Abstract
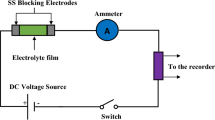
This research is about the preparation of polymer blend electrolytes based on chitosan using solution cast technique. Field emission scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) routes were utilized for studying morphological and structural properties, respectively. Electrical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was engaged for determining the direct current electrical conductivity of the films. The ion association at the highest salt concentration was actually present as confirmed by EIS and FTIR achievements. The sample surface displays the protrude salts at the highest salt concentration. Proton conducting polymer electrolyte with NH4Br as H+ (proton) provider has been used in electric double-layer capacitor (EDLC) applications. The highest conducting sample was used to fabricate EDLC. The transference number measurement indicated that the sample is mostly includes ion charge carriers which are vital for application in electrochemical devices. The linear sweep voltammetry study revealed that the decomposition of the sample takes place above 1.54 V. The fabricated EDLC device was performed capacitive behavior, as it can be seen from the cyclic voltammetry (CV) plot. Since no redox peaks have appeared, it can be concluded that the EDLC did not undergo either oxidation or reduction. The acquired value of specific capacitance (132.5 Fg−1) is considered to be of great interest from the application viewpoints.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orlins S, Guan D (2016) China's toxic informal e-waste recycling: local approaches to a global environmental problem. J Clean Prod 114:71–80
Nyuk CM, Isa MIN (2018) Solid biopolymer electrolytes based on carboxymethyl cellulose for use in coin cell proton batteries. J Sustain Sci Manag 2017:42–48
Liew CW, Ramesh S, Arof AK (2014) Good prospect of ionic liquid based-poly(vinyl alcohol) polymer electrolytes for supercapacitors with excellent electrical, electrochemical and thermal properties. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:2953–2963
Sarwat F, Ahmed N, Aman A, Qader SAU (2013) Optimization of growth conditions for the isolation of dextran producing Leuconostoc spp. from indigenous food sources. Pak J Pharm Sci 26(4):793–797
Barsbay M, Guner A (2007) Miscibility of dextran and poly(ethylene glycol) in solid state: effect of the solvent choice. Carbohydr Polym 69:214–223
Hamsan MH, Shukur MF, Aziz SB, Kadir MFZ (2019) Dextran from leuconostoc mesenteroides doped ammonium salt based green polymer electrolyte. Bull Mater Sci 42:57
Misenan MSM, Isa MIN, Khiar ASA (2018) Electrical and structural studies of polymer electrolyte based on chitosan/methyl cellulose blend doped with BMIMTFSI. Mater Res Express 5:5
Tyagi A, Joshi MC, Shah A, Thakur VK, Gupta RK (2019) Hydrothermally tailored three-dimensional Ni-V layered double hydroxide nanosheets as high-performance hybrid supercapacitor applications. ACS Omega 4:3257–3267
Siwal SS, Zhang Q, Sun C, Thakur VK (2020) Graphitic carbon nitride doped copper–manganese alloy as high–performance electrode material in supercapacitor for energy storage. Nanomaterials 10:2
Siwal SS, Zhang Q, Devi N, Thakur VK (2020) Carbon-based polymer nanocomposite for high-performance energy storage applications. Polymers (Basel) 12:1–30
Hamsan MH, Shukur MF, Kadir MFZ (2017) The effect of NH4NO3 towards the conductivity enhancement and electrical behavior in methyl cellulose-starch blend based ionic conductors. Ionics 23:1137–1154
Lee D-Y, An G-H, Ahn H-J (2017) High-surface-area tofu based activated porous carbon for electrical double-layer capacitors. J Ind Eng Chem 52:121–127
Guo J, Jiang J, Yang B (2018) Low-voltage electric-double-layer MoS2 transistor gated via water solution. Solid State Electron 150:8–15
Andres B, Dahlstrom C, Blomquist N, Norgen M, Olin H (2018) Cellulose binders for electric double-layer capacitor electrodes: the influence of cellulose quality on electrical properties. Mater Des 141:342–349
Yang I, Kim SG, Kwon SH, Lee JH, Kim MS, Jung JC (2016) Pore size-controlled carbon aerogels for EDLC electrodes in organic electrolytes. Curr Appl Phys 16(6):665–672
Tran C, Kalra V (2013) Fabrication of porous carbon nanofibers with adjustable pore sizes as electrodes for supercapacitors. J Power Sources 235:289–296
Zhao XY, Wu Y, Cao JP, Zhuang QQ, Wan X, He S, Wei XY (2018) Preparation and characterization of activated carbons from oxygen-rich lignite for electric double-layer capacitor. Int J Electrochem Sci 13:2800–2816
Xu M, Li D, Yan Y, Guo T, Pang H, Xue H (2017) Porous high specific surface area-activated carbon with co-doping N, S and P for high-performance supercapacitors. RSC Adv 7:43780–43788
Iro ZS, Subramani C, Dash SS (2016) A brief review on electrode materials for supercapacitor. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:10628–10643
Inagaki M, Konno H, Tanaike O (2010) Carbon materials for electrochemical capacitors. J Power Sources 195(24):7880–7903
Zhang D, Zhang X, Chen Y, Yu P, Wang C, Ma Y (2011) Enhanced capacitance and rate capability of graphene/polypyrrole composite as electrode material for supercapacitors. J Power Sources 196(14):5990–5996
Pell WG, Conway BE (2004) Peculiarities and requirements of asymmetric capacitor devices based on combination of capacitor and battery-type electrodes. J Power Sources 136(2):334–345
Eftekhari A (2019) Surface diffusion and adsorption in supercapacitors. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:3692–3701
Eftekhari A (2018) The mechanism of ultrafast supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 6:2866–2876
Prajapati GK, Roshan R, Gupta PN (2010) Effect of plasticizer on ionic transport and dielectric properties of PVA–H3PO4 proton conducting polymeric electrolytes. J Phys Chem Solids 71:1717–1723
Gao H, Lian K (2014) Proton-conducting polymer electrolytes and their applications in solid supercapacitors: a review. R Soc Chem 4:33091–33113
Jonson DA (1982) Some thermodynamic aspects of inorganic chemistry, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge ISBN 0521242045
Buraidah MH, Arof AK (2011) Characterization of chitosan/PVA blended electrolyte doped with NH4I. J Non-Cryst Solids 357:3261–3266
Kadir MFZ, Hamsan MH (2018) Green electrolytes based on dextran-chitosan blend and the effect of NH4SCN as proton provider on the electrical response studies. Ionics 24(8):2379–2398
Aziz SB, Hamsan MH, Karim WO, Kadir MFZ, Brza MA, Abdullah OGh (2019) High proton conducting polymer blend electrolytes based on chitosan: dextran with constant specific capacitance and energy density. Biomolecules 9(7):267
Shukla R, Shukla S, Bivolarski V, Iliev I, Ivanova I, Goyal A (2011) Structural characterization of insoluble dextran produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides NRRL B-1149 in the presence of maltose. Food Technol Biotechnol 49(3):291–296
Vettori MHPB, Franchetti SMM, Contiero J (2012) Structural characterization of a new dextran with a low degree of branching produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides FT045B dextransucrase. Carbohyd Polym 88:1440–1444
Dumitrascu M, Meltzer V, Sima E, Virgolici M, Albu MG, Ficai A, Moise V, Minea R, Vancea C, Scarisoreanu A, Scarlat F (2011) Characterization of electron beam irradiated collagen-polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and collagen-dextran (DEX) blends. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 6(4):1793–1803
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ (2013) Electrical conduction mechanism in solid polymer electrolytes: new concepts to arrhenius equation. J Soft Matter 2013:323868
Nikoli GS, Caki M, Mitic Z, Ili B, Premovic P (2009) Attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy of copper(II) complexes with reduced dextran derivatives. Russ J Phys Chem A 83:1520–1525
Wei D, Sun W, Qian W, Ye Y, Ma X (2009) The synthesis of chitosan-based silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. Carbohyd Res 344(17):2375–2382
Mitic ŽO, Cakic M, Nikolic G (2010) Fourier-Transform IR spectroscopic investigations of Cobalt(II)–dextran complexes by using D2O isotopic exchange. Spectroscopy 24:269–275
Hamsan MH, Aziz SB, Shukur MF, Kadir MFZ (2019) Protonic cell performance employing electrolytes based on plasticized methylcellulose–potato starch–NH4NO3. Ionics 25:559–572
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ, Kadir MFZ (2015) Innovative method to avoid the reduction of silver ions to silver nanoparticles in silver ion conducting based polymer electrolytes. Phys Scr 90:035808
Hana CC, Shia W, Jin J (2013) Morphology and crystallization of crystalline/amorphous polymer blends. In: Palsule S (ed) Encyclopedia of polymers and composites. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–19
Aziz SB, Abdullah RM, Kadir MFZ, Ahmed HM (2019) Non suitability of silver ion conducting polymer electrolytes based on chitosan mediated by barium titanate (BaTiO3) for electrochemical device applications. Electrochim Acta 296:494–507
Aziz SB, Abdullah OGh, Rasheed MA, Ahmed HM (2017) Effect of high salt concentration (HSC) on structural, morphological, and electrical characteristics of chitosan based solid polymer electrolytes. Polymers 9(6):187
Shukur MF, Kadir MFZ (2015) Hydrogen ion conducting starch–chitosan blend based electrolyte for application in electrochemical devices. Electrochim Acta 158:152–165
Aziz SB, Kadir MFZ, Abidin ZHZ (2016) Structural, morphological and electrochemical impedance study of CS:LiTf based solid polymer electrolyte: reformulated Arrhenius equation for ion transport study. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:9228–9244
Mahato DK, Dutta A, Sinha TP (2010) Impedance spectroscopy analysis of double perovskite Ho2NiTiO6. J Mater Sci 45:6757–6762
Aziz SB, Woo TJ, Kadir MFZ, Ahmed HM (2018) A conceptual review on polymer electrolytes and ion transport models. J Science: Adv Mater Devices 3:1–17
Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Samantaray BK (2008) Studies of structural, thermal and electrical behavior of polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. eXPRESS Polym Lett 2(9):630–638
Qian X, Gu N, Cheng Z, Yang X, Wang E, Dong S (2001) Impedance study of (PEO)10LiClO4–Al2O3 composite polymer electrolyte with blocking electrodes. Electrochim Acta 46:1829–1836
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ (2015) Ion-transport study in nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes based on chitosan: electrical and dielectric analysis. J Appl Polym Sci 132:41774
Yap YL, You AH, Teo LL, Hanapei H (2013) Inorganic filler sizes effect on ionic conductivity in polyethylene oxide (PEO) composite polymer electrolyte. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:2154–2163
Jacob MME, Prabaharan SRS, Radhakrishna S (1997) Effect of PEO addition on the electrolytic and thermal properties of PVDF-LiClO4 polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion 104:267–276
Fonseca CP, Cavalcante F Jr, Amaral FA, Souza CAZ, Neves S (2007) Thermal and conduction properties of a PCL-biodegradable gel polymer electrolyte with LiClO4, LiF3CSO3, and LiBF4 Salts. Int J Electrochem Sci 2:52–63
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ, Arof AK (2010) Influence of silver ion reduction on electrical modulus parameters of solid polymer electrolyte based on chitosan-silver triflate electrolyte membrane. eXPRESS Polym Lett 4(5):300–310
Aziz SB, Abdullah RM (2018) Crystalline and amorphous phase identification from the tanδ relaxation peaks and impedance plots in polymer blend electrolytes based on [CS:AgNt]x:PEO(x–1)(10 ≤ x ≤ 50). Electrochim Acta 285:30–46
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ, Arof AK (2010) Effect of silver nanoparticles on the DC conductivity in chitosan–silver triflate polymer electrolyte. Phys B 405(21):4429–4433
Marf AS, Abdullah RM, Aziz SB (2020) Structural, morphological, electrical and electrochemical properties of PVA: CS-based proton-conducting polymer blend electrolytes. Membranes 10(4):71
Samsudin AS, Kuan ECH, Isa MIN (2011) Investigation of the potential of proton-conducting biopolymer electrolytes based methyl cellulose–glycolic acid. Int J Polym Anal Charact 16:477–485
Rani MSA, Ahmad A, Mohamed NS (2017) Influence of nano-sized fumed silica on physicochemical and electrochemical properties of cellulose derivatives-ionic liquid biopolymer electrolytes. Ionics 24:807–814
Reddy MJ, Chu PP (2002) Effect of Mg2+ on PEO morphology and conductivity. Solid State Ion 149:115
Vijaya N, Selvasekarapandian S, Malathi J, Iwai Y, Nithya H, Kawamura J (2013) NMR study on PVP-NH4Cl based-proton conducting polymer electrolyte. Indian J Appl Res 3:506–510
Ng LS, Mohamad AA (2008) Effect of temperature on the performance of proton batteries based on chitosan–NH4NO3–EC membrane. J Membr Sci 325:653–657
Kadir MFZ, Arof AK (2013) Application of PVA–chitosan blend polymer electrolyte membrane in electrical double layer capacitor. Mater Res Innov 15:217–220
Zhu W, Ou X, Lu Z, Chen K, Ling Y, Zhang H (2019) Enhanced performance of hierarchical CuS clusters applying TRGO as conductive carrier for supercapacitors. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30(6):5760–5770
Aziz SB, Brza MA, Mishra K, Hamsan MH, Karim WO, Abdullah RM, Kadir MFZ, Abdulwahid RT (2020) Fabrication of high performance energy storage EDLC device from proton conducting methylcellulose: dextran polymer blend electrolytes. J Mater Res Technol 9:1137–1150
Aziz SB, Brza MA, Hamsan MH, Kadir MFZ, Muzakir SK, Abdulwahid RT (2020) Effect of ohmic-drop on electrochemical performance of EDLC fabricated from PVA:dextran:NH4I based polymer blend electrolytes. J Mater Res Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.110
Jackel N, Rodner M, Schreiber A, Jeongwook J, Zeiger M, Aslan M, Weingarth D, Presser V (2016) Anomalous or regular capacitance? The influence of pore size dispersity on double-layer formation. J Power Sources 326:660–671
Fattah NFA, Ng HM, Mahipal YK, Numan A, Ramesh S, Ramesh K (2016) An approach to solid-state electrical double layer capacitors fabricated with graphene oxide-doped. Ionic liquid-based solid copolymer electrolytes. Materials 9:450
Pandey GP, Kumar Y, Hashmi SA (2011) Ionic liquid incorporated PEO based polymer electrolyte for electrical double layer capacitors: a comparative study with lithium and magnesium systems. Solid State Ion 190:93–98
Costentin C, Porter TR, Saveant JM (2017) How do pseudocapacitors store energy? Theoretical analysis and experimental illustration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:8649–8658
Woo HJ, Liew C, Majid SR, Arof AK (2014) Poly (ε-caprolactone)-based polymer electrolyte for electrical double-layer capacitors. High Perform Polym 26:637–640
Yusof YM, Majid NA, Kasmani RM, Illias HA, Kadir MFZ (2014) The effect of plasticization on conductivity and other properties of starch/chitosan blend biopolymer electrolyte incorporated with ammonium iodide. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 1:73–88
Liew CW, Ramesh S (2015) Electrical, structural, thermal and electrochemical properties of corn starch-based biopolymer electrolytes. Carbohydr Polym 124:222–228
Hashim MA, Yatim NM, Mahmud NCA, Sazali N, Hamdan D, Yahya MA, Ngah CW, Suhaimi S (2018) Hybrid solid polymer electrolyte from diapers as separator for electrochemical double layer capacitor (EDLC). In AIP conference proceedings, vol 1972, p 020001
Liew CW, Ramesh S, Arof AK (2016) Enhanced capacitance of EDLCs (electrical double layer capacitors) based on ionic liquid-added polymer electrolytes. Energy 109:546–556
Sudhakar YN, Selvakumar M, Bhat D (2015) Lithium salts doped biodegradable gel polymer electrolytes for supercapacitor application. J Mater Environ Sci 6:1218–1227
Stepniak I, Galinski M, Nowacki K, Wysokowski M, Jakubowska P, Jesionowski T (2016) A novel chitosan/sponge chitin origin material as a membrane for supercapacitors—preparation and characterization. RSC Adv 6:4007
Stoller MD, Ruoff R (2010) Review of best practice methods for determining an electrode material's performance for ultracapacitors. Energy Environ Sci 3:9
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support for this study from Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research-Kurdish National Research Council (KNRC), KRG/Iraq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aziz, S.B., Brza, M.A., Hamsan, H.M. et al. Electrochemical characteristics of solid state double-layer capacitor constructed from proton conducting chitosan-based polymer blend electrolytes. Polym. Bull. 78, 3149–3167 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03278-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03278-1