Abstract
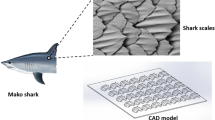
The skin of fast sharks exhibits a rather intriguing three-dimensional rib pattern. Therefore, the question arises whether or not such three-dimensional riblet surfaces may produce an equivalent or even higher drag reduction than straight two-dimensional riblets. Previously, the latter have been shown to reduce turbulent wall shear stress by up to 10%. Hence, the drag reduction by three-dimensional riblet surfaces is investigated experimentally. Our idealized 3D-surface consists of sharp-edged fin-shaped elements arranged in an interlocking array. The turbulent wall shear stress on this surface is measured using direct force balances. In a first attempt, wind tunnel experiments with about 365,000 tiny fin elements per test surface have been carried out. Due to the complexity of the surface manufacturing process, a comprehensive parametric study was not possible. These initial wind tunnel data, however, hinted at an appreciable drag reduction. Subsequently, in order to have a better judgement on the potential of these 3D-surfaces, oil channel experiments are carried out. In our new oil channel, the geometrical dimensions of the fins can be magnified 10 times in size as compared to the initial wind tunnel experiments, i.e., from typically 0.5 mm to 5 mm. For these latter oil channel experiments, novel test plates with variable fin configuration have been manufactured, with 1,920–4,000 fins. This enhanced variability permits measurements with a comparatively large parameter range. As a result of our measurements, it can be concluded, that 3D-riblet surfaces do indeed produce an appreciable drag reduction. We found as much as 7.3% decreased turbulent shear stress, as compared to a smooth reference plate. However, in direct comparison with 2D riblets, the performance of 3D-riblets is still inferior by about 1.7%. On the other hand, it appears conceivable, with a careful design of the fin shape (possibly supported by theory), that this inferiority in performance might be reduced. Nevertheless, at present, it seems to be rather unlikely, that 3D-riblets can significantly outperform 2D-riblets. Finally, one interesting finding remains to be mentioned: The optimum drag reduction for short 3D-riblets occurs at a lower rib height than for longer 3D-riblets or for infinitely long 2D-riblets. The same observation had been made previously on shark scales of different species with differing rib lengths, but no explanation could be given.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 March 1999/Accepted: 16 July 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bechert, D., Bruse, M. & Hage, W. Experiments with three-dimensional riblets as an idealized model of shark skin. Experiments in Fluids 28, 403–412 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050400
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050400