Abstract
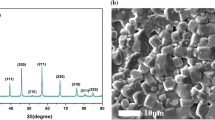
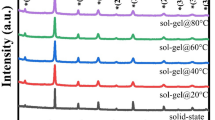
The effect of a dc bias field on the diffuse phase transition and nonlinear dielectric properties of sol-gel derived Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 (BZT) ceramics are investigated. Diffuse phase transitions were observed in BZT ceramics and the Curie–Weiss exponent (CWE) was γ∼2.0. The dielectric constant versus temperature characteristics and the γ in the modified Curie–Weiss law, ε −1=ε −1 m [1+(T−T m )γ/C1](1≤γ≤2), as a function of the dc bias field was obtained for BZT ceramics. The results indicated that γ is a function of dc bias field, and the γ value decreased from 2.04 to 1.73 with dc bias field increasing from 0 to 20 kV/cm. The dielectric constant decreases with increasing dc bias field, indicating a field-induced phase transition. The dc bias field has a strong effect on the position of the dielectric peak and affects the magnitude of the dielectric properties over a rather wide temperature range. The peak temperature of the dielectric loss does not coincide with the dielectric peak and an obvious minimum value for the dielectric loss at the temperature of the dielectric peaks is observed. At room temperature, 300 K, the high tunability (K=80%), the low loss tangent (≈0.01) and the large FOM (74), clearly imply that these ceramics are promising materials for tunable capacitor-device applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Hennings, A. Schnell, G. Simon, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 65, 539 (1982)
S. Hoffmann, R.W. Waser, Integr. Ferroelectr. 17, 141 (1997)
P.W. Rehrig, S.E. Park, S. Trolier-MsKinstry, G.L. Messing, B. Jones, T.R. Shrout, J. Appl. Phys. 86, 1657 (1999)
Z. Yu, R. Guo, A.S. Bhalla, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 410 (2000)
Y. Zhi, A. Chen, R. Guo, A.S. Bhalla, J. Appl. Phys. 92, 2655 (2002)
Y. Zhi, A. Chen, R. Guo, A.S. Bhalla, Mater. Lett. 61, 326 (2007)
U. Weber, G. Greuel, U. Boettger, S. Weber, D. Hennings, R. Waser, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 759 (2001)
S.M. Mukhopadhayay, T.C.S. Chen, J. Mater. Res. 10, 1502 (1995)
S. Hoffmann, R. Waser, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19, 1339 (1999)
X.G. Tang, K.H. Chew, H.L.W. Chan, Acta Mater. 52, 5177 (2004)
S. Halder, T. Schneller, U. Böttger, R. Waser, Appl. Phys. A 81, 25 (2005)
A.A. Bokov, M. Maglione, Z.G. Ye, J. Phys., Condens. Matter 19, 092001 (2007)
N. Sawangwan, J. Barrel, K. MacKenzie, T. Tunkasiri, Appl. Phys. A 90, 723 (2008)
W.S. Choi, B.S. Jang, D.G. Lim, J. Yi, B. Hong, J. Cryst. Growth 237–239, 438 (2002)
A. Dixit, S.B. Majumder, R.S. Katiyar, A.S. Bhalla, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 2679 (2003)
X.G. Tang, H.L.W. Chan, A.L. Ding, Thin Solid Films 460, 227 (2004)
S. Halder, T. Schneller, U. Böttger, R. Waser, Appl. Phys. A 81, 25 (2005)
X.G. Tang, X.X. Wang, K.H. Wong, H.L.W. Chan, Appl. Phys. A 81, 1253 (2005)
S.K. Rout, T. Badapanda, E. Sinha, S. Panigrahi, P.K. Barhai, T.P. Sinha, Appl. Phys. A 91, 101 (2008)
W.J. Merz, Phys. Rev. 91, 513 (1953)
K. Uchino, S. Nomura, Ferroelectr. Lett. Sect. 44, 55 (1982)
D. Viehland, M. Wuttig, L.E. Cross, Ferroelectrics 120, 71 (1991)
B.E. Vugmeister, M.D. Glinichuk, Rev. Mod. Phys. 62, 993 (1990)
K.M. Johnson, J. Appl. Phys. 33, 2826 (1962)
M.E. Lines, A.M. Glass, Principle and Application of Ferroelectrics and Related Materials (Oxford University Press, New York, 1977)
K.L. Bye, P.W. Whips, E.T. Keve, Ferroelectrics 4, 253 (1972)
X.X. Xi, H.C. Li, W. Si, A.A. Sirenko, I.A. Akimov, J.R. Fox, A.M. Clark, J. Hao, J. Electroceram. 4, 393 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X.G., Liu, Q.X., Wang, J. et al. Electric-field dependence of dielectric properties of sol-gel derived Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 96, 945–952 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-009-5103-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-009-5103-8