Abstract
Objective
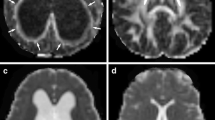
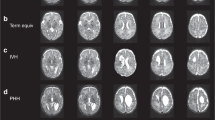
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a non-invasive MRI technique that has been used to quantify white matter (WM) abnormality in both clinical and experimental hydrocephalus (HCP). However, no DTI study has been conducted to characterize anisotropic diffusion properties in an animal model of infantile HCP. This DTI study was designed to investigate a rat model of HCP induced at postnatal day 21, a time developmentally equivalent to the human infancy.
Methods
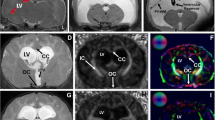
DTI data were acquired at approximately 4 weeks after the induction of HCP with kaolin injection. Using a 7 Tesla small animal MRI scanner we performed high-resolution DTI on 12 rats with HCP and 6 saline controls. Regions of interest (ROI) examined with quantitative comparisons include the genu, body, and splenium of the corpus callosum (gCC, bCC, and sCC, respectively), anterior, middle, and posterior external capsule (aEC, mEC, and pEC, respectively), internal capsule (IC), and fornix (FX). For each ROI, DTI metrics including fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (Dax), and radial diffusivity (Drad) were calculated.
Results
We found that the anisotropic diffusion properties were abnormal across multiple WM regions in the brains of the HCP rats. Statistically significant differences included: (1) decreased FA and increased MD and Drad values in the gCC and bCC; (2) increased Dax in the sCC; (3) increased FA and Dax in the aEC; (4) increased FA in the mEC; (5) increased MD and Drad in the pEC; (6) increased FA and Dax in IC; (7) increased FA in FX.
Conclusions
These preliminary results provide the first evidence of WM injury quantified by DTI in a rat model of infantile HCP. Our data showed that DTI is a sensitive tool to characterize patterns of WM abnormalities and support the notion that WM impairment is region specific in response to HCP.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Del Bigio MR (1993) Neuropathological changes caused by hydrocephalus. Acta Neuropathol 85:573–585
Del Bigio MR, Wilson MJ, Enno T (2003) Chronic hydrocephalus in rats and humans: white matter loss and behavior changes. Ann Neurol 53:337–346
Eskandari R, McAllister JP 2nd, Miller JM, Ding Y, Ham SD, Shearer DM, Way JS (2004) Effects of hydrocephalus and ventriculoperitoneal shunt therapy on afferent and efferent connections in the feline sensorimotor cortex. J Neurosurg 101:196–210
Kriebel RM, McAllister JP 2nd (2000) Pathology of the hippocampus in experimental feline infantile hydrocephalus. Neurol Res 22:29–36
Rosenberg GA, Saland L, Kyner WT (1983) Pathophysiology of periventricular tissue changes with raised CSF pressure in cats. J Neurosurg 59:606–611
Fletcher JM, Bohan TP, Brandt ME, Brookshire BL, Beaver SR, Francis DJ, Davidson KC, Thompson NM, Miner ME (1992) Cerebral white matter and cognition in hydrocephalic children. Arch Neurol 49:818–824
Fletcher JM, Bohan TP, Brandt ME, Kramer LA, Brookshire BL, Thorstad K, Davidson KC, Francis DJ, McCauley SR, Baumgartner JE (1996) Morphometric evaluation of the hydrocephalic brain: relationships with cognitive development. Childs Nerv Syst 12:192–199
Fletcher JM, McCauley SR, Brandt ME, Bohan TP, Kramer LA, Francis DJ, Thorstad K, Brookshire BL (1996) Regional brain tissue composition in children with hydrocephalus. Relationships with cognitive development. Arch Neurol 53:549–557
Hannay HJ (2000) Functioning of the corpus callosum in children with early hydrocephalus. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 6:351–361
Tashiro Y, Drake JM (1998) Reversibility of functionally injured neurotransmitter systems with shunt placement in hydrocephalic rats: implications for intellectual impairment in hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 88:709–717
Wunschmann A, Oglesbee M (2001) Periventricular changes associated with spontaneous canine hydrocephalus. Vet Pathol 38:67–73
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455
Air EL, Yuan W, Holland SK, Jones BV, Bierbrauer K, Altaye M, Mangano FT (2010) Longitudinal comparison of pre- and postoperative diffusion tensor imaging parameters in young children with hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:385–391
Assaf Y, Ben-Sira L, Constantini S, Chang LC, Beni-Adani L (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging in hydrocephalus: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1717–1724
Yuan W, Mangano FT, Air EL, Holland SK, Jones BV, Altaye M, Bierbrauer K (2009) Anisotropic diffusion properties in infants with hydrocephalus: a diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(9):1792–1798
Yuan W, Deren KE, McAllister JP 2nd, Holland SK, Lindquist DM, Cancelliere A, Mason M, Shereen A, Hertzler DA, Altaye M, Mangano FT (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging correlates with cytopathology in a rat model of neonatal hydrocephalus. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res 7:19
de Graaf-Peters VB, Hadders-Algra M (2006) Ontogeny of the human central nervous system: what is happening when? Early Hum Dev 82:257–266
Del Bigio MR, Kanfer JN, Zhang YW (1997) Myelination delay in the cerebral white matter of immature rats with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus is reversible. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:1053–1066
Del Bigio MR, Zhang YW (1998) Cell death, axonal damage, and cell birth in the immature rat brain following induction of hydrocephalus. Exp Neurol 154:157–169
Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Kim J, Pearlson GD, Mori S (2006) DtiStudio: resource program for diffusion tensor computation and fiber bundle tracking. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 81(2):106–116
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J 66:259–267
Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, Barnett A, Di Chiro G (1996) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201:637–648
Evans W (1942) An encephalographic ratio for estimating ventricular enlargement and cerebral atrophy. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 47:7
Hanson J, Levander B, Liliequist B (1975) Size of the intracerebral ventricles as measured with computer tomography, encephalography and echoventriculography. Acta Radiol Suppl 346:98–106
Lloyd SP (1982) Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans Information Theory 28(2):129–137
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Stat Soc Ser B 57:1919–1925
Yuan W, Holland SK, Jones BV, Crone K, Mangano FT (2008) Characterization of abnormal diffusion properties of supratentorial brain tumors: a preliminary diffusion tensor imaging study. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1(4):263–269
Budde MD, Kim JH, Liang HF, Russell JH, Cross AH, Song SK (2008) Axonal injury detected by in vivo diffusion tensor imaging correlates with neurological disability in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. NMR Biomed 21(6):589–597
Song SK, Sun SW, Ju WK, Lin SJ, Cross AH, Neufeld AH (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal ischemia. NeuroImage 20(3):1714–1722
Song SK, Yoshino J, Le TQ, Lin SJ, Sun SW, Cross AH, Armstrong RC (2005) Demyelination increases radial diffusivity in corpus callosum of mouse brain. NeuroImage 26(1):132–140
Goebell E, Paustenbach S, Vaeterlein O, Ding XQ, Heese O, Fiehler J, Kucinski T, Hagel C, Westphal M, Zeumer H (2006) Low-grade and anaplastic gliomas: differences in architecture evaluated with diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 239(1):217–222
Hanigan WC, Bogner D (2010) Cerebrovascular physiology in perinates with congenital hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 26(6):775–780
Leliefeld PH, Gooskens RH, Vincken KL, Ramos LM, van der Grond J, Tulleken CA et al (2008) Magnetic resonance imaging for quantitative flow measurement in infants with hydrocephalus: a prospective study. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2:163–170
Shirane R, Sato S, Sato K, Kameyama M, Ogawa A, Yoshimoto T et al (1992) Cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism in infants with hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 8:118–123
da Silva MC, Michowicz S, Drake JM, Chumas PD, Tuor UI (1995) Reduced local cerebral blood flow in periventricular white matter in experimental neonatal hydrocephalus—restoration with CSF shunting. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15:1057–1065
Higashi K, Asahisa H, Ueda N, Kobayashi K, Hara K, Noda Y (1986) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in experimental hydrocephalus. Neurol Res 8:169–176
Jones HC, Richards HK, Bucknall RM, Pickard JD (1993) Local cerebral blood flow in rats with congenital hydrocephalus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13:531–534
Richards HK, Bucknall RM, Jones HC, Pickard JD (1995) Uncoupling of LCBF and LCGU in two different models of hydrocephalus: a review. Childs Nerv Syst 11:288–292
Chumas PD, Drake JM, Del Bigio MR, da Silva MC, Tuor UI (1994) Anaerobic glycolysis preceding white-matter destruction in experimental neonatal hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 80:491–501
Deren KE, Packer M, Forsyth J, Milash B, Abdullah OM, Hsu EW et al (2010) Reactive astrocytosis, microgliosis and inflammation in rats with neonatal hydrocephalus. Exp Neurol 226:110–119
Eskandari R, Harris CA, McAllister JP, II (2011) Reactive astrocytosis in feline neonatal hydrocephalus: acute, chronic and shunt-induced changes. Childs Nerv Syst [Epub ahead of print]
Miller JM, McAllister JP (2007) Reduction of astrogliosis and microgliosis by cerebrospinal fluid shunting in experimental hydrocephalus. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res 4:5
Acknowledgments
This study is supported in part by the Robert L. McLaurin, MD, Faculty Development Scholarship in Neurosurgery at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, the Department of Neurosurgery at the University of Utah, and Primary Children’s Medical Center Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, W., McAllister, J.P., Lindquist, D.M. et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter injury in a rat model of infantile hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 28, 47–54 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1590-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1590-y