Abstract
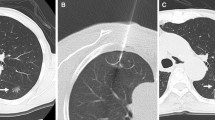
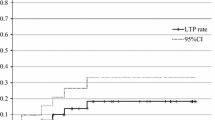
We retrospectively reviewed the imaging of patients after radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of lung metastases performed at our institution to assess the usefulness of ground glass opacification (GGO) margin for the prediction of complete tumor ablation. From January 2004 to March 2007, patients were identified where there was a postprocedure thin collimation scan to allow multiplanar reformatting, either immediately or at 24 h and at least 6 months of imaging follow-up. Thirty-six tumors in 22 patients were identified. The scans were assessed for the presence and width of GGO margin, and minimal and maximal dimensions were measured. A second reviewer, blinded to the outcome of the postprocedure assessment, reviewed the follow-up imaging for recurrence. The recurrence group had larger tumors (p = 0.045) and smaller mean minimal GGO margin width (p = 0.0001). Multivariate binary regression analysis confirmed that the minimal GGO margin was significantly (p < 0.005) associated with tumor recurrence. Receiver operator characteristic curve analysis suggests a cutoff of 4.5 mm for complete tumor ablation. There was substantial agreement (κ = 0.759) between the site of absent GGO margin and the site of tumor recurrence. The point on the tumor surface where there is no GGO margin is likely to be the site of future recurrence. In our experience, a circumferential GGO margin of >5 mm is the minimal margion required to ensure complete tumor ablation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steinke K, Sewell PE, Dupuy D et al (2004) Pulmonary radiofrequency ablation—an international study survey. Anticancer Res 24:339–343
Yan TD, King J, Sjarif A et al (2006) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary metastases from colorectal carcinoma: prognostic determinants for survival. Ann Surg Oncol 13:1529–1537
Yamakado K, Hase S, Matsuoka T et al (2007) Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of unresectable lung metastases in patients with colorectal cancer: a multicenter study in Japan. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18:393–398
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, DiPetrillo TA et al (2007) Pulmonary radiofrequency ablation: long-term safety and efficacy in 153 patients. Radiology 243:268–275
Yan TD, King J, Sjarif A et al (2007) Treatment failure after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for nonsurgical candidates with pulmonary metastases from colorectal carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 14:1718–1726
Gillams AR, Lees WR (2008) Radiofrequency ablation of lung metastases: factors influencing success. Eur Radiol 18:672–677
Okuma T, Matsuoka T, Yamamoto A et al (2008) Frequency and risk factors of various complications after computed tomography-guided radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31:122–130
de Baere T, Palussiere J, Auperin A et al (2006) Midterm local efficacy and survival after radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors with minimum follow-up of 1 year: prospective evaluation. Radiology 240:587–596
Yamamoto A, Nakamura K, Matsuoka T et al (2005) Radiofrequency ablation in a porcine lung model: correlation between CT and histopathologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 185:1299–1306
Bojarski JD, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW (2005) CT imaging findings of pulmonary neoplasms after treatment with radiofrequency ablation: results in 32 tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 185:466–471
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Lencioni R, Crocetti L, Cioni R et al (2008) Response to radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary tumours: a prospective, intention-to-treat, multicentre clinical trial (the RAPTURE study). Lancet Oncol 9:621–628
Hiraki T, Sakurai J, Tsuda T et al (2006) Risk factors for local progression after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors: evaluation based on a preliminary review of 342 tumors. Cancer 107:2873–2880
Gadaleta C, Mattioli V, Colucci G et al (2004) Radiofrequency ablation of 40 lung neoplasms: preliminary results. AJR Am J Roentgenol 183:361–368
Kang S, Luo R, Liao W et al (2004) Single group study to evaluate the feasibility and complications of radiofrequency ablation and usefulness of post treatment position emission tomography in lung tumours. World J Surg Oncol 2:30
Okuma T, Okamura T, Matsuoka T et al (2006) Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for assessment of patients with unresectable recurrent or metastatic lung cancers after CT-guided radiofrequency ablation: preliminary results. Ann Nucl Med 20:115–121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, E.M., Lees, W.R. & Gillams, A.R. Early Indicators of Treatment Success After Percutaneous Radiofrequency of Pulmonary Tumors. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32, 478–483 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-008-9482-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-008-9482-6