Summary
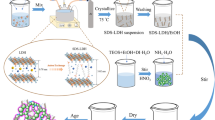
Polyimide/silica hybrid materials were prepared via a novel sol-gel route using silicic acid oligomer (SAO) extracted from water glass. The decomposition temperatures of the hybrid samples were higher than pure polyimide. The transparency of the hybrid films could be maintained at up to 40 wt.-% silica content with the addition of γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) results confirmed the formation and dispersion of nanometer-scale size of inorganic particles within polyimide matrix with APTES. The coefficients of thermal expansion (CTEs) of the hybrid films were lower than pure polyimide and decreased with the increasing content of silica.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhong, W., Du, Q. et al. Novel Polyimide/Silica Nanohybrids from Water Glass. Polymer Bulletin 51, 63–68 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-003-0188-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-003-0188-2