Abstract
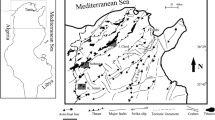
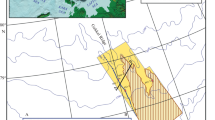
On the passive margin of the Nile deep-sea fan, the active Cheops mud volcano (MV; ca. 1,500 m diameter, ~20–30 m above seafloor, 3,010–3,020 m water depth) comprises a crater lake with hot (up to ca. 42 °C) methane-rich muddy brines in places overflowing down the MV flanks. During the Medeco2 cruise in fall 2007, ROV dives enabled detailed sampling of the brine fluid, bottom lake sediments at ca. 450 m lake depth, sub-surface sediments from the MV flanks, and carbonate crusts at the MV foot. Based on mineralogical, elemental and stable isotope analyses, this study aims at exploring the origin of the brine fluid and the key biogeochemical processes controlling the formation of these deep-sea authigenic carbonates. In addition to their patchy occurrence in crusts outcropping at the seafloor, authigenic carbonates occur as small concretions disseminated within sub-seafloor sediments, as well as in the bottom sediments and muddy brine of the crater lake. Aragonite and Mg-calcite dominate in the carbonate crusts and in sub-seafloor concretions at the MV foot, whereas Mg-calcite, dolomite and ankerite dominate in the muddy brine lake and in sub-seafloor concretions near the crater rim. The carbonate crusts and sub-seafloor concretions at the MV foot precipitated in isotopic equilibrium with bottom seawater temperature; their low δ13C values (–42.6 to –24.5‰) indicate that anaerobic oxidation of methane was the main driver of carbonate precipitation. By contrast, carbonates from the muddy lake brine, bottom lake concretions and crater rim concretions display much higher δ13C (up to –5.2‰) and low δ18O values (down to –2.8‰); this is consistent with their formation in warm fluids of deep origin characterized by 13C-rich CO2 and, as confirmed by independent evidence, slightly higher heavy rare earth element signatures, the main driver of carbonate precipitation being methanogenesis. Moreover, the benthic activity within the seafloor sediment enhances aerobic oxidation of methane and of sulphide that promotes carbonate dissolution and gypsum precipitation. These findings imply that the coupling of carbon and sulphur microbial reactions represents the major link for the transfer of elements and for carbon isotope fractionation between fluids and authigenic minerals. A new challenge awaiting future studies in cold seep environments is to expand this work to oxidized and reduced sulphur authigenic minerals.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloisi G, Pierre C, Rouchy JM, Foucher JP, Woodside J, the Medinaut Scientific Party (2000) Methane-related authigenic carbonates of eastern Mediterranean Sea mud volcanoes and their possible relation to gas hydrate destabilisation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 184:231–338
Aloisi G, Wallmann K, Bollwerk SM, Derkachev A, Bohrmann G, Suess E (2004) The effect of dissolved barium on biogeochemical processes at cold seeps. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68(8):1735–1748
Alperin MJ, Reeburg WS, Whiticar MJ (1988) Carbon and hydrogen isotope fractionation resulting from anaerobic methane oxidation. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 2(3):279–288
Barrat JA, Keller F, Amossé J, Taylor RN, Nesbitt RW, Hirata T (1996) Determination of rare earth element in sixteen silicate reference samples by ICP-MS after Tm addition and ion exchange separation. Geostand Newslett 20:133–139
Bayon G, Loncke L, Dupré S, Caprais JC, Ducassou E, Duperron S, Etoubleau J, Foucher JP, Fouquet Y, Gontharet S, Henderson GM, Hughen C, Klaucke I, Mascle J, Migeon S, Olu-Le Roy K, Ondréas H, Pierre C, Sibuet M, Stadnitskaia A, Woodside J (2009) Multidisciplinary investigation of fluid seepage on an unstable margin: the case of the Central Nile Deep-sea fan. Mar Geol 261:92–104
Bayon G, Birot D, Ruffine L, Caprais JC, Ponzevera E, Bollinger C, Donval JP, Charlou JL, Voisset M (2011) Evidence for intense REE scavenging at cold seeps from the Niger Delta margin. Earth Planet Sci Lett 312:443–452
Bayon G, Dupré S, Ponzevera E, Etoubleau J, Chéron S, Pierre C, Mascle J, Boetius A, de Lange G (2013) Formation of carbonate chimneys in the Mediterranean Sea linked to deep-water oxygen depletion. Nat Geosci 6:755–760. doi:10.1038/ngeo1888
Boetius A, Wenzhöfer F (2013) Seafloor oxygen consumption fuelled by methane from cold seeps. Nat Geosci 6:725–734. doi:10.1038/ngeo1926
Boetius A, Ravenschlag K, Schubert CJ, Rickert D, Widdel F, Gieseke A, Amann R, Jørgensen BB, Witte U, Pfannkuche O (2000) A marine consortium apparently mediating anaerobic oxidation of methane. Nature 407:623–626
Bottinga Y (1969) Calculated fractionation factors for carbon and hydrogen isotope exchange in the system calcite-CO2-graphite-methane-hydrogen and water vapor. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 33:49–64
Burton EA, Walter LM (1987) Relative precipitation rates of aragonite and Mg calcite from seawater: temperature or carbonate ion control? Geology 15:111–114
Carothers WW, Adami LH, Rosenbauer RJ (1988) Experimental oxygen isotope fractionation between siderite-water and phosphoric acid-liberated CO2-siderite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2445–2450
Claypool GE, Kaplan IR (1974) The origin and distribution of methane in marine sediments. In: Kaplan IR (ed) Natural gases in marine sediments. Plenum, New York, pp 99–139
Claypool GE, Threlkeld CN (1983) Anoxic diagenesis and methane generation in sediments of the Blake Outer Ridge, Deep Sea Drilling Project Site 553, Leg 76. In: Sheridan RE, Gradstein FM (eds) Init Repts DSDP 76. US Govt Printing Office, Washington, pp 391–402
Craig H (1957) Isotopic standards for carbon and oxygen and correction factors for mass-spectrometric analysis of carbon dioxide. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 12:133–149
Crémière A, Pierre C, Blanc-Valleron MM, Zitter T, Cagatay NM, Henry P (2012) Methane-derived authigenic carbonates along the North Anatolian fault system in the Sea of Marmara (Turkey). Deep Sea Res I 66:114–130
Dickens GR (2001) Sulfate profiles and barium fronts in sediment on the Blake Ridge: present and past methane fluxes through a large gas hydrate reservoir. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:529–543
Dupré S, Woodside J, Foucher JP, de Lange G, Mascle J, Boetius A, Mastalerz V, Stadnistskaia A, Ondréas H, Huguen C, Harmégnies F, Gontharet S, Loncke L, Deville E, Niemann H, Omoregie E, Olu-Le Roy K, Fiala-Medioni A, Dählmann A, Caprais JC, Prinzhofer A, Sibuet M, Pierre C, Sinninghe Damsté J (2007) Seafloor geological studies above active gas chimneys off Egypt (Central Nile deepsea fan). Deep Sea Res I 54:1146–1172
Dupré S, Buffet G, Mascle J, Foucher J-P, Gauger S, Boetius A, Marfia C, the AsterX AUV Team, the Quest ROV Team, the BIONIL Scientific Party (2008) High-resolution mapping of large gas emitting mud volcanoes on the Egyptian continental margin (Nile Deep Sea Fan) by AUV surveys. Mar Geophys Res 29(4):275–290
Dupré S, Woodside J, Klaucke I, Mascle J, Foucher J-P (2010) Widespread active seepage activity on the Nile Deep Sea Fan (offshore Egypt) revealed by high-definition geophysical imagery. Mar Geol 275(1/4):1–19
Feng D, Lin ZJ, Bian YY, Chen DF, Peckmann J, Bohrmann G, Roberts HH (2013) Rare earth elements of seep carbonates: indication for redox variations and microbiological processes at modern seep sites. J Asian Earth Sci 65:27–33
Foucher J-P, Westbrook GK, Boetius A, Ceramicola S, Dupré S, Mascle J, Mienert J, Pfannkuche O, Pierre C, Praeg D (2009) Structure and drivers of hydrocarbon seep ecosystems in the European seas: an overview from HERMES results. Oceanography 22(1):92–109
Fritz P, Smith DGW (1970) The isotopic composition of secondary dolomites. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 34:1161–1173
Goldsmith JR, Graf DL, Heard HC (1961) Lattice constants of the calcium-magnesium carbonates. Am Mineral 46:453–457
Gontharet S, Pierre C, Blanc-Valleron MM, Rouchy JM, Fouquet Y, Bayon G, Foucher JP, Woodside J, Mascle J, the Nautinil scientific party (2007) Nature and origin of diagenetic carbonate crusts and concretions from mud volcanoes and pockmarks of the Nile deep-sea fan (eastern Mediterranean Sea). Deep Sea Res II 54:1292–1311
Gontharet S, Stadnitskaia A, Bouloubassi I, Pierre C, Dinninghe Damsté JS (2009) Palaeo methane-seepage history traced by biomarker patterns in a carbonate crust, Nile deep-sea fan (Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Mar Geol 261:105–113
Grossman EL, Ku TL (1986) Carbon and oxygen isotope fractionation in biogenic aragonite: temperature effects. Chem Geol 59:59–74
Himmler T, Brinkmann F, Bohrmann G, Peckmann J (2011) Corrosion patterns of seep-carbonates from the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Terra Nova 23:206–212
Himmler T, Haley BA, Torres ME, Klinkhammer GP, Bohrmann G, Peckmann J (2013) Rare earth element geochemistry in cold-seep pore waters of Hydrate Ridge, northeast Pacific Ocean. Geo-Mar Lett 33(5):369–379. doi:10.1007/s00367-013-0334-2
Hinrichs KU, Summons RE, Orphan V, Sylva SP, Hayes JM (2000) Molecular and isotopic analysis of anaerobic methane-oxidizing communities in marine sediments. Org Geochem 31:1685–1701
Huguen C, Mascle J, Chaumillon E, Kopf A, Woodside J, Zitter T (2004) Structural setting and tectonic control of mud volcanoes in the central Mediterranean Ridge (Eastern Mediterranean). Mar Geol 209:245–263
Huguen C, Zitter T, Woodside J, Mascle J, Foucher JP (2005) Mud volcanoes and mud domes of the Central Mediterranean Ridge: near bottom and in situ observations. Deep Sea Res 52:1911–1931
Huguen C, Foucher JP, Mascle J, Ondréas H, Thouement M, Gontharet S, Stadnitskaia A, Pierre C, Bayon G, Loncke L, Boetius A, Bouloubassi I, de Lange G, Caprais JC, Fouquet Y, Woodside JM, Dupré S, the NAUTINIL Scientific Party (2009) Menes caldera, a highly active site of brine seepage in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea: in situ observations from the Nautinil expedition (2003). Mar Geol 261:138–152
Joye SB, Samarkin VA, Orcutt BN, MacDonald IR, Hinrichs KU, Elvert M, Teske AP, Lloyd KG, Lever MA, Montoya JP, Meile CD (2009) Metabolic variability in seafloor brines revealed by carbon and sulphur dynamics. Nat Geosci 2:349–354. doi:10.1038/ngeo475
Judd AG, Hovland M (2007) Seabed fluid flow. The impact on geology, biology and the marine environment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kim ST, O’Neil JR (1997) Equilibrium and nonequilibrium oxygen isotope effects in synthetic carbonates. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61(16):3461–3475
Loncke L (2002) Le delta profond du Nil: structure et évolution depuis le Messinien. Thèse de doctorat, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris
Loncke L, Mascle J (2004) Mud volcanoes, gas chimneys, pockmarks and mounds on the Nile deep sea-fan (Eastern Mediterranean): geophysical evidences. Mar Pet Geol 21:669–689
Loncke L, Mascle J, Fanil Scientific Parties (2004) Mud volcanoes, gas chimneys, pockmarks and mounds on the Nile deep sea-fan (Eastern Mediterranean): geophysical evidences. Mar Pet Geol 21:669–689
Loncke L, Gaullier V, Mascle J, Vendeville B, Camera L (2006) The Nile deep-sea fan: an example of interacting sedimentation, salt tectonics, and inherited subsalt paleotopographic features. Mar Pet Geol 23(3):297–315
Mascle J, Mascle G (2012) Morphotectonic of the Mediterranean Sea, 1/4 000 000 map. CCGM, Paris
Mascle J, Mary F, Praeg D, Brosolo L, Camera L, Ceramicola S, Dupré S (2014) Distribution and geological control of mud volcanoes and other fluid/free gas seepage features in the Mediterranean Sea and nearby Gulf of Cadiz. Geo-Mar Lett. doi:10.1007/s00367-014-0356-4
Mastalerz V, de Lange GJ, Dählmann A (2009) Differential aerobic and anaerobic oxidation of hydrocarbon gases discharged at mud volcanoes in the Nile deep-sea fan. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73(13):3849–3863
Omoregie EO, Mastalerz V, de Lange G, Straub KL, Kappler A, Roy H, Stadnitskaia A, Foucher J-P, Boetius A (2008) Biogeochemistry and community composition of iron and sulfur precipitating microbial mats at the Chefren mud volcano (Nile Deep-sea fan, Eastern Mediterranean). Appl Environ Microbiol 74(10):3198–3215
Orphan VJ, House CH, Hinrichs KU, McKeegan KD, DeLong EF (2001) Methane-consuming archaea revealed by directly coupled isotopic and phylogenetic analysis. Science 293:484–487
Peckmann J, Reimer A, Luth U, Luth C, Hansen BT, Heinicke C, Hoefs J, Reitner J (2001) Methane-derived carbonates and authigenic pyrite from the northwestern Black Sea. Mar Geol 177:129–150
Pierre C, Mascle J, Dupré S, the Medeco Leg2 Scientific Party (2008) MEDECO Leg 2 cruise report, R/V Pourquoi pas? 02 to 30 November 2007, Rhodes-Toulon. Ifremer, Paris. http://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00134/24550/
Pierre C, Blanc-Valleron M-M, Demange J, Boudouma O, Foucher J-P, Pape T, Himmler T, Fekete N, Spiess V (2012) Authigenic carbonates from active methane seeps offshore southwest Africa. Geo-Mar Lett 32(5/6):501–513. doi:10.1007/s00367-012-0295-x
Prinzhofer A, Deville E (2013) Origins of hydrocarbon gas seeping out from offshore mud volcanoes in the Nile delta. Tectonophysics 591:52–61
Ritt B, Pierre C, Gauthier O, Wenzhöfer F, Boetius A, Sarrazin J (2011) Diversity and distribution of cold-seep fauna associated with different geological and environmental settings at mud volcanoes and pockmarks of the Nile Deep-Sea Fan. Mar Biol 158(6):1187–1210. doi:10.1007/s00227-011-1679-6
Rongemaille E, Bayon G, Pierre C, Bollinger C, Chu NC, Favreau E, Fouquet Y, Riboulot V, Voisset M (2011) Rare earth elements in cold seep carbonates from the Niger Delta. Chem Geol 286:196–206
Rosenfeld WD, Silverman SR (1959) Carbon isotope fractionation in bacterial production of methane. Science 130:1658–1659
Sardou O, Mascle J (2003) Cartography by multibeam echo-sounder of the Nile deep-sea Fan and surrounding areas. 2 sheets, special publication CIESM, Monaco
Stadnitskaia A, Nadezhkin D, Abbas B, Blinova V, Ivanov MK, Sinninghe Damsté JS (2008) Carbonate formation by anaerobic oxidation of methane: evidence from lipid biomarker and fossil 16S rDNA. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:1824–1836
Tarutani T, Clayton RN, Mayeda TK (1969) The effect of polymorphism and magnesium substitution of oxygen isotope fractionation between calcium carbonate and water. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 33:987–996
Torres ME, Bohrmann G, Dubé TE, Poole FG (2003) Formation of modern and Paleozoic stratiform barite at cold methane seeps on continental margins. Geology 31:897–900
Vandré C, Cramer B, Gerling P, Winsemann J (2007) Natural gas formation in the western Nile delta (Eastern Mediterranean): thermogenic versus microbial. Org Geochem 38:523–539
Wallmann K, Aloisi G, Haeckel M, Tishchenko P, Pavlova G, Greinert J, Kutterfolf S, Eisenhauer A (2008) Silicate weathering in anoxic marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:3067–3090
Whiticar MJ (1999) Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane. Chem Geol 161:291–314
Woodside JM, Volgin AV (1996) Brine pools associated with Mediterranean Ridge mud diapirs: an interpretation of echo-free patches in deep tow sidescan sonar data. Mar Geol 132:55–61
Acknowledgements
We thank the crews and scientific party of the Medeco2 expedition aboard the R/V Pourquoi pas? with the Ifremer ROV Victor, and are especially grateful to Laëtitia Brosolo for the processing of bathymetric data. The work was supported by HERMES (EC Contract No. GOCE-CT-2005-511234) and HERMIONE (EC Contract No. FP7-ENV-2008-1-226354) programmes funded by the European Commission’s Framework Six and Seven programmes. We acknowledge two anonymous reviewers and Patrice Imbert as a guest editor of the Special Issue GIMS11 Nice for their valuable comments on the earlier version of the manuscript, as well as the journal editors for additional remarks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible guest editor: P. Imbert
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 76 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierre, C., Bayon, G., Blanc-Valleron, MM. et al. Authigenic carbonates related to active seepage of methane-rich hot brines at the Cheops mud volcano, Menes caldera (Nile deep-sea fan, eastern Mediterranean Sea). Geo-Mar Lett 34, 253–267 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-014-0362-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-014-0362-6