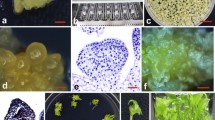
Abstract
Genetically transformed plants of Cymbidium were regenerated after cocultivating protocorm-like bodies (PLB) with Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA101 (pIG121Hm) that harbored genes for β-glucuronidase (gus), hygromycin phosphotransferase (hpt) and neomycin phosphotransferase II (nptII). PLB of three genotypes maintained in liquid new Dogashima medium (NDM), were subjected to transformation experiments. The PLB inoculated with Agrobacterium produced secondary PLB, 4 weeks after transfer onto 2.5 g L−1 gellan gum-solidified NDM containing 10 g L−1 sucrose, 20 mg L−1 hygromycin and 40 mg L−1 meropenem. Transformation efficiency was affected by genotype and the presence of acetosyringone during cocultivation. The highest transformation efficiency was obtained when PLB from the genotype L4 were infected and cocultivated with Agrobacterium on medium containing 100 μM acetosyringone. Transformation of the hygromycin-resistant plantlets regenerated from different sites of inoculated PLB was confirmed by histochemical GUS assay, PCR analysis and Southern blot hybridization.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
Acetosyringone
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- Hm:
-
Hygromycin
- Km:
-
Kanamycin
- ND:
-
New Dogashima
- PLB:
-
Protocorm-like body
Reference
Anzai H, Ishii Y, Shichinohe M, Katsumata K, Nojiri C, Morikawa H, Tanaka M (1996) Transformation of Phalaenopsis by particle bombardment. Plant Tissue Cult Lett 13:265–271
Ashby AM, Watson MD, Shaw CH (1987) A Ti-plasmid determined function is responsible for chemotaxis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens towards the plant wound product acetosyringone. FEMS Microbiol Lett 41:189–192
Belarmino MM, Mii M (2000) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of a Phalaenopsis orchid. Plant Cell Rep 19:435–442
Chai ML, Xu CJ, Senthil KK, Kim JY, Kim DH (2002) Stable transformation of protocorm-like bodies in Phalaenopsis orchid mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Sci Hortic 96:213–224
Chan YL, Lin KH, Sanjaya, Liao LJ, Chen WH, Chan MT (2005) Gene stacking in Phalaenopsis orchid enhances dual tolerance to pathogen attack. Transgenic Res 14:279–288
Chen L, Hatano T, Niimi Y (2002) High efficiency of Agrobacterium-mediated rhizome transformation in Cymbidium. Lindleyana 17:130–134
Chia TF, Hew CS, Loh CS, Lee YK (1988) Carbon/nitrogen ratio and greening and protocorm formation in orchid callus tissues. HortScience 23:599–601
Chia TF, Chan YS, Chua NH (1994) The firefly luciferase gene as a non-invasive reporter for Dendrobium transformation. Plant J 6:441–446
Drake PMW, John A, Power JB, Davey MR (1997) Expression of the gusA gene in embryogenic cell lines of Sitka spruce following Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. J Exp Bot 48:151–155
Eady CC, Lister CE (1998) A comparison of four selective agents for use with Allium cepa L. immature embryos and immature embryo-derived cultures. Plant Cell Rep 18:117–121
Escudero J, Hohn B (1997) Transfer and integration of T-DNA without cell injury in the host plant. Plant Cell 9:2135–2142
Hauptmann RM, Vasil V, Ozias-Akins P, Tabaeizadeh Z, Rogers SG, Fraley RT, Horsch RB, Vasil IK (1988) Evaluation of selectable markers for obtaining stable transformants in the Gramineae. Plant Physiol 86:602–606
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–82
Hood EE, Helmer GL, Fraley RT, Chilton MD (1986) The hypervirulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens A281 is encoded in a region of pTiBo542 outside of T DNA. J Bacteriol 168:1291–1304
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Knapp JE, Kausch AP, Chandlee JM (2000) Transformation of three genera of orchid using the bar gene as a selectable marker. Plant Cell Rep 19:893–898
Kuehnle AR, Sugii N (1992) Transformation of Dendrobium orchid using particle bombardment of protocorms. Plant Cell Rep 11:484–488
Liau CH, You SJ, Prasad V, Hsiao HH, Lu JC, Yang NS, Chan MT (2003a) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of an Oncidium orchid. Plant Cell Rep 21:993–998
Liau CH, Lu JC, Prasad V, Hsiao HH, You SJ, Lee JT, Yang NS, Huang HE, Feng TY, Chen WH, Chan MT (2003b) The sweet pepper ferredoxin-like protein (pflp) conferred resistance against soft rot disease in Oncidium orchid. Transgenic Res 12:329–336
Men S, Ming X, Liu R, Wei C, Li Y (2003) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of a Dendrobium orchid. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 75:63–71
Mishiba K, Chin DP, Mii M (2005) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Phalaenopsis by targeting protocorms at an early stage after germination. Plant Cell Rep 24:297–303
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nan GL, Tang CS, Kuehnle AR, Kado CI (1997) Dendrobium orchid contain an inducer of Agrobacterium virulence genes. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 51:391–399
Ogawa Y, Mii M (2004) Screening for highly active β-lactam antibiotics against Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Arch Microbiol 181:331–336
Ohta S, Mita S, Hattori T, Nakamura K (1990) Construction and expression in tobacco of a β-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene containing an intron within the coding sequence. Plant Cell Physiol 31:805–813
Sjahril R, Chin DP, Khan RS, Yamamura S, Nakamura I, Amemiya Y, Mii M (2006) Transgenic Phalaenopsis plants with resistance to Erwinia carotovora produced by introducing wasabi defensin gene using Agrobacterium method. Plant Biotechnol 23:191–194
Sjahril R, Mii M (2006) High-efficiency Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Phalaenopsis using meropenem, a novel antibiotic to eliminate Agrobacterium. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 81:458–464
Song GQ, Sink KC (2004) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.). Plant Cell Rep 23:475–484
Tee CS, Maziah M, Tan CS, Abdullah MP (2003) Evaluation of different promoters driving the GFP reporter gene and selected target tissues for particle bombardment of Dendrobium Sonia 17. Plant Cell Rep 21:452–458
Tokuhara K, Mii M (1993) Micropropagation of Phalaenopsis and Doritaenopsis by culturing shoot tips of flower stalk buds. Plant Cell Rep 13:7–11
Tokuhara K, Mii M (2003) Highly-efficient somatic embryogenesis from cell suspension cultures of phalaenopsis orchids by adjusting carbohydrate sources. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 39:635–639
Yang J, Lee H, Shin DH, Oh SK, Seon JH, Paek KY, Han K (1999) Genetic transformation of Cymbidium orchid by particle bombardment. Plant Cell Rep 18:978–984
Yu H, Yang SH, Goh CJ (2001) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of a Dendrobium orchid with the 1 knox gene DOH1. Plant Cell Rep 20:301–305
Yu ZH, Chen MY, Nie L, Lu HF, Ming XT, Zheng HH, Qu LJ, Chen ZL (1999) Recovery of transgenic orchid plants with hygromycin selection by particle bombardment to protocorms. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 58:87–92
Acknowledgements
We Thank Hitaka Orchid Co., Ltd. for providing Cymbidium seeds and Mukoyama Orchids Co., Ltd. for providing PLB of RY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. K. Kamo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chin, D.P., Mishiba, Ki. & Mii, M. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of protocorm-like bodies in Cymbidium . Plant Cell Rep 26, 735–743 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0284-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0284-5