Abstract
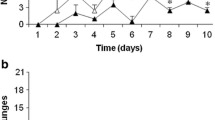
The current study explored Aurelia aurita and Rhopilema esculent um consumption by silver pomfret juveniles, as well as their prey selection between the two jellyfish species. Silver pomfret juveniles weighing 1±0.1 g actively preyed on both the species. Their daily A. aurita consumption was 11.6 times their own body weights regardless of the size of A. aurita medusae. Their daily R. esculent um consumption was 13, 9.1, 5, and 4.1 times their own body weights when the R. esculentum medusae were 10, 20, 30, and 40 mm in bell diameter, respectively. The survival rates of the R. esculent um were higher than those of the A. aurita. When the R. esculent um medusae were more than 30 mm in bell diameter, their survival rate exceeded 92%. Silver pomfrets serve as a type of potential predators on A. aurita in coastal waters, and they have little influence on R. esculent um with a size exceeding 30 mm. Besides, A. aurita may be able to be used as fish prey in silver pomfret artificial breeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai M N. 2001. Pelagic coelenterates and eutrophication: a review. Hydrobiologia, 451(1–3): 69–87.
Arai M N. 2005. Predation on pelagic coelenterates: a review. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK, 85(3): 523–536.
Chopra S. 1960. A note on the sudden outburst of ctenophores and medusae in the waters off Bombay. Curr. Sci., 29(10): 392–393.
Costello J H, Colin S P. 1994. Morphology, fluid motion and predation by the scyphomedusa Aurelia aurita. Mar. Biol., 121(2): 327–334.
Dadzie S, Abou-Seedo F, Al-Qattan E. 2000. The food and feeding habits of the silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen), in Kuwait waters. J. Appl. Ichthyol., 16(2): 61–67.
Davis P, Wheeler A. 1985. The occurrence of Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen, 1788), (Osteichthyes, Perciformes, Stromateiodei, Stromateidae) in the North Sea. J. Fish. Biol., 26(2): 105–109.
Dawson M N, Martin L E. 2001. Geographic variation and ecological adaptation in Aurelia (Scyphozoa, Semaeostomeae): some implications from molecular phylogenetics. Hydrobiologia, 451(1–3): 259–273.
Dong J, Jiang L X, Tan K F, Liu H Y, Purcell J E, Li P J, Ye C C. 2009. Stock enhancement of the edible jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye) in Liaodong Bay, China: a review. Hydrobiologia, 616(1): 113–118.
Dong Z J, Liu D Y, Keesing J K. 2010. Jellyfish blooms in China: dominant species, causes and consequences. Mar. Pollut. Bull., 60(7): 954–963.
Graham W M, Bayha K M. 2007. Biological invasions by marine jellyfish. In: Nentwig W ed. Biological Invasions: Ecological Studies, vol. 193. Springer-Verlag Press, Berlin, Heidelberg. p.239–255.
Graham W M, Pages F, Hamner W M. 2001. A physical context for gelatinous zooplankton aggregations: a review. Hydrobiologia, 451(1–3): 199–212.
Greenberg N, Garthwaite R L, Potts D C. 1996. Allozyme and morphological evidence for a newly introduced species of Aurelia in San Francisco Bay, California. Mar. Biol., 125(2): 401–410.
Hamner W M, Gilmer R W, Hamner P P. 1982. The physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of a stratified, saline, sulfide lake in Palau. Limnol. Oceanogr., 27(5): 896–909.
Hamner W M, Hamner P P, Strand S W. 1994. Sun-compass migration by Aurelia aurita (Scyphozoa): population retention and reproduction in Saanich Inlet, British Columbia. Mar. Biol., 119(3): 347–356.
Harris L G. 1987. Aeolid nudibranchs as predators and prey. Am. Malacol. Bull., 5: 287–292.
Hay S. 2006. Marine ecology: gelatinous bells may ring change in marine ecosystems. Curr. Biol., 16(17): R679–R682.
Hernroth L, Gröndahl F. 1983. On the biology of Aurelia aurita (L.) 1. Release and growth of Aurelia aurita (L.) ephyrae in the Gullmar fjord, western Sweden, 1982–83. Ophelia, 22(2): 189–199.
Holland D L, Davenport J, East J. 1990. The fatty acid composition of the leatherback turtle Dermochelys coriacea and its jellyfish prey. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK, 70(4): 761–770.
Hsieh Y H P, Leong F M, Rudloe J. 2001. Jellyfish as food. Hydrobiologia, 451(1–3): 11–17.
James C M, Almatar S. 2007. A breakthrough in the spawning of domesticated silver pomfret. Aquac. Asia — Pacific, 3(1): 26–28.
Kramp P L. 1961. Synopsis of the medusae of the world. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK, 40: 1–469.
Liu D H, Zhang J H, Cheng S Q, Fang J G, Yan J P, Liu C S, Zhang M L, Gao Y P. 2011. Study on the morphological and growth characteristics of Rhopilema esculenta: from ephyra to juvenile jellyfish. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 32(3): 51–56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu J, Li C, Li X. 2002. Phylogeny and biogeography of Chinese pomfret fishes (Pisces: Stromateidae). Studia Marina Sinica, 44: 235–239. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu X G, Yu H H, Li X G, Li Z E, Xu Z H, Li P C. 2006. Simultaneous determination of some constant and trace elements in fresh and cured jellyfish. Acta Oceanol. Sinica, 28(2): 151–155.
Liu X. 2008. North China Power. 24: 66–69. (in Chinese)
Lu J. 2009. Jellyfish visit Qingdao. Peninsula City Newspaper, 2009-7-8 (A8). (in Chinese)
Lucas C H, Williams J A. 1994. Population dynamics of the scyphomedusa Aurelia aurita in Southampton Water. J. Plankton. Res., 16(7): 879–895.
Mills C E. 2001. Jellyfish blooms: are populations increasing globally in response to changing ocean conditions? Hydrobiologia, 451(1–3): 55–68.
Miyajima Y, Masuda R, Kurihara A, Kamata R, Yamashita Y, Takeuchi T. 2011. Juveniles of threadsail filefish, Stephanolepis cirrhifer, can survive and grow by feeding on moon jellyfish Aurelia aurita. Fish. Sci., 77(1): 41–48.
Möller H. 1984. Reduction of a larval herring population by jellyfish predator. Science, 224(4649): 621–622.
Morikawa T. 1984. Jellyfish. FAO INFOFISH Marketing Digest, 1: 37–39.
Mutlu E, Bingel F, Gücü A C, Melnikov V V, Niermann U, Ostr N A, Zaika V E. 1994. Distribution of the new invader Mnemiopsis sp. and the resident Aurelia aurita and Pleurobrachia pileus populations in the Black Sea in the years 1991–1993. ICES. J. Mar. Sci., 51(4): 407–421.
Mutlu E. 2001. Distribution and abundance of moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita) and its zooplankton food in the Bleak Sea. Mar. Biol., 138(2): 329–339.
Omori M, Ishii H, Fujinaga A. 1995. Life history strategy of Aurelia aurita (Cnidaria, Scyphomedusae) and its impact on the zooplankton community of Tokyo Bay. ICES. J. Mar. Sci., 52(3–4): 597–603.
Ovchinnikova T V, Balandin S V, Aleshina G M, Tagaev A A, Leonova Y F, Krasnodembsky E D, Men’shenin A V, Kokryakov V N. 2006. Aurelin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from jellyfish Aurelia aurita with structural features of defensins and channel-blocking toxins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 348(2): 514–523.
Oviatt C A, Kremer P M. 1977. Predation on the ctenophore, Mnemiopsis leidyi, by butterfish, Peprilus triacanthus, in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island. Chesapeake Sci., 18(2): 236–240.
Papathanassiou E, Panayotidis P, Anagnostaki K. 1987. Notes on the biology and ecology of the jellyfish Aurelia aurita Lam. in Elefsis Bay (Saronikos Gulf, Greece). Mar. Ecol., 8(1): 49–58.
Pati S. 1980. Food and feeding habits of silver pomfret Pampus argenteus (Euphrasen) from Bay of Bengal with a note on its significance in fishery. Indian J. Fish., 27(1–2): 244–256.
Peng S M, Shi Z H, Sun P, Yin F, Wang J G. 2012. Effects of diet composition on growth rate, muscle amino acid and fatty acid composition of juvenile silver pomfret (Pampus argenteus). Marine Fisheries, 34(1): 51–56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Purcell J E, Arai M N. 2001. Interactions of pelagic cnidarians and ctenophores with fish: a review. Hydrobiologia, 451(1–3): 27–44.
Purcell J E. 2005. Climate effects on formation of jellyfish and ctenophore blooms: a review. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK, 85(3): 461–476.
Rasmussen E. 1973. Systematics and ecology of the Isefjord marine fauna (Denmark) with a survey of the Eelgrass (Zostera) vegetation and its communities. Ophelia, 11(1): 1–507.
Runge J A, Pepin P, Silvert W. 1987. Feeding behavior of the Atlantic mackerel Scomber scombrus on the hydromedusa Aglantha digitale. Mar. Biol., 94(3): 329–333.
Russell F S. 1970. The Medusae of the British Isles: II. Pelagic Scyphozoa with a Supplement to the First Volume on Hydromedusae. Cambridge Univ. Press, London. p.284.
Shi Z H, Wang J G, Gao L J, Lan J Z. 2005. Advances on the studies of reproductive biology and artificial breeding technology in silver pomfret Pampus argenteus. Marine Fisheries, 27(3): 247–250. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shushkina E A, Arnotauv G N. 1985. Quantitative distribution of the medusa Aurelia and its role in the Black Sea ecosystem. Oceanology, 25(1): 102–106.
Suazo C G. 2008. Black-browed albatross foraging on jellyfish prey in the southeast Pacific coast, southern Chile. Polar. Biol., 31(6): 755–757.
Suyehiro Y. 1942. A study on the digestive system and feeding habits of fish. Jap. J. Zool., 10(1): 1–303.
Uye S. 2008. Blooms of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai: a threat to the fisheries sustainability of the East Asian Marginal Seas. Plankton. Benthos Res., 3(Suppl.): 125–131.
Wakabayashi K, Sato R, Ishii H, Akiba T, Nogata Y, Tanaka Y. 2012. Culture of phyllosomas of Ibacus novemdentatus (Decapoda: Scyllaridae) in a closed recirculating system using jellyfish as food. Aquaculture, 330–333: 162–166.
Yasuda T. 1969. Ecological studies on the jelly-fish, Aurelia aurita, in Urazoko Bay, Fukui Prefecture-I occurrence pattern of the medusa. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish., 35(1): 1–6. (in Japanese with English abstract)
Yu H H, Liu X G, Dong X L, Li C P, Xing R G, Liu S, Li P C. 2005. Insecticidal activity of proteinous venom from tentacle of jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye. Bloorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 15(22): 4 949–4 952.
Yuan Y Y, Ye Z J, Liu Q, Wang Y J, Yang Y H. 2009. Spatio-Temporal variation of fishing ground of Pampus argenteus in the Southern Yellow Sea in spring. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 39(Sup.): 333–337. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang F, Sun S, Li C L. 2009. Research advances in marine medusae ecology. Natural Science, 19(2): 121–130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng Y J, Chen X Z, Chen J H. 2003. Biological Resources and the Environment of the East China Sea Continental Shelf. Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers Press, Shanghai. p.379–401. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2011CB403605), the Key Science and Technology Program of Qingdao (No. 11-3-1-6-hy), the Special Funds for the Basic R&D Program in the Central Non-Profit Research Institutes (No. 20603022011008), the National Key Technology R&D Program during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan Period (No. 2011BAD13B01)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Zhuang, Z., Chen, S. et al. Medusa consumption and prey selection of silver pomfret Pampus argenteus juveniles. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 32, 71–80 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-014-3034-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-014-3034-5