Summary
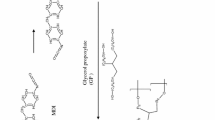
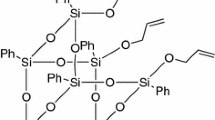
A series of poly(vinylphenol-co-vinylpyrrolidone-co-isobutylstyryl polyhedral oligosilsesquioxane (PVPh-co-PVP-co-POSS) copolymers were prepared by free radical copolymerization of acetoxystyrene, vinylpyrrolidone with POSS (PAS-co-PVP-co-POSS) following by selective removal of the acetyl protective group, and results in significant glass transition temperature increase. The thermal properties and hydrogen bonding of these copolymers were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry and fourier transfer infrared spectroscopy and good correlation between thermal behaviors and infrared spectroscopy results were observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 April 2002 / Revised version: 16 May 2002 / Accepted: 22 May 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Kuo, SW. & Chang, FC. Significant glass transition temperature increase based on polyhedral oligomeric silsequioxane (POSS) copolymer through hydrogen bonding. Polymer Bulletin 48, 469–474 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-002-0061-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-002-0061-8