au S, Ho Kang B, Yu Lau WC, Deng Z, Xia J, Liu T (2019) Modular enzyme assembly for enhanced cascade biocatalysis and metabolic flux. Nat Commun 10(1):4248. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12247-w
Kang CK, Jeong S, Yang JE, Choi YJ (2020) High-yield production of lycopene from corn steep liquor and glycerol using the metabolically engineered Deinococcus radiodurans R1 Strain. J Agric Food Chem 68(18):5147–5153. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01024
Kim MJ, Noh MH, Woo S, Lim HG, Jung GY (2019) Enhanced lycopene production in Escherichia coli by expression of two MEP pathway enzymes from Vibrio sp. Dhg Catalysts 9:1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9121003
Li X, Wang Z, Zhang G, Yi L (2019) Improving lycopene production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through optimizing pathway and chassis metabolism. Chem Eng Sci 193:364–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2018.09.030
Li C, Swofford CA, Sinskey AJ (2020) Modular engineering for microbial production of carotenoids. Metab Eng 10:e118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mec.2019.e00118
Liang M, Hao Y, Li Y, Liang Y, Jiang J (2016) Inhibiting lycopene cyclases to accumulate lycopene in high beta-carotene-accumulating Dunaliella bardawil. Food Bioprocess Technol 9(6):1002–1009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1681-6
Liang X, Ma C, Yan X, Liu X, Liu F (2019) Advances in research on bioactivity, metabolism, stability and delivery systems of lycopene. Trends Food Sci Technol 93:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.08.019
Liu X, Liu R, Li H, Tang Y (2012) Lycopene production from synthetic medium by Blakeslea trispora NRRL 2895 (+) and 2896 (-) in a stirred-tank fermenter. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 35(5):739–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0654-4
Liu Y, Li X, Lu S, Yu C, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Yao J (2019a) Comparative metabolic responses induced by pyridine and imidazole in Blakeslea trispora. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:347. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00347
Liu D, Liu H, Qi H, Guo X, Jia B, Zhang J, Yuan Y (2019b) Constructing yeast chimeric pathways to boost lipophilic terpene synthesis. ACS Synth Biol 8(4):724–733. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.8b00360
Liu N, Liu B, Wang G, Soong YV, Tao Y, Liu W, Xie D (2020) Lycopene production from glucose, fatty acid and waste cooking oil by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Biochem Eng J 155:107488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2020.107488
Lopez-Nieto MJ, Costa J, Peiro E, Mendez E, Rodriguez-Saiz M, de la Fuente JL, Cabri W, Barredo JL (2004) Biotechnological lycopene production by mated fermentation of Blakeslea trispora. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66(2):153–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1669-4
Luo Z, Liu N, Lazar Z, Chatzivasileiou A, Ward V, Chen J, Zhou J, Stephanopoulos G (2020) Enhancing isoprenoid synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica by expressing the isopentenol utilization pathway and modulating intracellular hydrophobicity. Metab Eng 61:344–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2020.07.010
Ma T, Deng Z, Liu T (2016) Microbial production strategies and applications of lycopene and other terpenoids. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1975-2
Ma T, Shi B, Ye Z, Li X, Liu M, Chen Y, Xia J, Nielsen J, Deng Z, Liu T (2019a) Lipid engineering combined with systematic metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-yield production of lycopene. Metab Eng 52:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.11.009
Ma Y, Wang K, Wang W, Ding Y, Shi T, Huang H, Ji X (2019b) Advances in the metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for the production of terpenoids. Bioresour Technol 281:449–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.02.116
Mantzouridou FT, Naziri E (2017) Scale translation from shaken to diffused bubble aerated systems for lycopene production by Blakeslea trispora under stimulated conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(5):1845–1856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7943-4
Mao X, Liu Z, Sun J, Lee SY (2017) Metabolic engineering for the microbial production of marine bioactive compounds. Biotechnol Adv 35(8):1004–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.03.001
Markham KA, Alper HS (2018) Synthetic biology expands the industrial potential of Yarrowia lipolytica. Trends Biotechnol 36(10):1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.05.004
Mata-Gomez LC, Montanez JC, Mendez-Zavala A, Aguilar CN (2014) Biotechnological production of carotenoids by yeasts: an overview. Microb Cell Factories 13:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-13-12
Matthäus F, Ketelhot M, Gatter M, Barth G (2014) Production of lycopene in the non-carotenoid-producing yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(5):1660–1669. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03167-13
Mehta BJ, Obraztsova IN, Cerda-Olmedo E (2003) Mutants and intersexual heterokaryons of Blakeslea trispora for production of β-carotene and lycopene. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(7):4043–4048. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.7.4043-4048.2003
Moise AR, Al-Babili S, Wurtzel ET (2014) Mechanistic aspects of carotenoid biosynthesis. Chem Rev 114(1):164–193. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400106y
Moran NE, Erdman JW, Clinton SK (2013) Complex interactions between dietary and genetic factors impact lycopene metabolism and distribution. Arch Biochem Biophys 539(2):171–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2013.06.017
Müller L, Caris-Veyrat C, Lowe G, Böhm V (2016) Lycopene and its antioxidant role in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases-a critical review. Crit Rev Food Sci 56(11):1868–1879. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2013.801827
Nasrabadi MRN, Razavi SH (2010) High levels lycopene accumulation by Dietzia natronolimnaea HS-1 using lycopene cyclase inhibitors in a fed-batch process. Food Sci Biotechnol 19(4):899–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-010-0127-6
Nicolas-Molina FE, Navarro E, Ruiz-Vazquez RM (2008) Lycopene over-accumulation by disruption of the negative regulator gene crgA in Mucor circinelloides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78(1):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1281-5
Przybylska S (2020) Lycopene–a bioactive carotenoid offering multiple health benefits: a review. Int J Food Sci Technol 55(1):11–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14260
Qiang W, Ling-ran F, Luo W, Han-guang L, Lin W, Ya Z, Xiao-bin Y (2014) Mutation breeding of lycopene-producing strain Blakeslea Trispora by a novel atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP). Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174(1):452–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0998-8
Qu J, Cao S, Wei Q, Zhang H, Wang R, Kang W, Ma T, Zhang L, Liu T, Wing-Ngor Au S, Sun F, Xia J (2019) Synthetic multienzyme complexes, catalytic nanomachineries for cascade biosynthesis in vivo. ACS Nano 13(9):9895–9906. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b03631
Rad SA, Zahiri HS, Noghabi KA, Rajaei S, Heidari R, Mojallali L (2012) Type 2 IDI performs better than type 1 for improving lycopene production in metabolically engineered E. coli strains. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 28(1):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0821-4
Rao AV, Ray MR, Rao LG (2006) Lycopene. Adv Food Nutr Res 51:99–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1043-4526(06)51002-2
Reynaud E, Aydemir G, Ruehl R, Dangles O, Caris-Veyrat C (2011) Organic synthesis of new putative lycopene metabolites and preliminary investigation of their cell-signaling effects. JJ Agric Food Chem 59(4):1457–1463. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf104092e
Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Avalos J, Luisa Bonet M, Boronat A, Gomez-Gomez L, Hornero-Mendez D, Carmen Limon M, Melendez-Martinez AJ, Olmedilla-Alonso B, Palou A, Ribot J, Rodrigo MJ, Zacarias L, Zhu C (2018) A global perspective on carotenoids: metabolism, biotechnology, and benefits for nutrition and health. Prog Lipid Res 70:62–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2018.04.004
Saini RK, Keum Y (2019) Microbial platforms to produce commercially vital carotenoids at industrial scale: an updated review of critical issues. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46(5):657–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-018-2104-7
Saini RK, Nile SH, Park SW (2015) Carotenoids from fruits and vegetables: chemistry, analysis, occurrence, bioavailability and biological activities. Food Res Int 76:735–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.07.047
Schwartz C, Frogue K, Misa J, Wheeldon I (2017) Host and pathway engineering for enhanced lycopene biosynthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica. Front Microbiol 8:2233. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02233
Sevgili A, Erkmen O (2019) Improved lycopene production from different substrates by mated fermentation of Blakeslea Trispora. Foods 8(1204):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8040120
Shi J, Le Maguer M (2000) Lycopene in tomatoes: chemical and physical properties affected by food processing. Crit Rev Biotechnol 20(4):293–334. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388550091144212
Shi Y, Xin X, Yuan Q (2012) Improved lycopene production by Blakeslea trispora with isopentenyl compounds and metabolic precursors. Biotechnol Lett 34(5):849–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0839-6
Shi B, Ma T, Ye Z, Li X, Huang Y, Zhou Z, Ding Y, Deng Z, Liu T (2019) Systematic metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for lycopene overproduction. J Agric Food Chem 67(40):11148–11157. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04519
Singh P, Goyal GK (2008) Dietary lycopene: its properties and anticarcinogenic effects. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 7(3):255–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2008.00044.x
Su A, Chi S, Li Y, Tan S, Qiang S, Chen Z, Meng Y (2018) Metabolic redesign of Rhodobacter sphaeroides for lycopene production. J Agric Food Chem 66(23):5879–5885. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00855
Sun Y, Yuan Q, Vriesekoop F (2007) Effect of two ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors on lycopene production by Blakeslea trispora. Process Biochem 42(10):1460–1464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2007.06.006
Sun T, Miao L, Li Q, Dai G, Lu F, Liu T, Zhang X, Ma Y (2014) Production of lycopene by metabolically-engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 36(7):1515–1522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1543-0
Vallecilla-Yepez L, Ciftci ON (2018) Increasing cis-lycopene content of the oleoresin from tomato processing byproducts using supercritical carbon dioxide. LWT Food Sci Technol 95:354–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.04.065
Vereschagina OA, Memorskaya AS, Tereshina VM (2010) The role of exogenous lipids in lycopene synthesis in the mucoraceous fungus Blakeslea trispora. Microbiology 79(5):593–601. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261710050036
Vidhyavathi R, Sarada R, Ravishankar GA (2009) Expression of carotenogenic genes and carotenoid production in Haematococcus pluvialis under the influence of carotenoid and fatty acid synthesis inhibitors. Enzyme Microb Technol 45(2):88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2009.05.005
Wang G, Grammel H, Abou-Aisha K, Sägesser R, Ghosh R (2012a) High-level production of the industrial product lycopene by the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(20):7205–7215. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00545-12
Wang J, Liu X, Liu R, Li H, Tang Y (2012b) Optimization of the mated fermentation process for the production of lycopene by Blakeslea trispora NRRL 2895 (+) and NRRL 2896 (-). Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 35(4):553–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-011-0628-6
Wang Q, Luo W, Gu Q, Feng L, Li H, Yu X (2013) Enhanced lycopene content in Blakeslea trispora by effective mutation-screening method. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 171(7):1692–1700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0468-8
Wang H, He F, Lu M, Zhao C, Xiong L, Yu L (2014) High-quality lycopene overaccumulation via inhibition of γ-carotene and ergosterol biosyntheses in Blakeslea trispora. J Funct Foods 7:435–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2014.01.014
Wang Q, Feng L, Luo W, Li H, Zhou Y, Yu X (2015) Effect of inoculation process on lycopene production by Blakeslea trispora in a stirred-tank reactor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175(2):770–779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1327-y
Wang Y, Pang J, Zheng Y, Jiang P, Gong W, Chen X, Chen D (2017) Genetic manipulation of the bifunctional gene, carRA, to enhance lycopene content in Blakeslea trispora. Biochem Eng J 119:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2016.12.011
Wang C, Zhao S, Shao X, Park J, Jeong S, Park H, Kwak W, Wei G, Kim S (2019) Challenges and tackles in metabolic engineering for microbial production of carotenoids. Microb Cell Fact. 18(1):55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1105-1
Wang Z, Li X, Yu C, Lu S, Xiong S, Yuan Y (2020a) Continuous self-cycling fermentation leads to economical lycopene production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8(420):420. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00420
Wang Z, Sun J, Yang Q, Yang J (2020b) Metabolic engineering Escherichia coli for the production of lycopene. Molecules 25(14):3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143136
Ward V, Chatzivasileiou AO, Stephanopoulos G (2018) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of isoprenoids. FEMS Microbiol Lett 365(10). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fny079
Wei Y, Mohsin A, Hong Q, Guo M, Fang H (2018) Enhanced production of biosynthesized lycopene via heterogenous MVA pathway based on chromosomal multiple position integration strategy plus plasmid systems in Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 250:382–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.11.035
Wu T, Ye L, Zhao D, Li S, Li Q, Zhang B, Bi C (2018) Engineering membrane morphology and manipulating synthesis for increased lycopene accumulation in Escherichia coli cell factories. 3. Biotech 8(6):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1298-8
Xie W, Lv X, Ye L, Zhou P, Yu H (2015) Construction of lycopene-overproducing Saccharomyces cerevisiae by combining directed evolution and metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 30:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.04.009
Xu N, Zheng HZSC, Xu J (2006) The effect of cyclase inhibitors on the production of lycopene by mated culture of Blakeslea trispora. Chin J Antibiot 31(6):372–375
Xu F, Yuan Q, Zhu Y (2007) Improved production of lycopene and β-carotene by Blakeslea trispora with oxygen-vectors. Process Biochem 42(2):289–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2006.08.007
Zhang Y, Chen H, Navarro E, Lopez-Garcia S, Chen YQ, Zhang H, Chen W, Garre V (2017) Generation of lycopene-overproducing strains of the fungus Mucor circinelloides reveals important aspects of lycopene formation and accumulation. Biotechnol Lett 39(3):439–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2265-2
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Sun J, Xue C, Mao X (2018) Biotechnological production of zeaxanthin by microorganisms. Trends Food Sci Technol 71:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00050-09
Zhang X, Nie M, Chen J, Wei L, Hua Q (2019) Multicopy integrants of crt genes and co-expression of AMP deaminase improve lycopene production in Yarrowia lipolytica. J Biotechnol 289:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.11.009
Zhang X, Wang D, Duan Y, Zheng X, Lin Y, Liang S (2020) Production of lycopene by metabolically engineered Pichia pastoris. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 84(3):463–470. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2019.1693250
Zhou P, Xie W, Yao Z, Zhu Y, Ye L, Yu H (2018) Development of a temperature-responsive yeast cell factory using engineered Gal4 as a protein switch. Biotechnol Bioeng 115(5):1321–1330. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26544
Zhu F, Lu L, Fu S, Zhong X, Hu M, Deng Z, Liu T (2015) Targeted engineering and scale up of lycopene overproduction in Escherichia coli. Process Biochem 50(3):341–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.12.008
Zuo Z, Xue Q, Zhou J, Zhao D, Han J, Xiang H (2018) Engineering Haloferax mediterranei as an efficient platform for high level production of lycopene. Front Microbiol 9:2893. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02893
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFD0901904), the Taishan Scholar Project of Shandong Province (tsqn201812020), a Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (2019KJF012), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31922072), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (201941002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.L. and H.J. conducted literature search, prepared the tables or figures, and drafted the manuscript. Z.L. and X.M. contributed to the conception and design of the manuscript and reviewed and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This review does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Liu, Z., Jiang, H. et al. Biotechnological production of lycopene by microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 10307–10324 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10967-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10967-4