Abstract
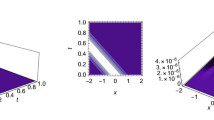
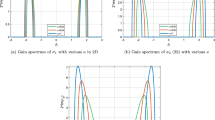
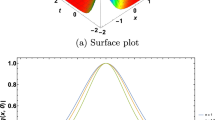
Rogue waves, by definition, are rare events of extreme amplitude. At the same time, they are surprisingly ubiquitous, in the sense that they can exist in a wide range of physical contexts and possess probability distributions that exhibit heavier tails than the normal Gaussian distribution. While many mechanisms have been demonstrated to explain the appearance of rogue waves in various specific systems, there is no known generic mechanism or general set of criteria shown to rule their appearance. Presupposing only the existence of a nonlinear Schrödinger-type equation together with a concave dispersion profile around a zero-dispersion wavelength, we demonstrate that solitons may experience acceleration and strong reshaping due to the interaction with continuum radiation, giving rise to extreme-value phenomena. The mechanism appears to be widely independent from interactions specific to the optical context, e.g., the Raman effect or other scattering processes that have no equivalent in other wave-supporting physical systems. In our system, a strong increase in the peak power may appear via reshaping while the pulse energy is nearly conserved. The conservative nature of the proposed reshaping-induced appearance of rogue waves makes this mechanism particularly robust.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Dysthe, H.E. Krogstad, P. Müller, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 40, 287 (2008)
A.N. Ganshin, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 065303 (2008)
Y.V. Bludov, V.V. Konotop, N. Akhmediev, Phys. Rev. A 80, 033610 (2009)
M.S. Ruderman, Eur. Phys. J. Special Top. 185, 57 (2010)
L. Stenflo, M. Marklund, J. Plasma Phys. 76, 293 (2010)
D.R. Solli, et al., Nat. Biotechnol. 450, 1054 (2007)
J. Kasparian, et al., Opt. Express 17, 12070 (2009)
D. Majus, et al., Phys. Rev. A 83, 025802 (2011)
C. Kharif, E. Pelinovsky, Eur. J. Mech. 22, 603 (2003)
P.A.E.M. Jannsen, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 33, 863 (2003)
M. Onorato, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 5831 (2001)
A. Mussot, et al., Opt. Exp. 17, 1502 (2009)
M. Taki, et al., Phys. Lett. A 374, 691 (2010)
D.R. Solli, C. Ropers, B. Jalali, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 233902 (2008)
J.M. Dudley, G. Genty, B.J. Eggleton, Opt. Exp. 16, 3644 (2008)
M. Erkintalo, G. Genty, J.M. Dudley, Opt. Lett. 35, 658 (2010)
G. Genty, J.M. Dudley, B.J. Eggleton, Appl. Phys. B 94, 187 (2009)
N. Akhmediev, J.M. Soto-Crespo, A. Ankiewicz, Phys. Rev. A 80, 043818 (2009)
N. Akhmediev, A. Ankiewicz, M. Taki, Phys. Lett. A 373, 675 (2009)
N. Akhmediev, A. Ankiewicz, J.M. Soto-Crespo, Phys. Rev. E 80, 026601 (2009)
B. Kibler, et al., Nat. Phys. 6, 790 (2010)
A. Demircan, S. Amiranashvili, C. Brée, C. Mahnke, F. Mitschke, G. Steinmeyer, Sci. Rep. 2, 850 (2012)
R. Smith, Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 78, 517 (1975)
C.M. De Sterke, Opt. Lett. 17, 914 (1992)
N. Rosanov, JETP Lett. 88, 501 (2008)
V.E. Lobanov, A.P. Sukhorukov, Phys. Rev. A 82, 033809 (2010)
A.V. Gorbach, D.V. Skryabin, Opt. Express. 15, 14560 (2008)
D.V. Skryabin, A.V. Gorbach, Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 1287 (2010)
M. Novello, M. Visser, G. Volovik (eds.), Artificial Black Holes. (World Scientific, New Jersey, London, Singapore, Hong Kong, 2002)
F. Belgiorno, S.L. Cacciatori, M. Clerici, V. Gorini, G. Ortenzi, L. Rizzi, E. Rubino, V.G. Sala, D. Faccio, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 203901 (2010)
T.G. Philbin, C. Kuklewicz, S. Robertson, S. Hill, F. König, U. Leonhardt, Sci. Agric. 319, 1367 (2008)
D. Faccio, Cont. Phys. 1, 1 (2012)
G. Agrawal, Nonlinear Fiber Optics. (Academic Press, San Diego, 2001)
L.J. Garay, J.R. Anglin, J.I. Cirac, P. Zoller, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 4643 (2000)
T.A. Jacobson, G.E. Volovik, Phys. Rev. D 58, 064021 (1998)
F. Belgiorno, S.L. Cacciatori, M. Clerici, V. Gorini, G. Ortenzi, L. Rizzi, E. Rubino, V.G. Sala, D. Faccio, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 203901 (2010)
G. Rousseaux, C. Mathis, P. Maïssa, T.G. Philbin, U. Leonhardt, New J. Phys. 10, 053015 (2008)
R. Driben, F. Mitschke, N. Zhavoronkov, Opt. Exp. 18, 25993 (2010)
V.E. Zakharov, E. Pushkarev, V.F. Shvets, V.V. Yan’kov, JETP Lett. 48, 83–87 (1988)
G. Genty, et al., Phys. Lett. A 374, 989 (2010)
V.E. Zakharov, V.S. L’vov, G. Falkovich, Kolmogorov Spectra of Turbulence 1. Wave turbulence. (Springer, Berlin, 1992)
S. Amiranashvili, A. Demircan, Phys. Rev. A 82, 013812 (2010)
S. Amiranashvili, A. Demircan, Adv. Opt. Tech. 2011, 989515 (2011)
J. Herrmann, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 173901 (2002)
S. Amiranashvili, U. Bandelow, A. Mielke, Opt. Commun. 283, 480 (2009)
A. Demircan, U. Bandelow, Opt. Comm. 244, 181 (2005)
J.M. Dudley, G. Genty, S. Coen, Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 1135 (2006)
M. Erkintalo, G. Genty, J.M. Dudley, Eur. Phys. J. Special Top. 185, 135 (2010)
N. Akhmediev, E. Pelinovsky, Eur. Phys. J. Special Top. 185, 1 (2010)
A. Demircan, U. Bandelow, Appl. Phys. B 86, 31 (2007)
A. Demircan, S. Amiranashvili, G. Steinmeyer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 163901 (2011)
S.-J. Im, A. Husakou, J. Herrmann, Opt. Exp. 18, 5367 (2010)
K.E. Lynch-Klarup, E.D. Mondloch, M.G. Raymer, D. Arrestier, F. Gerome, F. Benabid, Opt. Exp. 21, 13726 (2013)
A. Demircan, S. Amiranashvili, C. Brée, G. Steinmeyer, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 233901 (2013)
R. Driben, I. Babushkin, Opt. Lett. 37, 5157 (2012)
A.V. Yulin, R. Driben, B.A. Malomed, D.V. Skryabin, Opt. Exp. 21, 14481 (2013)
F.M. Mitschke, Mollenauer, Opt. Lett. 11, 659 (1986)
B. Kibler, K. Hammani, C. Michel, C. Finot, A. Picozzi, Phys. Lett. A 375, 3149 (2011)
H. Lamb, Hydrodynamics (6th ed). (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1994)
Acknowledgments
The following support is gratefully acknowledged: A. D. partially by DFG, Sh. A. by the DFG Research Center MATHEON (project D 14), F. M. by DFG, G. S. by the Academy of Finland (project Grant 128844), and C.M. partially by DFG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demircan, A., Amiranashvili, S., Brée, C. et al. Rogue wave formation by accelerated solitons at an optical event horizon. Appl. Phys. B 115, 343–354 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5609-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5609-9