Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to perform an updated systematic review of the literature over the last 10 years, analyzing and comparing the many published techniques with the hope of providing plastic surgeons with a new standard in creating the perfect umbilicus in the setting of both abdominoplasty and abdominally based free-flap breast reconstruction.
Methods
An initial search using the PubMed online database with the keyword “umbilicoplasty” was performed. These results were filtered to only include articles published within the last 10 years. The remaining articles were thoroughly reviewed by the authors and only those pertaining to techniques for umbilicoplasty in the setting of abdominoplasty and abdominally based free flap were included.
Results
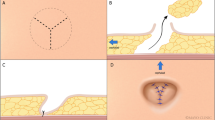
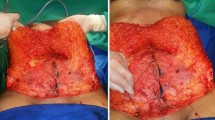
Of the 10 unique techniques yielded by our search, 9/10 (90 %) initially incised the native umbilicus with a round, oval, or vertical ellipse pattern. Of the 9 techniques that initially perform a round incision, 4 of them (44.4 %) later modify the round umbilicus with either an inferior or superior excision to create either a “U”- or “inverted U”-shaped umbilicus. In terms of the shape of the incision made in the abdominal flap for umbilical reinsertion, the most common were either a round incision or an inverted “V” or “U,” both of which accounted for 4/10 (40 %) and 3/10 (30 %), respectively. Almost all of the studies (8/10; 80 %) describe “defatting” or trimming of the subcutaneous adipose tissue around the incision to create a periumbilical concavity following inset of the umbilicus. 4/10 (40 %) of the techniques describe suturing the dermis of the umbilical skin to rectus fascia. Furthermore, 3/10 (30 %) advise that stalk plication is a necessary step to their technique. 7/9 techniques (77.8 %) preferred nondissolvable sutures for skin closure, with nylon being the most common suture material used. Only 2/9 (22.2 %) used dissolvable sutures.
Conclusion
Although future studies are necessary, it is our hope that this systematic review better elucidates the techniques and provides some guidance to both aesthetic and reconstructive plastic surgeons in the pursuit of creating the perfect umbilicus following abdominoplasty and TRAM/DIEP breast reconstruction.
No Level Assigned
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Society of Plastic Surgeons (2013) Plastic surgery statistics report. American Society of Plastic Surgeons, p. 23
Pallua N, Markowicz MP, Grosse F, Walter S (2010) Aesthetically pleasant umbilicoplasty. Ann Plast Surg 64:722–725
Lee MJ, Mustoe TA (2002) Simplified technique for creating a youthful umbilicus in abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:2136–2140
Matarasso A, Swift RW, Rankin M (2006) Abdominoplasty and abdominal contour surgery: a national plastic surgery survey. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1797–1808
Southwell-Keely JP, Berry MG (2011) Umbilical reconstruction: a review of techniques. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64:803–808
Malic CC, Spyrou GE, Hough M, Fourie L (2007) Patient satisfaction with two different methods of umbilicoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:357–361
Abhyankar SV, Rajguru AG, Patil PA (2006) Anatomical localization of the umbilicus: an Indian study. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1153–1157
Dudukovic M, Kisic H, Baez ML et al (2014) Anatomical prediction for surgical positioning of the umbilicus in a white population. Ann Plast Surg 75:135
Rodriguez-Feliz JR, Makhijani S, Przybyla A, Hill D, Chao J (2012) Intraoperative assessment of the umbilicopubic distance: a reliable anatomic landmark for transposition of the umbilicus. Aesthet Plast Surg 36:8–17
Lee SJ, Garg S, Lee HP (2014) Computer-aided analysis of the “Beautiful” umbilicus. Aesthet Surg J/Am Soc Aesthet Plast Surg 34:748–756
Mowlavi A, Huynh PM, Huynh DC, Wilhelmi BJ (2012) A new technique involving a spherical stainless steel device to optimize positioning of the umbilicus. Aesthet Plast Surg 36:1062–1065
Bruekers SE, van der Lei B, Tan TL, Luijendijk RW, Stevens HP (2009) “Scarless” umbilicoplasty: a new umbilicoplasty technique and a review of the English language literature. Ann Plast Surg 63:15–20
Dogan T (2010) Umbilicoplasty in abdominoplasty: a new approach. Ann Plast Surg 64:718–721
Castillo PF, Sepulveda CA, Prado AC, Troncoso AL, Villaman JJ (2007) Umbilical reinsertion in abdominoplasty: technique using deepithelialized skin flaps. Aesthet Plast Surg 31:519–520
Rozen SM, Redett R (2007) The two-dermal-flap umbilical transposition: a natural and aesthetic umbilicus after abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:2255–2262
Lesavoy MA, Fan K, Guenther DA, Herrera F, Little JW (2012) The inverted-v chevron umbilicoplasty for breast reconstruction and abdominoplasty. Aesthet Surg J/Am Soc Aesthet Plast Surg 32:110–116
Mazzocchi M, Trignano E, Armenti AF, Figus A, Dessy LA (2011) Long-term results of a versatile technique for umbilicoplasty in abdominoplasty. Aesthet Plast Surg 35:456–462
Clo TC, Nogueira DS (2012) A new umbilical reconstruction technique used for 306 consecutive abdominoplasties. Aesthet Plast Surg 36:1009–1014
Hazani R, Israeli R, Feingold RS (2009) Reconstructing a natural looking umbilicus: a new technique. Ann Plast Surg 63:358–360
Craig SB, Faller MS, Puckett CL (2000) In search of the ideal female umbilicus. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:389–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, W.J., Sinno, S., Brownstone, N.D. et al. Creating the Perfect Umbilicus: A Systematic Review of Recent Literature. Aesth Plast Surg 40, 372–379 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-016-0633-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-016-0633-x