Abstract
Objectives
Deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flaps have become the state of the art in breast reconstruction. We compared the diagnostic performance of multidetector computed tomography (CTA) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) in DIEP flap planning.
Methods
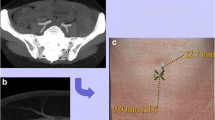
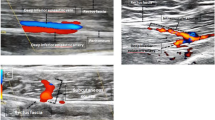
Twenty-three women (mean age 48.0 years, range 26–72 years) underwent preoperative blinded evaluation using 64-slice CTA and 1.5-T MRA. Perforator identification, measurement of their calibre, intramuscular course (IMC), assessment of direct venous connections (DVC) with main superficial veins, superficial venous communications (SVC) between the right and left hemi-abdomen and deep inferior epigastric artery (DIEA) branching type were performed. Surgery was carried out by the same team. Intraoperative findings were the standard of reference.
Results
Accuracy in identifying dominant perforators was 91.3 % for both techniques and mean error in calibre measurement 1.18 ± 0.35 mm for CTA and 1.63 ± 0.39 mm for MRA. Accuracy in assessing perforator IMCs was 97.1 % for CTA and 88.4 % for MRA, DVC 94.4 % for both techniques, SVC 91.3 % as well, and DIEA branching type 100 % for CTA and 91.3 % for MRA. Image acquisition and interpretation time was 21 ± 3 min for CTA (35 ± 5 min for MRA).
Conclusions
In a strategy to optimise DIEP flap planning avoiding radiation exposure, MRA can be proposed alternatively to CTA.
Key points
• Identification of deep inferior epigastric perforators (DIEP) is important before breast reconstruction.
• Both CT and MR angiography are accurate in identifying DIEA perforator branches.
• CTA and MRA are equivalent in demonstrating perforator-venous connections.
• MRA can be proposed as an alternative to CTA in DIEP planning.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DIEP:
-
Deep inferior epigastric perforator
- DIEA:
-
Deep inferior epigastric artery
- CTA:
-
Computed tomography angiography
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- IMC:
-
Intramuscular course
- DVC:
-
Direct perforator-venous connections
- SVC:
-
Superficial right-left venous communications
References
Munhoz AM, Arruda E, Montag E et al (2007) Immediate skin-sparing mastectomy reconstruction with deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flap: technical aspects and outcome. Breast J 13:470–478
Tønseth KA, Hokland BM, Tindholdt TT, Abyholm FE, Stavem K (2008) Quality of life, patient satisfaction and cosmetic outcome after breast reconstruction using DIEP flap or expandable breast implant. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:1188–1194
De Greef C (2005) Breast reconstruction by DIEP free flap: about 100 cases. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 50:56–61
Schaverien M, Saint-Cyr M, Arbique G, Brown SA (2008) Arterial and venous anatomies of the deep inferior epigastric perforator and superficial inferior epigastric artery flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:1909–1919
Patel SA, Keller A (2008) A theoretical model describing arterial flow in the DIEP flap related to number and size of perforator vessels. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:1316–1320
Wong C, Saint-Cyr M, Mojallal A et al (2010) Perforasomes of the DIEP flap: vascular anatomy of the lateral versus medial row perforators and clinical implications. Plast Reconstr Surg 125:772–782
Rozen WM, Garcia-Tutor E, Alonso-Burgos A et al (2010) Planning and optimising DIEP flaps with virtual surgery: the Navarra experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:289–297
Rozen WM, Anavekar NS, Ashton MW et al (2008) Does the preoperative imaging of perforators with CT angiography improve operative outcomes in breast reconstruction? Microsurgery 28:516–523
Giunta RE, Geisweid A, Feller AM (2000) The value of preoperative Doppler sonography for planning free perforator flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:2381–2386
Tsukino A, Kurachi K, Inamiya T, Tanigaki T (2004) Preoperative color Doppler assessment in planning of anterolateral thigh flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:241–246
Phillips TJ, Stella DL, Rozen WM, Ashton M, Taylor GI (2008) Abdominal wall CT angiography: a detailed account of a newly established preoperative imaging technique. Radiology 249:32–44
Rozen WM, Stella DL, Bowden J, Taylor GI, Ashton MW (2009) Advances in the pre-operative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps: magnetic resonance angiography. Microsurgery 29:119–123
Blondeel PN, Beyens G, Verhaeghe R et al (1998) Doppler flowmetry in the planning of perforator flaps. Br J Plast Surg 51:202–209
Rozen WM, Phillips TJ, Ashton MW, Stella DL, Gibson RN, Taylor GI (2008) Preoperative imaging for DIEA perforator flaps: a comparative study of computed tomographic angiography and Doppler ultrasound. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:9–16
Rozen WM, Ashton MW, Stella DL, Phillips TJ, Taylor GI (2008) The accuracy of CT angiography for mapping the perforators of the DIEA: a cadaveric study. Plast Reconstr Surg 122:363–369
Masia J, Clavero JA, Larrañaga JR, Alomar X, Pons G, Serret P (2006) Multidetector-row computed tomography in the planning of abdominal perforator flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:594–599
Fukaya E, Grossman RF, Saloner D, Leon P, Nozaki M, Mathes SJ (2007) Magnetic resonance angiography for free fibula flap transfer. J Reconstr Microsurg 23:205–211
Rozen WM, Ashton MW, Grinsell D (2010) The branching pattern of the deep inferior epigastric artery revisited in-vivo: a new classification based on CT angiography. Clin Anat 23:87–92
Granzow JW, Levine JL, Chiu ES, Allen RJ (2006) Breast reconstruction using perforator flaps. J Surg Oncol 94:441–454
Rozen WM, Palmer KP, Suami H et al (2008) The DIEA branching pattern and its relationship to perforators: the importance of preoperative computed tomography for DIEA perforator flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:367–373
Cina A, Salgarello M, Barone-Adesi L, Rinaldi P, Bonomo L (2010) Planning breast reconstruction with deep inferior epigastric artery perforating vessels: multidetector CT angiography versus color Doppler US. Radiology 255:979–987
De Frene B, Van Landuyt K, Hamdi M et al (2006) Free DIEAP and SGAP flap breast reconstruction after abdominal/gluteal liposuction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:1031–1036
Greenspun D, Vasile J, Levine JL et al (2010) Anatomic imaging of abdominal perforator flaps without ionizing radiation: seeing is believing with magnetic resonance imaging angiography. J Reconstr Microsurg 26:37–44
Smit JM, Dimopoulou A, Liss AG et al (2009) Preoperative CT angiography reduces surgery time in perforator flap reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62:1112–1117
Rozen WM, Ashton MW, Grinsell D et al (2008) Establishing the case for CT angiography in the preoperative imaging of abdominal wall perforators. Microsurgery 28:306–313
Blondeel PN, Arnstein M, Verstraete K (2000) Venous congestion and blood flow in free transverse rectus abdominus myocutaneous and deep inferior epigastric perforator flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:1295–1299
Schaverien M, Ludman C, Neil-Dwyer J, Perks GB et al (2011) Contrast-Enhanced magnetic resonance angiography for preoperative imaging in DIEP flap breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 128:56–62
Alonso-Burgos A, García-Tutor E, Bastarrika G, Cano D, Martínez-Cuesta A, Pina LJ (2006) Preoperative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap reconstruction with multislice-CT angiography: imaging findings and initial experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:585–593
Chernyak V, Rozenblit AM, Greenspun DT et al (2009) Breast reconstruction with deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap: 3.0-T gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging for preoperative localization of abdominal wall perforators. Radiology 250:417–424
Gacto-Sánchez P, Sicilia-Castro D, Gómez-Cía T et al (2010) Computed tomographic angiography with VirSSPA three-dimensional software for perforator navigation improves perioperative outcomes in DIEP flap breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 125:24–31
Newman TM, Vasile J, Levine JL et al (2010) Perforator flap magnetic resonance angiography for reconstructive breast surgery: a review of 25 deep inferior epigastric and gluteal perforator artery flap patients. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:1176–1184
Alonso-Burgos A, García-Tutor E, Bastarrika G, Benito A, Domínguez PD, Zubieta JL (2010) Preoperative planning of DIEP and SGAP flaps: preliminary experience with magnetic resonance angiography using 3-Tesla equipment and blood-pool contrast medium. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:298–304
Katayama H, Yamaguchi K, Kozuca T et al (1990) Adverse reactions to ionic and nonionic contrast media. Radiology 175:621–628
Dillman JR, Ellis JH, Cohan RH et al (2007) Frequency and severity of acute allergic-like reactions to gadolinium-containing iv contrast media in children and adults. Am J Roentgenol 189:1533–1538
Cowper SE (2001-2007) Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy [NFD/NSF Website]. Available via http://www.icnfdr.org. Accessed 7 August 2008
Scheinfeld NS, Cowper SE (2008) Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy. Available via http://www.emedicine.com/derm/topic934.htm. Accessed 7 August 2008
Lauffer RB, Parmelee DJ, Dunham SU et al (1998) MS-325: albumin-targeted contrast agent for MR angiography. Radiology 207:529–538
Ersoy H, Jacobs P, Kent CK, Prince MR (2004) Blood pool MR angiography of aortic stent-graft endoleak. AJR Am J Roentgenol 182:1181–1186
Zou Z, Lee HK, Levine JL et al (2012) Gadofosveset trisodium-enhanced abdominal perforator MRA. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:711–716
Klessen C, Hein PA, Huppertz A et al (2007) First-pass whole-body magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) using the blood-pool contrast medium gadofosveset trisodium: comparison to gadopentetate dimeglumine. Invest Radiol 42:659–664
Hadizadeh DR, Gieseke J, Lohmaier SH et al (2008) Peripheral MR angiography with blood pool contrast agent: prospective intraindividual comparative study of high-spatial-resolution steady-state MR angiography versus standard-resolution first-pass MR angiography and DSA. Radiology 249:701–711
Giovagnoni A, Catalano C (2007) Application of blood-pool agents in visualization of peripheral vessels. Eur Radiol 17:18–23
Zou Z, Kate Lee H, Levine JL et al (2012) Gadofosveset trisodium-enhanced abdominal perforator MRA. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:711–716
Wedeen VJ, Meuli RA, Edelman RR et al (1985) Projective imaging of pulsatile flow with magnetic resonance. Science 230:946–948
Miyazaki M, Takai H, Sugiura S et al (2003) Peripheral MR angiography: separation of arteries from veins with flow-spoiled gradient pulses in electrocardiographically-triggered three-dimensional half-Fourier fast spin-echo imaging. Radiology 227:890–896
Hoey ET, Ganeshan A, Puni R, Henderson J, Crowe PM (2010) Fresh blood imaging of the peripheral vasculature: an emerging unenhanced MR technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:1444–1448
Masia J, Navarro C, Clavero JA et al (2001) Noncontrast magnetic resonance imaging for preoperative perforator mapping. Clin Plast Surg 38:253–261
Masia J, Kosutic D, Cervelli D et al (2010) In search of the ideal method in perforator mapping: noncontrast magnetic resonance imaging. J Reconstr Microsurg 26:29–35
Vasile JV, Newman TM, Prince MR et al (2011) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography. Clin Plast Surg 38:263–275
Schaverien MV, Ludman CN, Neil-Dwyer J et al (2011) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography for preoperative imaging of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps: advantages and disadvantages compared with computed tomography angiography. A United Kingdom perspective. Ann Plast Surg 67:671–674
Mathes DW, Neligan PC (2010) Current techniques in preoperative imaging for abdomen-based perforator flap microsurgical breast reconstruction. J Reconstr Microsurg 26:3–10
Mathes DW, Neligan PC (2010) Preoperative imaging techniques for perforator selection in abdomen-based microsurgical breast reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 37:581–591
Kuekrek H, Müller D, Paepke S, Dobritz M, Machens HG, Giunta RE (2011) Preoperative CT angiography for planning free perforator flaps in breast reconstruction. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 43:88–94
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cina, A., Barone-Adesi, L., Rinaldi, P. et al. Planning deep inferior epigastric perforator flaps for breast reconstruction: a comparison between multidetector computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography. Eur Radiol 23, 2333–2343 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2834-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-013-2834-x