Abstract
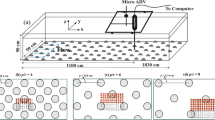
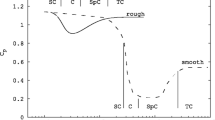
This study deals with the behavior of shallow turbulent wakes generated on smooth and rough surfaces. The wake generator used is a flat plate placed normal to the flow. Experiments were conducted at flow depths of 40 and 80 mm. The boundary layer thickness in the approaching flow occupies 60–75% of the flow depth. The Reynolds number based on the plate width and approaching freestream velocity varies from 13.0 × 103 to 14.5 × 103. Velocity measurements were carried out in the near-wake region (1–10 plate widths) using a laser-Doppler anemometer. The mean velocity distributions at various axial stations collapse onto a single curve by a proper choice of the length and velocity scales. It is important to note that a sense of self-similarity is attained even in the near-wake region. Attempts were made to clarify the relative effects of the transverse shear and bed friction in shallow open channel wakes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 February 1999/Accepted: 30 August 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tachie, M., Balachandar, R. Shallow wakes generated on smooth and rough surfaces. Experiments in Fluids 30, 467–474 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480000228
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480000228