Abstract
Rapeseed yield parameters have been altered due to the increased exposure to abiotic stresses. The changing climatic conditions have reduced biomass production and seed yield, which ultimately affect the success of rapeseed crops. The severity and ability of abiotic stresses to act in tandem are a growing concern for agriculture producers across the globe. Rapeseed is one of the most vital cultivars in the world, serving as a major player in edible oil production. Abiotic stress conditions impose various effects on plant metabolism associated with growth stages, soil water storage capacity and plant physiological aspects. Modern agriculture aims to increased plant productivity to ensure global food security for the future. This can be achieved using quality seed, appropriate agricultural practices, measuring pest reduction techniques and understanding crop production challenges. Important tools, including conventional breeding and biotechnological approaches, can be employed to develop abiotic stress tolerance rapeseed. This review highlights the physiological and biochemical responses of rapeseed to abiotic stresses. The review also addresses conventional and modern stress mitigation strategies for the development of climate-smart rapeseed.


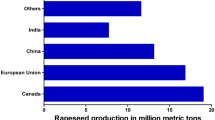
Source: USDA Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS), European Union (EU). EU-28 Oilseeds and Products Annual 2019-USDA GAIN reports. https://gain.fas.usda.gov/Recent%20GAIN%20Publications/Oilseeds%20and%20Products%20Annual_Vienna_EU-28_3-28-2019.pdf

Source: USDA Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS), World Agricultural Production, May 2019. https://apps.fas.usda.gov/psdonline/circulars/production.pdf

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad G, Jan A, Arif M, Jan M, Khattak R (2007) Influence of nitrogen and sulfur fertilization on quality of canola (Brassica napus L.) under rainfed conditions. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 8:731–737
Ahmad P (2010) Growth and antioxidant responses in mustard (Brassica juncea L.) plants subjected to combined effect of gibberellic acid and salinity. Arch Agron Soil Sci 56:575–588
Ahmadi M, Bahrani MJ (2009) Yield and yield components of rapeseed as influenced by water stress at different growth stages and nitrogen levels. Amerrcane Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 5:755–761
Angadi S, Cutforth H, Miller P, McConkey B, Entz M, Brandt S, Volkmar K (2000) Response of three Brassica species to high temperature stress during reproductive growth. Can J Plant Sci 80:693–701
Azimzadeh S, Azimzadeh S (2013) Effect of nitroxin biofertilizer and nitrogen chemical fertilizer on yield and yield components of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Int J Agric Crop Sci 6:1284–1291
AOF (2015) Australian oilseeds federation crop reports. www.australianoilseeds.com/oilseeds_industry/crop_report_assets
Al Mahmud J, Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Rahman A, Fujita M (2017) Relative tolerance of different species of Brassica to cadmium toxicity: coordinated role of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Plant Omics 10:107
Ali B, Tao Q, Zhou Y, Gill RA, Ali S, Rafiq MT, Xu L, Zhou W (2013) 5-Aminolevolinic acid mitigates the cadmium-induced changes in Brassica napus as revealed by the biochemical and ultra-structural evaluation of roots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 92:271–280
Ali S, Gill R, Mwamba T, Zhang N, Lv M, Ul Hassan Z, Islam F, Zhou W (2018) Differential cobalt-induced effects on plant growth, ultrastructural modifications, and antioxidative response among four Brassica napus (L) cultivars. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:2685–2700
Angelova V, Ivanova R, Todorov J, Ivanov K (2017) Potential of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) for phytoremediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals. Environ Prot Ecol 18:468–478
Akram NA, IqbalM MA, AshrafM A-Q, Shafiq S (2018) Aminolevulinic acid and nitric oxide regulate oxidative defense and secondary metabolisms in canola (Brassica napus L.) under drought stress. Protoplasma 255:163–174
Bal SK, Minhas PS (2017) Atmospheric stressors: challenges and coping strategies. Abiotic stress management for resilient agriculture. Springer, Singapore, pp 9–50
Bancroft I et al (2011) Dissecting the genome of the polyploid crop oilseed rape by transcriptome sequencing. Nat Biotechnol 29:762
Babula-Skowro´nska D, Ludwików A, Cie´sla A et al (2015) Involvement of genes encoding ABI1 protein phosphatases in the response of Brassica napus L. to drought stress. Plant Mol Biol 88:445–457
Baud S, Lepiniec L (2010) Physiological and developmental regulation of seed oil production. Prog Lipid Res 49:235–249
Bueckert RA, Clarke JM (2013) Review: annual crop adaptation to abiotic stress on the Canadian prairies: six case studies. Can J Plant Sci 93:375–385
Benincasa P, Pace R, Quinet M, Lutts S (2013) Effect of salinity and priming on seedling growth in rapeseed (Brassica napus var oleifera Del.). Acta Sci Agron 35:479–486
Beszterda M, Nogala-Kałucka M (2019) Current research developments on the processing and improving the nutritional quality of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): a review. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1002/EJLT.201800045
Bhattacharyya R et al (2015) Soil degradation in India: challenges and potential solutions. Sustainability 7:3528–3570
Billard V, Ourry A, Maillard A, Garnica M, Coquet L et al (2014) Copper-deficiency in Brassica napus induces copper remobilization, molybdenum accumulation andmodification of the expression of chloroplastic proteins. PLoS ONE 9:e109889
Brunetto G et al (2016) Copper accumulation in vineyard soils: rhizosphere processes and agronomic practices to limit its toxicity. Chemosphere 162:293–307
Bybordi A, Ebrahimian E (2011) Effect of salinity stress on activity of enzymes involved in nitrogen and phosphorous metabolism case study: canola (Brassica napus L.). Asian J Agric Res 5:208–214
Ceccarelli S et al (2010) Plant breeding and climate changes. J Agric Sci 148:627–637
Chakraborty K, Sairam RK, Bhattacharya R (2012) Differential expression of salt overly sensitive pathway genes determines salinity stress tolerance in Brassica genotypes. Plant Physiol Biochem 51:90–101
Chakraborty K, Sairam RK, Bhaduri D (2016) Effects of different levels of soil salinity on yield attributes accumulation of nitrogen, and micronutrients in Brassica Spp. J Plant Nutr 39:1026–1037
Chai L et al (2019) Rapid identification of enhanced drought and salt tolerances in Arabidopsis conferred by BnBADH1 gene. Int J Agric Biol 22:633–638
Chalhoub B et al (2014) Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345:950–953
Chaturvedi P, Ghatak A, Weckwerth W (2016) Pollen proteomics: from stress physiology to developmental priming. Plant Reprod 29:119–132
Chen B et al (2016) Identification, cloning and characterization of R2R3-MYB gene family in canola (Brassica napus L.) identify a novel member modulating ROS accumulation and hypersensitive-like cell death. DNA Res 23:101–114
Chen L, Ren F, Zhong H, Jiang W, Li X (2009) Identification and expression analysis of genes in response to high-salinity and drought stresses in Brassica napus. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 42:154–164
Chen L, Ren F, Zhou L, Wang Q-Q, Zhong H, Li X-B (2012) The Brassica napus calcineurin B-Like 1/CBL-interacting protein kinase 6 (CBL1/CIPK6) component is involved in the plant response to abiotic stress and ABA signalling. J Exp Bot 63:6211–6222
Chen L, Zhong H, Ren F, Guo Q-Q, Hu X-P, Li X-B (2011) A novel cold-regulated gene, COR25, of Brassica napus is involved in plant response and tolerance to cold stress. Plant Cell Rep 30:463–471
Deng Z et al (2005) A novel ABA-dependent dehydrin ERD10 gene from Brassica napus. DNA Seq 16:28–35
Di F et al (2018) Genome-wide analysis of the PYL gene family and identification of PYL genes that respond to abiotic stress in Brassica napus. Genes 9:156
Dolatabadi N, Toorchi M, Valizadeh M, Bandehagh A (2019) The proteome response of salt-sensitive rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) genotype to salt stress. Not Bot Horti Agrobot Cluj Napoca 47:17–23
Dordas CA, Sioulas C (2008) Safflower yield, chlorophyll content, photosynthesis, and water use efficiency response to nitrogen fertilization under rainfed conditions. Ind Crop Prod 27:75–85
Du C, Hu K, Xian S, Liu C, Fan J, Tu J, Fu T (2016) Dynamic transcriptome analysis reveals AP2/ERF transcription factors responsible for cold stress in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Mol Genet Genomics 291:1053–1067
Downing WL, Mauxion F, Fauvarque MO et al (1992) A Brassica napus transcript encoding a protein related to the Künitz protease inhibitor family accumulates upon water stress in leaves, not in seeds. Plant J 2:685–693
D’Hooghe P, Dubousset L, Gallardo K, Kopriva S, Avice J-C, Trouverie J (2014) Evidence for proteomic and metabolic adaptations associated to alterations of seed yield and quality in sulphurlimited Brassica napus L. Mol Cell Proteom 13:1165–1183
Ebrahimian E, Bybordi A, Seyyedi SM (2017) How nitrogen and zinc levels affect seed yield, quality, and nutrient uptake of canola irrigated with saline and ultra-saline water. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 48:345–355
El-Habbasha S, Taha M (2011) Integration between nitrogen fertilizer levels and bio-inoculants and its effect on canola (Brassica napus L.) plants. Am-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 11:786–791
Elferjani R, Soolanayakanahally R (2018) Canola responses to drought, heat, and combined stress: shared and specific effects on carbon assimilation, seed yield, and oil composition. Front Plant Sci 9:1224
Eskandari H, Alizadeh-Amraie A (2017) Comparison of the ability of wheat, clover and rapeseed in phytoremediation of cadmium from soils for reducing heavy metal stress. Environ Stress Crop Sci. https://doi.org/10.22077/escs.2017.589
FAS (2019) World Agricultural Production, May 2019. https://apps.fas.usda.gov/psdonline/circulars/production.pdf
FAOSTAT (2017) Rapeseed production, 2014; Crops/Regions/World list/Production Quantity (pick lists). https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data. Accessed Dec 22, 2017
FAS EU (2019) EU-28 Oilseeds and Products Annual 2019-USDA GAIN reports. https://gain.fas.usda.gov/Recent%2520GAIN%2520Publications/Oilseeds%2520and%2520Products%2520Annual_Vienna_EU-28_3-28-2019.pdf
Farhoudi R, Modhej A, Afrous A (2011) Effect of salt stress on physiological and morphological parameters of rapeseed cultivars. Adv Environ Biol 5:2501–2508
Farid M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Saeed R, Tauqeer HM, Sallah-Ud-Din R, Azam A, Raza N (2017) Microwave irradiation and citric acid assisted seed germination and phytoextraction of nickel (Ni) by Brassica napus L.: morpho-physiological and biochemical alterations under Ni stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:21050–21064
Friedt W, Tu J, Fu T (2018) Academic and economic importance of Brassica napus rapeseed. The Brassica napus genome. Springer, Cham, pp 1–20
Fu D-H et al (2016) Research progress and strategies for multifunctional rapeseed: a case study of China. J Integr Agric 15:1673–1684
Gao M-J, Allard G, Byass L, Flanagan AM, Singh J (2002) Regulation and characterization of four CBF transcription factors from Brassica napus. Plant Mol Biol 49:459–471
Ghobadi M, Bakhshandeh M, Fathi G, Gharineh MH, AlamieSaid K, Naderi A, Ghobadi ME (2006) Short and long periods of water stress during different growth stages of canola (Brassica napus L.): effect on yield, yield components, seed oil and protein contents. J Agron 5:336e341
Gopal R, Rizvi AH (2008) Excess lead alters growth, metabolism and translocation of certain nutrients in radish. Chemosphere 70:1539–1544
Grant C, Mahli S, Karamanos R (2012) Sulfur management for rapeseed. Field Crop Res 128:119–128
Habibzadeh F, Sorooshzadeh A, Pirdashti H, Sanavy S (2012) Effect of nitrogen compounds and tricyclazole on some biochemical and morphological characteristics of waterlogged-canola. Inter Res J Appl Basic Sci 3:77–84
Hajiebrahimi A, Owji H, Hemmati S (2017) Genome-wide identification, functional prediction, and evolutionary analysis of the R2R3-MYB superfamily in Brassica napus. Genome 60:797–814
Han H, Wang Q, He L-y, Sheng X-f (2018) Increased biomass and reduced rapeseed Cd accumulation of oilseed rape in the presence of Cd-immobilizing and polyamine-producing bacteria. J Hazard Mater 353:280–289
Hashem HA, Hassanein RA, Bekheta MA, El-Kady FA (2013) Protective role of selenium in canola (Brassica napus L.) plant subjected to salt stress. Egypt J Exp Biol (Bot) 9:199–211
Hawkins G, Nykiforuk C, Johnson-Flanagan A, Boothe J (1996) Inheritance and expression patterns of BN28, a low temperature induced gene in Brassica napus, throughout the Brassicaceae. Genome 39:704–710
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan MHM, Zulfiqar F, Raza A, Mohsin SM, Mahmud JA, Fujita M, Fotopoulos V (2020a) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants 9:681
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Khan MIR, Al Mahmud J, Alam MM, Fujita M (2020b) Regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolism and glyoxalase systems by exogenous osmolytes confers thermotolerance in Brassica napus. Gesunde Pflanz 72:3–16
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan MB, Raza A, Hawrylak-Nowak B, Matraszek-Gawron R, Al Mahmud J, Nahar K, Fujita M (2020c) Selenium in plants: boon or bane? Environ Exp Bot 178:104170
Hasanuzzaman M, Hossain MA, Fujita M (2012) Exogenous selenium pretreatment protects rapeseed seedlings from cadmium-induced oxidative stress by upregulating antioxidant defense and methylglyoxal detoxification systems. Biol Trace Element Res 149:248–261
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Anee TI, Fujita M (2017a) Exogenous silicon attenuates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Brassica napus L. by modulating AsA-GSH pathway and glyoxalase system. Front Plant Sci 8:1061
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Gill SS, Alharby HF, Razafindrabe BH, Fujita M (2017b) Hydrogen peroxide pretreatment mitigates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Brassica napus L.: an intrinsic study on antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Front Plant Sci 8:115
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Anee T, Khan M, Fujita M (2018) Silicon-mediated regulation of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems confers drought stress tolerance in Brassica napus L. South Afr J Bot 115:50–57
Hemmati M, Delkhosh B, Rad AHS, Mohammadi GN (2019) Effect of the application of foliar selenium on canola cultivars as influenced by different irrigation regimes. J Agric Sci 25:309–318
Hossain MF, Shenggang P, Meiyang D, Zhaowen M, Karbo MB, Bano A, Xiangru T (2015) Photosynthesis and antioxidant response to winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) as affected by boron. Pak J Bot 47:675–684
He Y et al (2016) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factors under multiple stresses in Brassica napus. PLoS ONE 11:e0157558
He J, Zhao X, Laroche A, Lu ZX, Liu H, Li Z (2014) Genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS), an ultimate marker-assisted selection (MAS) tool to accelerate plant breeding. Front Plant Sci 5:484
Hu Q et al (2017) Rapeseed research and production in China. Crop J 5:127–135
Hu H, Xiong L (2014) Genetic engineering and breeding of droughte resistant crops. Ann Rev Plant Biol 65:715–741
Jaglo KR et al (2001) Components of the Arabidopsis C-repeat/dehydration-responsive element binding factor cold-response pathway are conserved in Brassica napus and other plant species. Plant Physiol 127:910–917
Jahani M, Khavari-Nejad RA, Mahmoodzadeh H, Saadatmand S (2020) Effects of cobalt oxide nanoparticles (Co3O4 NPs) on ion leakage, total phenol, antioxidant enzymes activities and cobalt accumulation in Brassica napus L. Not Bot Hortic Agrobot Cluj-Napoca. https://doi.org/10.15835/nbha48311766
Jiang C, Iu B, Singh J (1996) Requirement of a CCGAC cis-acting element for cold induction of the BN115 gene from winter Brassica napus. Plant Mol Biol 30:679–684
Ji MG, Park HJ, Cha J-Y, Kim JA, Shin G-I, Jeong SY, Lee ES, Yun D-J, Lee SY, Kim W-Y (2020) Expression of Arabidopsis thaliana Thioredoxin-h2 in Brassica napus enhances antioxidant defenses and improves salt tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 147:313–321
Kahrizi D, Alaahvarand T (2012) Estimation and interrelationships of genetic variability parameters of some morpho-phenological traits in spring rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Asian J Biol Sci 5:358–364
Kamran M, Malik Z, Parveen A, Huang L, Riaz M, Bashir S, Mustafa A, Abbasi GH, Xue B, Ali U (2020) Ameliorative effects of biochar on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) growth and heavy metal immobilization in soil irrigated with untreated wastewater. J Plant Growth Regul 39:266–281
Kaur S, Francki MG, Forster JW (2012) Identification, characterization and interpretation of single-nucleotide sequence variation in allopolyploid crop species. Plant Biotechnol J 10:125–138
Kaur L, Sardana V, Sharma P (2018) Effect of sowing dates and nitrogen application on growth and productivity of canola oilseed rape (Brassica napus). J Oilseed Brassica 9:114–121
Khattak MJKFA, Khan MA (2000) Influence of sowing methods on the productivity of canola grown in saline field. Pak J Biol Sci 3:687–691
King GJ, Baten A (2018) Brassica napus genomic resources. The Brassica napus genome. Springer, Cham, pp 233–244
Krishna P, Sacco M, Cherutti JF, Hill S (1995) Cold-induced accumulation of hsp90 transcripts in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol 107:915–923
Krishnan P, Ramakrishnan B, Reddy KR, Reddy V (2011) High-temperature effects on rice growth, yield, and grain quality. Advances in agronomy. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 87–206
Kong F, Mao S, Du K, Wu M, Zhou X, Chu C, Wang Y (2011) Comparative proteomics analysis of OsNAS1 transgenic Brassica napus under salt stress. Chin Sci Bull 56:2343–2350
LaFramboise T (2009) Single nucleotide polymorphism arrays: a decade of biological, computational and technological advances. Nucleic Acids Res 37:4181–4193
Larden A, Triboi-Blondel A (1994) Freezing injury to ovules, pollen and seeds in winter rape. J Exp Bot 45:1177–1181
Liang Y et al (2016) Genome-wide identification, structural analysis and new insights into late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) gene family formation pattern in Brassica napus. Sci Rep 6:24265
Liang S-X, Gao N, Li X, Xi X (2018) Toxic effects of antimony on the seed germination and seedlings accumulation in Raphanus sativus L. radish and Brassica napus L. Mol Biol Rep 45:2609–2614
Lipper L et al (2014) Climate-smart agriculture for food security. Nat Clim Change 4:1068
Li J, Zeng L, Cheng Y, Lu G, Fu G, Ma H, Liu Q, Zhang X, Zou X, Li C (2018) Exogenous melatonin alleviates damage from drought stress in Brassica napus L. (rapeseed) seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 40:43
Liu S et al (2016) A genome-wide association study reveals novel elite allelic variations in seed oil content of Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 129:1203–1215
Long Y et al (2011) Epigenetic QTL mapping in Brassica napus. Genetics 189:1093–1102
Luo J et al (2017) BnSIP1-1, a trihelix family gene, mediates abiotic stress tolerance and ABA signaling in Brassica napus. Front Plant Sci 8:44
Luo T, Xian M, Zhang C, Zhang C, Hu L, Xu Z (2019) Associating transcriptional regulation for rapid germination of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) under low temperature stress through weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Sci Rep 9:1–16
Lv Y, Fu S, Chen S, Zhang W, Qi C (2016) Ethylene response factor BnERF2-like (ERF2.4) from Brassica napus L. enhances submergence tolerance and alleviates oxidative damage caused by submergence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Crop J 4:199–211
Ma B, Herath A (2016) Timing and rates of nitrogen fertiliser application on seed yield, quality and nitrogen-use efficiency of canola. Crop Past Sci 67:167–180
Ma BL, Zhao H, Zheng ZM, Caldwell C, Mills A, Earl H, Vanasse A, Scott P, Smith DL (2016) Optimizing seeding dates and rates for canola production in the humid eastern Canadian agroecosystems. Agron J 108:1869–1879
Malhi S, Gill K (2007) Interactive effects of N and S fertilizers on canola yield and seed quality on S-deficient Gray Luvisol soils in northeastern Saskatchewan. Can J Plant Sci 87:211–222
Men S, Chen H, Chen S, Zheng S, Shen X, Wang C, Yang Z, Liu D (2020) Effects of supplemental nitrogen application on physiological characteristics, dry matter and nitrogen accumulation of winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) under waterlogging stress. Sci Rep 10:1–10
Malik AI, Colmer TD, Lambers H, Setter TL, Schortemeyer M (2002) Short-term waterlogging has long-term effects on the growth and physiology of wheat. New Phytol 153:225–236
Mansoori I (2012) Response of canola to nitrogen and sulfur fertilizers. Int J Agric Crop Sci 4:28–33
Matthaus B, Özcan MM, Al Juhaimi F (2016) Some rape/canola seed oils: fatty acid composition and tocopherols. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 71:73–77
McVetty PBE, Duncan RW (2015) Canola, rapeseed, and mustard: for biofuels and bioproducts. Industrial crops. Handbook of plant breeding. Springer, New York, pp 133–156
Meena H, Meena RS (2017) Assessment of sowing environments and bio-regulators as adaptation choice for clusterbean productivity in response to current climatic scenario. Bangladesh J Bot 46:241–244
Metzker ML (2010) Sequencing technologies—the next generation. Nat Rev Genet 11:31
Mohammadi G, Amiri F (2010) The effect of priming on seed performance of canola (Brassica napus L.) under drought stress. Am-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 9:202–207
Morton MJ, Awlia M, Al-Tamimi N, Saade S, Pailles Y, Negrão S, Tester M (2019) Salt stress under the scalpel–dissecting the genetics of salt tolerance. Plant J 97:148–163
Muneer S, Lee B, Kim KY, Park SH, Zhang Q (2014) Involvement of sulphur nutrition in modulating iron deficiency responses in photosynthetic organelles of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Photosynth Res 119:319–329
Nagaharu U (1935) Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot 7:389–452
Namvar A, Khandan T (2013) Response of wheat to mineral nitrogen fertilizer and biofertilizer (Azotobacter sp. and Azospirillum sp.) inoculation under different levels of weed interference. Ekologija 59:85–94
Namvar A, Khandan T (2015) Inoculation of rapeseed under different rates of inorganic nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer: impact on water relations, cell membrane stability, chlorophyll content and yield. Arch Agron Soil Sci 61:1137–1149
Naseri R, Mirzaei A, Emami T, Vafa P (2012) Effect of salinity on germination stage of rapeseed cultivars (Brassica napus L). Int J Agric Crop Sci 4:918–922
Nelson RJ, Naylor RL, Jahn MM (2004) The role of genomics research in improvement of" orphan" crops. Crop Sci 44:1901
Nouman W, Basra SMA, Yasmeen A, Gull T, Hussain SB, Zubair M, Gul R (2014) Seed priming improves the emergence potential, growth and antioxidant system of Moringa oleifera under saline conditions. Plant Growth Reg 73:267–278
OECD (2012) Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. Consensus document on the biology of the brassica crops (Brassica spp.). Series on Harmonisation of Regulatory oversight of Biotechnology, No 54, OECD, Paris, p. 142
Park YS et al (1993) Generation of expressed sequence tags of random root cDNA clones of Brassica napus by single-run partial sequencing. Plant Physiol 103:359–370
Perata P, Armstrong W, Voesenek LA (2011) Plants and flooding stress. New Phytol 190:269–273
Purty RS, Kumar G, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2008) Towards salinity tolerance in Brassica: an overview. Physiol Mol Biol Plant 14:39–49
Qian B, Jing Q, Bélanger G, Shang J, Huffman T, Liu J, Hoogenboom G (2018) Simulated canola yield responses to climate change and adaptation in Canada. Agron J 110:133–146
Rahaman M, Mamidi S, Rahman M (2017) Association mapping of agronomic traits of canola (Brassica napus L.) subject to heat stress under field conditions. Aust J Crop Sci 11:1094
Rakow G (2004) Species origin and economic importance of Brassica. In: Pua EC, Douglas CJ (eds) Brassica. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–11
Raman H et al (2016) Genome-wide association analyses reveal complex genetic architecture underlying natural variation for flowering time in canola. Plant Cell Environ 39:1228–1239
Raza A, Razzaq A, Mehmood SS, Zou X, Zhang X, Lv Y, Xu J (2019a) Impact of climate change on crops adaptation and strategies to tackle its outcome: a review. Plants 8:34
Raza A, Mehmood SS, Ashraf F, Khan RSA (2019b) Genetic diversity analysis of Brassica species using PCR-based SSR markers. Gesunde Pflanz 71:1–7
Raza A, Ashraf F, Zou X, Zhang X, Tosif H (2020a) Plant adaptation and tolerance to environmental stresses: mechanisms and perspectives. In: Plant ecophysiology and adaptation under climate change: mechanisms and perspectives I. Springer, Singapore, pp 117–145
Raza A, Hafeez MB, Zahra N, Shaukat K, Umbreen S, Tabassum J, Charagh S, Khan RSA, Hasanuzzaman M (2020b) The plant family Brassicaceae: introduction, biology, and importance. In: The plant family Brassicaceae. Springer, Singapore, pp 1–43
Raza A, Charagh S, Razzaq A, Javed R, Khan RSA, Hasanuzzaman M (2020c) Brassicaceae plants response and tolerance to drought stress: physiological and molecular interventions. In: The plant family Brassicaceae. Springer, Singapore, pp 229–261
Raza A, Habib M, Kakavand SN, Zahid Z, Zahra N, Sharif R, Hasanuzzaman M (2020d) Phytoremediation of cadmium: physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms. Biology 9:177
Reddy PP (2015) Climate resilient agriculture for ensuring food security, vol 373. Springer, New Delhi
Sabagh AE et al (2019) Drought and salinity stress management for higher and sustainable canola (Brassica napus L.) production: a critical review. Aust J Crop Sci 13:88
Sáez-Vásquez J, Raynal M, Meza-Basso L, Delseny M (1993) Two related, low-temperature-induced genes from Brassica napus are homologous to the human tumour bbc1 (breast basic conserved) gene. Plant Mol Biol 23:1211–1221
Salvagiotti F, Miralles DJ (2008) Radiation interception, biomass production and grain yield as affected by the interaction of nitrogen and sulfur fertilization in wheat. Eur J Agron 28:282–290
Salim N, Raza A (2020) Nutrient use efficiency (NUE) for sustainable wheat production: A review. J Plant Nutri 43:297–315.
Sahni S, Prasad BD, Liu Q, Grbic V, Sharpe A, Singh SP, Krishna P (2016) Overexpression of the brassinosteroid biosynthetic gene DWF4 in Brassica napus simultaneously increases seed yield and stress tolerance. Sci Rep 6:28298
Song JM et al (2020) Eight high-quality genomes reveal pan-genome architecture and ecotype differentiation of Brassica napus. Nat Plant 6:34–45
Sattar A, Cheema MA, Wahid M, Saleem M, Hassan M (2011) Interactive effect of sulphur and nitrogen on growth, yield and quality of canola. Crop Environ 2:32–37
Schadt EE, Turner S, Kasarskis A (2010) A window into third-generation sequencing. Hum Mol Genet 19:R227–R240
Setter T, Waters I (2003) Review of prospects for germplasm improvement for waterlogging tolerance in wheat, barley and oats. Plant Soil 253:1–34
Shabani A, Sepaskhah A, Kamgar-Haghighi A (2013) Growth and physiologic response of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) to deficit irrigation, water salinity and planting method. Int J Plant Prod 7:569–596
Shahbaz M, Noreen N, Perveen S (2013) Triacontanol modulates photosynthesis and osmoprotectants in canola (Brassica napus L.) under saline stress. J Plant Interact 8:350–359
Shekhawat K, Rathore S, Premi O, Kandpal B, Chauhan J (2012) Advances in agronomic management of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea (L.) Czernj. Cosson): an overview. Int J Agron 2012:408824
Shirazi FA, Razi H, Niazi A, Alemzadeh A (2019) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a stress-responsive WRKY transcription factor gene, BnWRKY57, from Brassica napus. Plant Omics 12:37
Snowdon RJ, Iniguez Luy FL (2012) Potential to improve oilseed rape and canola breeding in the genomics era. Plant Breed 131:351–360
Sulmon C et al (2015) Abiotic stressors and stress responses: What commonalities appear between species across biological organization levels? Environ Poll 202:66–77
Song F, Hu L, Zhou G, Wu J, Fu T (2010) Effects of waterlogging time on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) growth and yield. Acta Agron Sin 36:170–176
Tahir M, Ali A, Nadeem MA, Tanveer A, Sabir Q (2007) Performance of canola (Brassica napus L.) under different irrigation levels. Pak J Bot 39:739–746
Tayo T, Morgan D (1975) Quantitative analysis of the growth, development and distribution of flowers and pods in oil seed rape (Brassica napus L.). J Agric Sci 85:103–110
Tesfamariam EH, Annandale JG, Steyn JM (2010) Water stress effects on winter canola growth and yield. Agron J 102:658–666
Tester M, Langridge P (2010) Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 327:818–822
Thomas A, Guerreiro S, Sodek L (2005) Aerenchyma formation and recovery from hypoxia of the flooded root system of nodulated soybean. Ann Bot 96:1191–1198
USDA-ARS (2017) Germplasm resources information network (GRIN) taxonomy for plants. Taxon: Brassica napus L. United States Department of Agriculture. Agricultural Research Service, Beltsville Area. https://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/taxon.pl?7661
Ullah F, Bano A, Nosheen A (2012) Effects of plant growth regulators on growth and oil quality of canola (Brassica napus L.) under drought stress. Pak J Bot 44:1873–1880
Ulhassan Z, Gill RA, Huang H, Ali S, Mwamba TM, Ali B, Huang Q, Hamid Y, Khan AR, Wang J (2019) Selenium mitigates the chromium toxicity in Brassicca napus L. by ameliorating nutrients uptake, amino acids metabolism and antioxidant defense system. Plant Physiol Biochem 145:142–152
Ur Rehman H, Iqbal Q, Farooq M, Wahid A, Afzal I, Basra SM (2013) Sulphur application improves the growth, seed yield and oil quality of canola. Acta Pysiol Pant 35:2999–3006
Varshney R et al (2007) Extending the repertoire of microsatellite markers for genetic linkage mapping and germplasm screening in chickpea. J SAT Agric Res 5:1–3
Wahid A, Jamil A (2009) Inducing salt tolerance in canola (Brassica napus L.) by exogenous application of glycinebetaine and proline: response at the initial growth stages. Pak J Bot 41:1311–1319
Wang M-M et al (2018a) Global analysis of WOX transcription factor gene family in Brassica napus reveals their stress-and hormone-responsive patterns. Int J Mol Sci 19:3470
Wang P, Yang C, Chen H, Luo L, Leng Q, Li S, Han Z, Li X, Song C, Zhang X (2018b) Exploring transcription factors reveals crucial members and regulatory networks involved in different abiotic stresses in Brassica napus L. BMC Plant Biol 18:202
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Wang Y, Jin S, Xu Y, Li S, Zhang S, Yuan Z, Li J, Ni Y (2020) Overexpression of BnKCS1-1, BnKCS1-2, and BnCER1-2 promotes cuticular wax production and increases drought tolerance in Brassica napus. Crop J 8:26–37
Wang J, Zuo K, Wu W, Song J, Sun X, Lin J, Li X, Tang K (2004) Expression of a novel antiporter gene from Brassica napus resulted in enhanced salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants. Biol Plant 48:509–515
Wan H, Chen L, Guo J, Li Q, Wen J, Yi B, Ma C, Tu J, Fu T, Shen J (2017) Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic architecture underlying salt tolerance-related traits in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Front Plant Sci 8:593
Wu F, Bao W, Li F, Wu N (2008) Effects of drought stress and N supply on the growth, biomass partitioning and water-use efficiency of Sophora davidii seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 63:248–255
Wu Z, Yin X, Bañuelos GS, Lin Z-Q, Liu Y, Li M, Yuan L (2016) Indications of selenium protection against cadmium and lead toxicity in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Front Plant Sci 7:1875
Wu W, Ma BL (2016) A new method for assessing plant lodging and the impact of management options on lodging in canola crop production. Sci Rep 6:31890
Wu W, Ma BL, Whalen JK (2018) Enhancing rapeseed tolerance to heat and drought stresses in a changing climate: perspectives for stress adaptation from root system architecture. Advances in agronomy. Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 87–157
Xe S, Xx F, Li C, Zp Z, Lj W (2015) Study on salt tolerance with YHem1 transgenic canola (Brassica napus). Physiol Plant 154:223–242
Xiao Y, Chen L, Zou J, Tian E, Xia W, Meng J (2010) Development of a population for substantial new type Brassica napus diversified at both A/C genomes. Theor Appl Genet 121:1141–1150
Xu M et al (2015) The effect of waterlogging on yield and seed quality at the early flowering stage in Brassica napus L. Field Crop Res 180:238–245
Yan L, Riaz M, Wu X, Wang Y, Du C, Jiang C (2018) Interaction of boron and aluminum on the physiological characteristics of rape (Brassica napus L.) seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 40:33
Yao K, Lockhart KM, Kalanack JJ (2005) Cloning of dehydrin coding sequences from Brassica juncea and Brassica napus and their low temperature-inducible expression in germinating seeds. Plant Physiol Biochem 43:83–89
Ying L, Chen H, Cai W (2014) BnNAC485 is involved in abiotic stress responses and flowering time in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol Biochem 79:77–87
Zamani S, Nezami M, Habibi D, Khorshidi M (2010) Effect of quantitative and qualitative performance of four canola cultivars (Brassica napus L) to salinity conditions. Adv Environ Biol 1:422–428
Zaman QU, Li C, Cheng H, Hu Q (2019) Genome editing opens a new era of genetic improvement in polyploid crops. Crop J 7:141–150
Zhang H et al (2014a) Identification and characterization of CBL and CIPK gene families in canola (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol 14:8
Zhang T, Chang Y, Wang J, Wang N, Wang Y, Chen Q, Sun W (2013) Cloning and expression analysis of a BnICE1 from Brassica napus L. Sci Agric Sin 1:205–214
Zhang X, Lu G, Long W, Zou X, Li F, Nishio T (2014b) Recent progress in drought and salt tolerance studies in Brassica crops. Breed Sci 64:60–73
Zhao TJ, Liu Y, Yan YB, Feng F, Liu WQ, Zhou HM (2007) Identification of the amino acids crucial for the activities of drought responsive element binding factors (DREBs) of Brassica napus. FEBS Lett 581:3044–3050
Zhong L, Hu C, Tan Q, Liu J, Sun X (2012) Effects of sulfur application on sulfur and arsenic absorption by rapeseed in arsenic-contaminated soil. Plant Soil Environ 57:429–434
Zhu Y et al (2012) Analysis of gene expression profiles of two near-isogenic lines differing at a QTL region affecting oil content at high temperatures during seed maturation in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 124:515–531
Zirgoli MH, Kahrizi D (2015) Effects of end-season drought stress on yield and yield components of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) in warm regions of Kermanshah Province. Biharean Biol 9:133–140
Acknowledgements
The author wants to say special thanks to his wife (Aasma Ali) and a newly born baby girl for giving me time and consistent support to complete the revision of this manuscript. The author is grateful to the researchers whose contributions have been cited in this review, which have helped me to prepare this review paper. Further, the author also apologizes to all researchers whose relevant work could not be cited due to space limitations.
Funding
There was no external funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AR conceived the idea, wrote the manuscript and prepared the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raza, A. Eco-physiological and Biochemical Responses of Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) to Abiotic Stresses: Consequences and Mitigation Strategies. J Plant Growth Regul 40, 1368–1388 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10231-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10231-z