Abstract
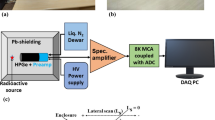
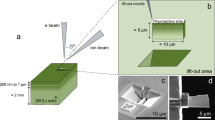
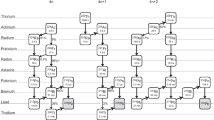
An element analysis method, coincidence Doppler broadening spectroscopy of slow positron annihilation, was employed to detect helium in ion-irradiated Fe9Cr alloys. Spectra with higher peak to background ratio were recorded using a two-HPGe detector coincidence measuring system. It means that information in the high-momentum area of the spectra can be used to identify helium in metals. This identification is not entirely dependent on the helium concentration in the specimens, but is related to the structure and microscopic arrangement of atoms surrounding the positron annihilation site. The results of Doppler broadening spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy show that vacancies and dislocations were formed in ion-irradiated specimens. Thermal helium desorption spectrometry was performed to obtain the types of He traps.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.K. Mansur, W.A. Coghlan, Mechanisms of helium interaction with radiation effects in metals and alloys: a review. J. Nucl. Mater. 119(1), 1–25 (1983)
K. Niwase, T. Ezawa, T. Tanabe, Dislocation loops and their depth profiles in He+ and D+ ion irradiated nickel. J. Nucl. Mater. 203(1), 56–66 (1993)
K. Arakawa, R. Imamura, K. Ohota, Evolution of point defect clusters in pure iron under low-energy He+ irradiation. J. Appl. Phys 89(9), 4752–4757 (2001)
T. Zhu, X.Z. Cao, S.X. Jin, J.P. Wu, Helium retention and thermal desorption from defects in Fe9Cr binary alloys. J. Nucl. Mater. 466, 522–525 (2015)
R.S. Blewer, Depth distribution of implanted helium and other low-z elements in metal films using proton backscattering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 23, 593–595 (1973)
T. Zhu, S. Jin, L. Guo, Y. Hu, E. Lu, J. Wu, B. Wang, L. Wei, X. Cao, Helium/hydrogen synergistic effect in reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel investigated by slow positron beam. Philos. Mag 96(3), 253–260 (2016)
K.G. Lynn, A.N. Goland, Observation of high momentum tails of positron-annihilation lineshapes. Solid State Commun. 18, 1549–1552 (1976)
P. Asoka-Kumar, M. Alatalo, V.J. Ghosh, Increased elemental specificity of positron annihilation spectra. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 2097–2100 (1996)
Q. Xu, T. Yoshiie, K. Sato, Dose dependence of Cu precipitate formation in Fe–Cu model alloys irradiated with fission neutrons. Phys. Rev. B 73, 134115 (2006)
Y. Nagai, T. Honma, Z. Tang, K. Hono, M. Hasegawa, Coincidence Doppler broadening study of the pre-precipitation stage of an Al[sbnd]Cu[sbnd]Mg[sbnd]Ag alloy. Philos. Mag. A 82, 1559–1572 (2002)
C. Hugenschmidt, P. Pikart, M. Stadlbauer, K. Schreckenbach, High elemental selectivity to Sn submonolayers embedded in Al using positron annihilation spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 77, 092105 (2008)
M. Alatalo, H. Kauppinen, K. Saarinen, Identification of vacancy defects in compound semiconductors by core-electron annihilation: application to InP. Phys. Rev. B 51, 4176–4185 (1995)
U. Myler, R.D. Goldberg, A.P. Knights, Chemical information in positron annihilation spectra. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69(22), 3333–3335 (1996)
J.P. Biersack, L.G. Haggmark, A Monte Carlo computer program for the transport of energetic ions in amorphous targets. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 174: 257–269 (1980).
I. Carvalho, H. Schut, A. Fedorov, Helium implanted Eurofer97 characterized by positron beam Doppler broadening and thermal desorption spectroscopy. J. Nucl. Mater. 442, 377–381 (2013)
V. Sabelova, V. Krsjak, J. Kuriplach, Characterization of helium implanted Fe–Cr alloys by means of positron annihilation methods. J. Nucl. Mater. 450, 54–58 (2014)
Acknowledgements
All authors acknowledge support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Grant Nos. 11475193, 11505205 and 11505192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Zhu, T., Jin, S. et al. Detection of helium in irradiated Fe9Cr alloys by coincidence Doppler broadening of slow positron annihilation. Appl. Phys. A 123, 177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0827-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0827-3