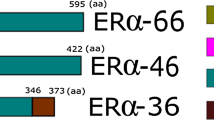
Abstract
Estrogen receptor (ER), mediating estrogen-signaling stimuli, is a dominant regulator and a key therapeutic target in breast cancer etiology and progression. Endocrine therapy, blocking the ER pathway, is one of the most important systemic therapies in breast cancer management, but de novo and acquired resistance is still a major clinical problem. New research highlights the role of both genomic and nongenomic ER activities and their intimate molecular crosstalk with growth factor receptor and other signaling kinase pathways in endocrine resistance. These signaling pathways, when overexpressed and/or hyperactivated, can modulate both activities of ER, resulting in endocrine resistance. Thus, these signal transduction receptors and signaling molecules may serve as both predictive markers and novel therapeutic targets to circumvent endocrine resistance. Compelling experimental and clinical evidence suggest that the epidermal growth factor/HER2/neu receptor (EGFR/HER2) pathway might play a distinct role in endocrine resistance, and especially in resistance to selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) such as tamoxifen. Results from preclinical studies of treatment combinations with various endocrine therapy drugs together with several potent anti-EGFR/HER2 inhibitors are very promising, and clinical trials to see whether this new strategy is effective in patients are now ongoing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Coombes RC (2002) Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 2:101–112
Ali S, Metzger D, Bornert JM, Chambon P (1993) Modulation of transcriptional activation by ligand-dependent phosphorylation of the human oestrogen receptor A/B region. EMBO J 12:1153–1160
Anzick SL, Kononen J, Walker RL, Azorsa DO, Tanner MM, Guan XY, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP, Trent JM, Meltzer PS (1997) AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277:965–968
Aronica SM, Katzenellenbogen BS (1993) Stimulation of estrogen receptor-mediated transcription and alteration in the phosphorylation state of the rat uterine estrogen receptor by estrogen, cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and insulin-like growth factor-I. Mol Endocrinol 7:743–752
Balasenthil S, Vadlamudi RK (2003) Functional interactions between the estrogen receptor coactivator PELP1/MNAR and retinoblastoma protein. J Biol Chem 278:22119–22127
Bardou VJ, Arpino G, Elledge RM, Osborne CK, Clark GM (2003) Progesterone receptor status significantly improves outcome prediction over estrogen receptor status alone for adjuvant endocrine therapy in two large breast cancer databases. J Clin Oncol 21:1973–1979
Baum M, Buzdar A (2003) The current status of aromatase inhibitors in the management of breast cancer. Surg Clin North Am 83:973–994
Beatson GT (1896) On the treatment of inoperable cases of carcinogen of the mamma: suggestions for a new method of treatment with illustrative cases. Lancet 2:104–107, 162–165
Benz CC, Scott GK, Sarup JC, Johnson RM, Tripathy D, Coronado E, Shepard HM, Osborne CK (1992) Estrogen-dependent, tamoxifen-resistant tumorigenic growth of MCF-7 cells transfected with HER2/neu. Breast Cancer Res Treat 24:85–95
Buzdar A, O’Shaughnessy JA, Booser DJ, Pippen JE Jr, Jones SE, Munster PN, Peterson P, Melemed AS, Winer E, Hudis C (2003) Phase II, randomized, double-blind study of two dose levels of arzoxifene in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 21:1007–1014
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 276:9817–9824
Carlson RW (2002) Sequencing of endocrine therapies in breast cancer—integration of recent data. Breast Cancer Res Treat 75(Suppl 1):S27–S32; discussion S33–S35
Cato AC, Nestl A, Mink S (2002) Rapid actions of steroid receptors in cellular signaling pathways. Sci STKE 138:RE9
Chu I, Blackwell K, Chen S, Slingerland J (2005) The dual ErbB1/ErbB2 inhibitor, lapatinib (GW572016), cooperates with tamoxifen to inhibit both cell proliferation- and estrogen-dependent gene expression in antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:18–25
Chung YL, Sheu ML, Yang SC, Lin CH, Yen SH (2002) Resistance to tamoxifen-induced apoptosis is associated with direct interaction between Her2/neu and cell membrane estrogen receptor in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 97:306–312
Cui X, Zhang P, Deng W, Oesterreich S, Lu Y, Mills GB, Lee AV (2003) Insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibits progesterone receptor expression in breast cancer cells via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway: progesterone receptor as a potential indicator of growth factor activity in breast cancer. Mol Endocrinol 17:575–588
Dobrzycka KM, Townson SM, Jiang S, Oesterreich S (2003) Estrogen receptor corepressors—a role in human breast cancer? Endocr Relat Cancer 10:517–536
Dowsett M (2003) Analysis of time to recurrence in the ATAC (arimidex, tamoxifen, alone or in combination) trial according to estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status. Breast Cancer Res Treat 82(Suppl 1):p S7 (abstract 4)
Dowsett M, Harper-Wynne C, Boeddinghaus I, Salter J, Hills M, Dixon M, Ebbs S, Gui G, Sacks N, Smith I (2001) HER-2 amplification impedes the antiproliferative effects of hormone therapy in estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer. Cancer Res 61:8452–8458
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 365:1687–1717
Ellis MJ, Coop A, Singh B, Mauriac L, Llombert-Cussac A, Janicke F, Miller WR, Evans DB, Dugan M, Brady C, Quebe-Fehling E, Borgs M (2001) Letrozole is more effective neoadjuvant endocrine therapy than tamoxifen for ErbB-1- and/or ErbB-2-positive, estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer: evidence from a phase III randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 19:3808–3816
Figtree GA, Webb CM, Collins P (2000) Tamoxifen acutely relaxes coronary arteries by an endothelium-, nitric oxide-, and estrogen receptor-dependent mechanism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:519–523
Figtree GA, McDonald D, Watkins H, Channon KM (2003) Truncated estrogen receptor alpha 46-kDa isoform in human endothelial cells: relationship to acute activation of nitric oxide synthase. Circulation 107:120–126
Filardo EJ (2002) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) transactivation by estrogen via the G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR30: a novel signaling pathway with potential significance for breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 80:231–238
Font de Mora J, Brown M (2000) AIB1 is a conduit for kinase-mediated growth factor signaling to the estrogen receptor. Mol Cell Biol 20:5041–5047
Green S, Walter P, Greene G, Krust A, Goffin C, Jensen E, Scrace G, Waterfield M, Chambon P (1986) Cloning of the human oestrogen receptor cDNA. J Steroid Biochem 24:77–83
Gross GE, Clark GM, Chamness GC, McGuire WL (1984) Multiple progesterone receptor assays in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 44:836–840
Gutierrez MC, Detre S, Johnston S, Mohsin SK, Shou J, Allred DC, Schiff R, Osborne CK, Dowsett M (2005) Molecular changes in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: relationship between estrogen receptor, HER-2, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Clin Oncol 23:2469–2476
Hall JM, McDonnell DP (1999) The estrogen receptor beta-isoform (ERbeta) of the human estrogen receptor modulates ERalpha transcriptional activity and is a key regulator of the cellular response to estrogens and antiestrogens. Endocrinology 140:5566–5578
Hong SH, Privalsky ML (2000) The SMRT corepressor is regulated by a MEK-1 kinase pathway: inhibition of corepressor function is associated with SMRT phosphorylation and nuclear export. Mol Cell Biol 20:6612–6625
Hopp TA, Weiss HL, Parra IS, Cui Y, Osborne CK, Fuqua SA (2004) Low levels of estrogen receptor beta protein predict resistance to tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:7490–7499
Howell A, Cuzick J, Baum M, Budar A, Dowsett M, Forbes JF, Hoctin-Boes G, Houghton J, Locker GY, Tobias JS (2005) Results of the ATAC (Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination) trial after completion of 5 years’ adjuvant treatment for breast cancer. Lancet 365:60–62
Jensen EV (1991) Overview of the nuclear receptor family. In: Parker MG (ed) Nuclear hormone receptors: molecular mechanisms, cellular functions, clinical abnormalities. Academic Press, London, pp 1–13
Joel PB, Smith J, Sturgill TW, Fisher TL, Blenis J, Lannigan DA (1998) pp90rsk1 regulates estrogen receptor-mediated transcription through phosphorylation of Ser-167. Mol Cell Biol 18:1978–1984
Kahlert S, Nuedling S, van Eickels M, Vetter H, Meyer R, Grohe C (2000) Estrogen receptor alpha rapidly activates the IGF-1 receptor pathway. J Biol Chem 275:18447–18453
Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhiro Y, Kitamoto T, Uchiyama S, Sasaki H, Masushige S, Gotoh Y, Nishida E, Kawashima H, Metzger D, Chambon P (1995) Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 270:1491–1494
Klinge CM (2001) Estrogen receptor interaction with estrogen response elements. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2905–2919
Konecny G, Pauletti G, Pegram M, Untch M, Dandekar S, Aguilar Z, Wilson C, Rong HM, Bauerfeind I, Felber M, Wang HJ, Beryt M, Seshadri R, Hepp H, Slamon DJ (2003) Quantitative association between HER-2/neu and steroid hormone receptors in hormone receptor-positive primary breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:142–153
Kousteni S, Chen JR, Bellido T, Han L, Ali AA, O’Brien CA, Plotkin L, Fu Q, Mancino AT, Wen Y, Vertino AM, Powers CC, Stewart SA, Ebert R, Parfitt AM, Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Manolagas SC (2002) Reversal of bone loss in mice by nongenotropic signaling of sex steroids. Science 298:843–846
Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (1996) Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5925–5930
Kumar R, Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Talukder AH, Mandal M, Yang Z, Bagheri-Yarmand R, Sahin A, Hortobagyi G, Adam L, Barnes CJ, Vadlamudi RK (2002) A naturally occurring MTA1 variant sequesters oestrogen receptor-alpha in the cytoplasm. Nature 418:654–657
Kumar R, Wang RA, Bagheri-Yarmand R (2003) Emerging roles of MTA family members in human cancers. Semin Oncol 30(5 Suppl 16):30–37
Kurokawa H, Lenferink AE, Simpson JF, Pisacane PI, Sliwkowski MX, Forbes JT, Arteaga CL (2000) Inhibition of HER2/neu (erbB-2) and mitogen-activated protein kinases enhances tamoxifen action against HER2-overexpressing, tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 60:5887–5894
Kushner PJ, Agard DA, Greene GL, Scanlan TS, Shiau AK, Uht RM, Webb P (2000) Estrogen receptor pathways to AP-1. Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 74:311–317
Lacassagne A (1936) Hormonal pathogenesis of adenocarcinoma of the breast. Am J Cancer 27:217–225
Lavinsky RM, Jepsen K, Heinzel T, Torchia J, Mullen TM, Schiff R, Del-Rio AL, Ricote M, Ngo S, Gemsch J, Hilsenbeck SG, Osborne CK, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG, Rose DW (1998) Diverse signaling pathways modulate nuclear receptor recruitment of N-CoR and SMRT complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2920–2925
Le Goff P, Montano MM, Schodin DJ, Katzenellenbogen BS (1994) Phosphorylation of the human estrogen receptor. Identification of hormone-regulated sites and examination of their influence on transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 269:4458–4466
Lee AV, Cui X, Oesterreich S (2001) Cross-talk among estrogen receptor, epidermal growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7(12 Suppl):s4429–s4435; discussion 4411s–4412s
Levin ER (2001) Cell localization, physiology, and nongenomic actions of estrogen receptors. J Appl Physiol 91:1860–1867
Levin ER (2002) Cellular functions of plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Steroids 67:471–475
Li L, Haynes MP, Bender JR (2003) Plasma membrane localization and function of the estrogen receptor alpha variant (ER46) in human endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4807–4812
List HJ, Reiter R, Singh B, Wellstein A, Riegel AT (2001) Expression of the nuclear coactivator AIB1 in normal and malignant breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat 68:21–28
Lopez GN, Turck CW, Schaufele F, Stallcup MR, Kushner PJ (2001) Growth factors signal to steroid receptors through mitogen-activated protein kinase regulation of p160 coactivator activity. J Biol Chem 276:22177–22182
Mass R (2000) The role of HER-2 expression in predicting response to therapy in breast cancer. Semin Oncol 27(6 Suppl 11):46–52; discussion 92–100
McInerney EM, Katzenellenbogen BS (1996) Different regions in activation function-1 of the human estrogen receptor required for antiestrogen- and estradiol-dependent transcription activation. J Biol Chem 271:24172–24178
McKenna NJ, Lanz RB, O’Malley BW (1999). Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocr Rev 20:321–344
Meng S, Tripathy D, Shete S, Ashfaq R, Haley B, Perkins S, Beitsch P, Khan A, Euhus D, Osborne C, Frenkel E, Hoover S, Leitch M, Clifford E, Vitetta E, Morrison L, Herlyn D, Terstappen LW, Fleming T, Fehm T, Tucker T, Lane N, Wang J, Uhr J (2004) HER-2 gene amplification can be acquired as breast cancer progresses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9393–9398
Migliaccio A, Castoria G, Di Domenico M, de Falco A, Bilancio A, Lombardi M, Bottero D, Varricchio L, Nanayakkara M, Rotondi A, Auricchio F (2002) Sex steroid hormones act as growth factors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 83:31–35
Miller CP (2002) SERMs: evolutionary chemistry, revolutionary biology. Curr Pharm Des 8:2089–2111
Morris C, Wakeling A (2002) Fulvestrant (Faslodex)—a new treatment option for patients progressing on prior endocrine therapy. Endocr Relat Cancer 9:267–276
Murphy LC, Simon SL, Parkes A, Leygue E, Dotzlaw H, Snell L, Troup S, Adeyinka A, Watson PH (2000) Altered expression of estrogen receptor coregulators during human breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 60:6266–6271
Nemere I, Pietras RJ, Blackmore PF (2003) Membrane receptors for steroid hormones: signal transduction and physiological significance. J Cell Biochem 88:438–445
Nicholson RI, McClelland RA, Robertson JF, Gee JM (1999) Involvement of steroid hormone and growth factor cross-talk in endocrine response in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 6:373–387
Nicholson RI, Hutcheson IR, Harper ME, Knowlden JM, Barrow D, McClelland RA, Jones HE, Wakeling AE, Gee JM (2002) Modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor in endocrine-resistant, estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 963:104–115
Osborne CK (1998) Tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 339:1609–1618
Osborne CK, Zhao H, Fuqua SA (2000) Selective estrogen receptor modulators: structure, function, and clinical use. J Clin Oncol 18:3172–3186
Osborne CK, Bardou V, Hopp TA, Chamness GC, Hilsenbeck SG, Fuqua SA, Wong J, Allred DC, Clark GM, Schiff R (2003) Role of the estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 (SRC-3) and HER-2/neu in tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:353–361
Pietras RJ (2003) Improved antitumor therapy with Herceptin and Faslodex for dual targeting of HER-2 and estrogen receptor signaling pathways in human breast cancers with overexpression of HER-2/neu gene. Breast Cancer Res Treat 82(Suppl 1):S12 (abstract 22)
Ravdin PM, Green S, Dorr TM, McGuire WL, Fabian C, Pugh RP, Carter RD, Rivkin SE, Borst JR, Belt RJ, Metch B, Osborne CK (1992) Prognostic significance of progesterone receptor levels in estrogen receptor-positive patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with tamoxifen: results of a prospective Southwest Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 10:1284–1291
Razandi M, Pedram A, Park ST, Levin ER (2003) Proximal events in signaling by plasma membrane estrogen receptors. J Biol Chem 278:2701–2712
Robertson JF, Come SE, Jones SE, Beex L, Kaufmann M, Makris A, Nortier JW, Possinger K, Rutqvist LE (2005) Endocrine treatment options for advanced breast cancer—the role of fulvestrant. Eur J Cancer 41:346–356
Rogatsky I, Trowbridge JM, Garabedian MJ (1999) Potentiation of human estrogen receptor alpha transcriptional activation through phosphorylation of serines 104 and 106 by the cyclin A-CDK2 complex. J Biol Chem 274:22296–22302
Sanchez R, Nguyen D, Rocha W, White JH, Mader S (2002) Diversity in the mechanisms of gene regulation by estrogen receptors. Bioessays 24:244–254
Santen RJ, Song RX, McPherson R, Kumar R, Adam L, Jeng MH, Yue W (2002) The role of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 80:239–256
Schiff R, Fuqua S (2002) The importance of the estrogen receptor in breast cancer. In: Pasqualini J (ed) Breast cancer: prognosis, treatment, and prevention. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 149–186
Schiff R, Massarweh SA, Shou J, Bharwani L, Mohsin SK, Osborne CK (2004) Cross-talk between estrogen receptor and growth factor pathways as a molecular target for overcoming endocrine resistance. Clin Cancer Res 10:S331–S336
Shiau AK, Barstad D, Loria PM, Cheng L, Kushner PJ, Agard DA, Greene GL (1998) The structural basis of estrogen receptor/coactivator recognition and the antagonism of this interaction by tamoxifen. Cell 95:927–937
Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Wakeling AE, Ali S, Weiss H, Schiff R (2004) Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:926–935
Smith IE, Dowsett M (2003) Comparison of anastrozole vs tamoxifen alone and in combination as neoadjuvant treatment of estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) operable breast cancer in postmenopausal women: the IMPACT trial. Breast Cancer Res 82(Suppl 1):S6
Smith CL, Conneely OM, O’Malley BW (1993) Modulation of the ligand-independent activation of the human estrogen receptor by hormone and antihormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:6120–6124
Smith CL, Nawaz Z, O’Malley BW (1997) Coactivator and corepressor regulation of the agonist/antagonist activity of the mixed antiestrogen, 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Mol Endocrinol 11:657–666
Song RX, McPherson RA, Adam L, Bao Y, Shupnik M, Kumar R, Santen RJ (2002) Linkage of rapid estrogen action to MAPK activation by ERalpha-Shc association and Shc pathway activation. Mol Endocrinol 16:116–127
Speirs V (2002) Oestrogen receptor beta in breast cancer: good, bad or still too early to tell? J Pathol 197:143–147
Stoica GE, Franke TF, Wellstein A, Morgan E, Czubayko F, List HJ, Reiter R, Martin MB, Stoica A (2003) Heregulin-beta1 regulates the estrogen receptor-alpha gene expression and activity via the ErbB2/PI 3-K/Akt pathway. Oncogene 22:2073–2087
Sun M, Paciga JE, Feldman RI, Yuan Z, Coppola D, Lu YY, Shelley SA, Nicosia SV, Cheng JQ (2001) Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase (PI3K)/AKT2, activated in breast cancer, regulates and is induced by estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) via interaction between ERalpha and PI3K. Cancer Res 61:5985–5991
Takimoto GS, Graham JD, Jackson TA, Tung L, Powell RL, Horwitz LD, Horwitz KB (1999) Tamoxifen resistant breast cancer: coregulators determine the direction of transcription by antagonist-occupied steroid receptors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 69:45–50
Torres-Arzayus MI, De Mora JF, Yuan J, Vazquez F, Bronson R, Rue M, Sellers WR, Brown M (2004) High tumor incidence and activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in transgenic mice define AIB1 as an oncogene. Cancer Cell 6:263–274
Tovey S, Dunne B, Witton CJ, Forsyth A, Cooke TG, Bartlett JM (2005) Can molecular markers predict when to implement treatment with aromatase inhibitors in invasive breast cancer? Clin Cancer Res 11:4835–4842
Vadlamudi RK, Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Kim Y, Shin J, Sahin A, Kumar R (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of PELP1, a novel human coregulator of estrogen receptor alpha. J Biol Chem 276:38272–38279
Versea L, Rosenzweig M (2003) Hormonal therapy for breast cancer: focus on fulvestrant. Clin J Oncol Nurs 7:307–311
Webb P, Nguyen P, Shinsako J, Anderson C, Feng W, Nguyen MP, Chen D, Huang SM, Subramanian S, McKinerney E, Katzenellenbogen BS, Stallcup MR, Kushner PJ (1998) Estrogen receptor activation function 1 works by binding p160 coactivator proteins. Mol Endocrinol 12:1605–1618
Winer EP, Hudis C, Burstein HJ, Chlebowski RT, Ingle JN, Edge SB, Mamounas EP, Gralow J, Goldstein LJ, Pritchard KI, Braun S, Cobleigh MA, Langer AS, Perotti J, Powles TJ, Whelan TJ, Browman GP (2002) American Society of Clinical Oncology technology assessment on the use of aromatase inhibitors as adjuvant therapy for women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: status report 2002. J Clin Oncol 20:3317–3327
Witters L, Engle L, Lipton A (2002) Restoration of estrogen responsiveness by blocking the HER-2/neu pathway. Oncol Rep 9:1163–1166
Wong CW, McNally C, Nickbarg E, Komm BS, Cheskis BJ (2002) Estrogen receptor-interacting protein that modulates its nongenomic activity-crosstalk with Src/Erk phosphorylation cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14783–14788
Wu RC, Qin J, Hashimoto Y, Wong J, Xu J, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O’Malley BW (2002) Regulation of SRC-3 (pCIP/ACTR/AIB-1/RAC-3/TRAM-1) coactivator activity by I kappa B kinase. Mol Cell Biol 22:3549–3561
Wu RC, Qin J, Yi P, Wong J, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O’Malley BW (2004) Selective phosphorylations of the SRC-3/AIB1 coactivator integrate genomic responses to multiple cellular signaling pathways. Mol Cell 15:937–949
Zhu L, Chow LW, Loo WT, Guan XY, Toi M (2004) Her2/neu expression predicts the response to antiaromatase neoadjuvant therapy in primary breast cancer: subgroup analysis from celecoxib antiaromatase neoadjuvant trial. Clin Cancer Res 10:4639–4644
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a breast cancer Specialized Program of Research Excellence (SPORE) grant P50 CA58183 from the National Cancer Institute and by a research grant from AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schiff, R., Massarweh, S.A., Shou, J. et al. Advanced concepts in estrogen receptor biology and breast cancer endocrine resistance: implicated role of growth factor signaling and estrogen receptor coregulators. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 56 (Suppl 1), 10–20 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-005-0108-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-005-0108-2