Abstract.
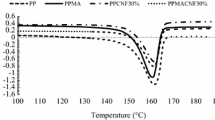
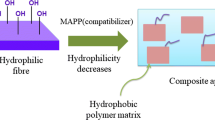
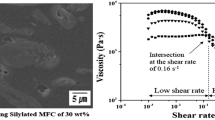
The thermal and viscoelastic properties of polypropylene (PP)/cellulose as well as PP/Xylan composites were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and dynamic mechanical thermoanalysis (DMTA). Morphological aspects were available by using polarizing light microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Three types of fillers were incorporated in PP: xylan fillers (XL), cellulose microfibers (CM) and short fibers of spun cellulose (CS). The compatibilizer maleic anhydride modified PP (MAPP) was added to the composites. The crystallization temperature and crystallinity of PP apparently increased in the presence of all fiber types. The cellulose fiber surfaces act as nucleating agents for PP, resulting in the formation of transcrystalline regions around the fibers. The DMTA spectra of PP/filler composites revealed a significant increase in the stiffness and a remarkable decrease of the damping values. This effect was stronger for PP/CS than for the other composites. The results verify that improved compatibility and interfacial adhesion between fiber and matrix markedly contribute to an improvement of the mechanical properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 October 1997/Revised version: 11 December 1997/Accepted: 12 December 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amash, A., Zugenmaier, P. Study on cellulose and xylan filled polypropylene composites. Polymer Bulletin 40, 251–258 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890050249
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002890050249