Abstract
Purpose
Cerebellar mutism is a serious neurosurgical complication after posterior fossa surgery, but the cause, incidence and outcome remain incompletely defined. The aim of this paper was to identify and review all reports of this phenomenon to better delineate and improve the evidence base.
Methods
A systematic search and retrieval of databases was conducted using advanced search techniques. Review/outcomes criteria were developed, and study quality was determined.
Results
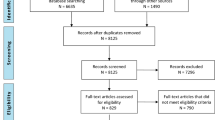
The retrieval identified 2,281 papers of which 96 were relevant, identifying 650 children with cerebellar mutism. Causative factors, clinical features and outcomes were reported variably; papers focussed on multiple areas, the majority reporting incidence in single or series of case studies with little or no analysis further than description.
Conclusions
The complexity and variability of data reporting, likely contributing factors and outcomes make cerebellar mutism difficult to predict in incidence and the degree of impact that may ensue. A clear and accepted universal definition would help improve reporting, as would the application of agreed outcome measures. Clear and consistent reporting of surgical technique remains absent. Recommendations for practice are provided.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clerico A, Sordi A, Ragni G, Festa A, Cappelli C, Maini CL (2002) Brief report: transient mutism following posterior fossa surgery studied by single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). Med Pediatr Oncol 38:445–448
Ersahin Y, Mutluer S, Cagli S, Duman Y (1996) Cerebellar mutism: report of seven cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 38:60–66
Watanabe Y, Yamasaki F, Nakamura K, Kajiwara Y, Takayasu T, Nosaka R, Sugiyama K, Kobayashi M, Kurisu K (2012) Evaluation of cerebellar mutism by arterial spin-labeling perfusion magnetic resonance imaging in a patient with atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT): a case report. Childs Nerv Syst 28:1257–1260
Daniels SR, Moores LE, DiFazio MP (2005) Visual disturbance associated with postoperative cerebellar mutism. Pediatr Neurol 32:127–130
Lewis FM, Murdoch BE (2011) Language outcomes following risk-adapted treatments for tumors located within the posterior fossa. J Child Neurol 26:440–452
Liu GT, Phillips PC, Molloy PT, Needle M, Galetta SL, Balcer LJ, Schut L, Duhaime A-C, Sutton LN (1998) Visual impairment associated with mutism after posterior fossa surgery in children. Neurosurgery 42:253–256
Zaheer SN, Wood M (2010) Experiences with the telovelar approach to fourth ventricular tumors in children. Pediatr Neurosurg 46:340–343
Morris EB, Phillips NS, Langingham FH, Patay Z, Gajjar A, Wallace D, Boop F, Sanford R, Ness KK, Ogg RJ (2009) Proximal dentatothalamocortical tract involvement in posterior fossa syndrome. Brain 132:3087–3095
Mortimer DS (2011) Clinical case study: a 4-year-old boy with posterior fossa syndrome after resection of a medulloblastoma. J Neurosci Nurs 43:225–229
Roka YB, Shrestha M, Aryal S (2011) Cerebellar mutism after pineal tumour excision: a case report. J Nepal Paediatr Soc 31:124–126
Shyu C, Burke K, Souweidane MM, Dunkel IJ, Gilheeney SW, Gershon T, Khakoo Y (2011) Novel use of zolpidem in cerebellar mutism syndrome. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 33:148–149
Akhaddar A, Salami M, El Asri AC, Boucetta M (2012) Treatment of postoperative cerebellar mutism with fluoxetine. Childs Nerv Syst 28:507–508
De Smet HJ, Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Aarsen F, Verhoeven J, Mariën P, Paquier PF (2012) Auditory-perceptual speech analysis in children with cerebellar tumours: a long-term follow-up study. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 16:434–442
Palmer SL, Hassall T, Evankovich K, Mabbott DJ, Bonner M, Deluca C, Cohn R, Fisher MJ, Morris EB, Borniscer A, Gajjar A (2010) Neurocognitive outcome 12 months following cerebellar mutism syndrome in pediatric patients with medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol 12:1311–1317
Rubens J, Lulla RR, Lai J-S, Fangusaro J (2012) A pilot study evaluating long-term impact of posterior fossa syndrome on quality of life in survivors of childhood medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol 14:ii111
Wells EM, Khademian ZP, Walsh KS, Vezina G, Sposto R, Keating RF, Packer RJ (2010) Postoperative cerebellar mutism syndrome following treatment of medulloblastoma: neuroradiographic features and origin. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:329–334
Rekate HL, Grubb RL, Aram DM, Hahn JF, Ratcheson RA (1985) Muteness of cerebellar origin. Arch Neurol 42:697–698
Di Rocco C, Chieffo D, Frassanito P, Caldarelli M, Massimi L, Tamburrini G (2011) Heralding cerebellar mutism: evidence for pre-surgical language impairment as primary risk factor in posterior fossa surgery. Cerebellum 10:551–562
El-Nabbout BH, DeLong GR (2002) Treatment of cerebellar mutism with fluoxetine: report on two patients. Annal Neurol 52(3):S161–S161
Gudrunardottir T, Sehested A, Juhler M, Schmiegelow K (2011) Cerebellar mutism: review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 27:355–363
Sagiuchi T, Ishii K, Aoki Y, Kan S, Utsuki S, Tanaka R, Fujii K, Hayakawa K (2001) Bilateral crossed cerebello-cerebral diaschisis and mutism after surgery for cerebellar medulloblastoma. Ann Nucl Med 15:157–160
Korah MP, Esiashvili N, Mazeski CM, Hudgins RJ, Tighiouart M, Janss AJ, Schwaibold FP, Crocker IR, Curran WJ, Marcus RB (2010) Incidence, risks, and sequelae of posterior fossa syndrome in pediatric medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:106–112
Küpeli S, Yalcin B, Bilginer B, Akalan N, Haksal P, Buyukpamukcu M (2011) Posterior fossa syndrome after posterior fossa surgery in children with brain tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 56:206–210
Robertson PL, Muraszko KM, Holmes EJ, Sposto R, Packer RJ, Gajjar A, Dias MS, Allen JC (2006) Incidence and severity of postoperative cerebellar mutism syndrome in children with medulloblastoma: a prospective study by the Children’s Oncology Group. J Neurosurg 105:444–451
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151:264–269
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2012) Appendix D: methodology checklist: cohort studies. In: Process and methods guides. The guidelines manual: appendices B–I. http://publications.nice.org.uk/the-guidelines-manual-appendices-bi-pmg6b/appendix-d-methodology-checklist-cohort-studies#notes-on-use-of-methodology-checklist-cohort-studies Accessed 30 Jul 2013
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2012) Appendix E: methodology checklist: case–control studies. In: Process and methods guides. The guidelines manual: appendices B–I. http://publications.nice.org.uk/the-guidelines-manual-appendices-bi-pmg6b/appendix-e-methodology-checklist-casecontrol-studies#notes-on-use-of-the-methodology-checklist-casecontrol-studies Accessed 30 Jul 2013
Phillips B, Ball C, Sackett D, Badenoch D, Straus S, Haynes B, Dawes M, Howick J (2009) Oxford centre for evidence-based medicine—levels of evidence 1 http://www.cebm.net/index.aspx?o=1025 Accessed 07 Nov 2013
Hayden JA, Côté P, Bombardier C (2006) Evaluation of the quality of prognosis studies in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med 144:427–437
Adachi J, Nishikawa R, Hirose T, Matsutani M (2005) Mixed neuronal-glial tumor of the fourth ventricle and successful treatment of postoperative mutism with bromocriptine: case report. Surg Neurol 63:375–379
Afshar M, Link M, Edwards MSB, Fisher PG, Fredrick D, Monje M (2012) Complete ocular paresis in a child with posterior fossa syndrome. Pediatr Neurosurg 48:51–54
Aguiar PH, Plese JPP, Ciquini O, Marino R (1995) Transient mutism following a posterior fossa approach to cerebellar tumors in children: a critical review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 11:306–310
Annett RD, Heideman RL (2004) Cerebellar mutism following surgical resection for pediatric medulloblastoma: a marker diaschisis and neuropsychological compromise. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 19:982–982
Al-Jarallah A, Cook JD, Gascon G, Kanaan I, Sigueira E (1994) Transient mutism following posterior fossa surgery in children. J Surg Oncol 55:126–131
Ammirati M, Mirzai S, Samii M (1989) Transient mutism following removal of a cerebellar tumor. A case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 5:12–14
Arslantas A, Erhan C, Emre E, Estref T (2002) Transient cerebellar mutism after posterior fossa surgery. J Postgrad Med 48:158–159
Asamoto M, Ito H, Suzuki N, Oiwa Y, Saito K, Haraoka J (1994) Transient mutism after posterior fossa surgery. Childs Nerv Syst 10:275–278
Bhatoe HS (1997) Mutism, oropharyngeal apraxia and dysarthria after posterior fossa tumour excision. Br J Neurosurg 11:341–343
Brinkman TM, Palmer SL, Chen S, Zhang H, Evankovich K, Swain MA, Bonner MJ, Janzen L, Knight S, Armstrong CL, Boyle R, Gajjar A (2012) Parent-reported social outcomes after treatment for pediatric embryonal tumors: a prospective longitudinal study. J Clin Oncol 30:4134–4140
Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Aarsen FK (2010) The spectrum of neurobehavioural deficits in the posterior fossa syndrome in children after cerebellar tumour surgery. Cortex 46:933–946
Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Van Dongen HR, Aarsen FK, Paquier PF (2003) Transient cerebellar eye closure and mutism after cerebellar tumor surgery: long-term clinical follow-up of neurologic and behavioral disturbances in a 14-year-old girl. Pediatr Neurosurg 38:122–127
Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Van Dongen HR, Mulder PGH, Paz y Gueze D, Paquier PF, Lequin MH (1999) Tumour type and size are high risk factors for the syndrome of “cerebellar” mutism and subsequent dysarthria. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:755–757
Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Van Dongen HR, Zwetsloot CP (1992) Transient loss of speech followed by dysarthria after removal of posterior fossa tumour. Dev Med Child Neurol 34:1102–1109
Dailey AT, McKhann GM II, Mitchel SB (1995) The pathophysiology of oral pharyngeal apraxia and mutism following posterior fossa tumor resection in children. J Neurosurg 83:467–475
De Smet HJ, Baillieux H, Wackenier P, De Praeter M, Engelborghs S, Paquier PF, De Deyn PP, Marien P (2009) Long-term cognitive deficits following posterior fossa tumor resection: a neuropsychological and functional neuroimaging follow-up study. Neuropsychology 23:694–704
Di Cataldo A, Dollo C, Astuto M, La Spina M, Ippolito S, Papotto M, Giuffrida S (2001) Mutism after surgical removal of a cerebellar tumor: two case reports. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 18:117–121
Dietze DD, Mickle JP (1991) Cerebellar mutism after posterior fossa surgery. Neurosurgery 16:25–31
Doxey D, Bruce D, Sklar F, Swift D, Shapiro K (1999) Posterior fossa syndrome: identifiable risk factors and irreversible complications. Pediatr Neurosurg 31:131–136
El Beltagy M, Atteya MME (2013) The benefits of navigated intraoperative ultrasonography during resection of fourth ventricular tumors in children. Childs Nerv Syst 29:1079–1088
Ellis DL, Kanter J, Walsh JW, Drury SS (2011) Posterior fossa syndrome after surgical removal of a pineal gland tumor. Pediatr Neurol 45:417–419
Ersahin Y, Mutluer S, Saydem S, Barcin E (1997) Cerebellar mutism: report of two unusual cases and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 99:130–134
Ersahin Y, Yararbas U, Duman Y, Mutluer S (2002) Single photon emission tomography following posterior fossa surgery in patients with and without mutism. Childs Nerv Syst 18:318–325
Ferrante L, Mastronardi L, Acqui M, Fortuna A (1990) Mutism after posterior fossa surgery in children. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg 72:959–963
Gajjar A, Sanford RA, Bhargava R, Heideman R, Walter A, Li Y, Langston JW, Jenkins JJ, Muhlbauer M, Boyett J, Kun LE (1996) Medulloblastoma with brain stem involvement: the impact of gross total resection on outcome. Pediatr Neurosurg 25:182–187
Gangemi M, Maiuri F, Signoa L, Sardo L (2000) Mutism after surgery for posterior fossa tumors in children. Neurol Psychiatr Brain Res 8:37–42
Germano A, Baldari S, Caruso G, Caffo M, Montemagno G, Cardia E, Tomasello F (1998) Reversible cerebral perfusion alterations in children with transient mutism after posterior fossa surgery. Childs Nerv Syst 14:114–119
Harrell LM, Marks WA, Murray JC, Colaluca B, Braly EZ (2010) Duration of in-patient neurorehabilitation course and improvement in neurologic function for posterior fossa syndrome: differences between benign and malignant tumors. Neuro Oncol 12(6):ii113
He X, Ma J, Ma C, Han Y (2012) The cerebellomedullary fissure approach is a better method for the patients with tumor in the fourth ventricle zone or at the back of the pons. Childs Nerv Syst 28:1611
Herb E, Thyen U (1992) Mutism after cerebellar medulloblastoma surgery. Neuropediatrics 23:144–146
Huber JF, Bradley K, Spiegler BJ, Dennis M (2006) Long-term effects of transient cerebellar mutism after cerebellar astrocytoma or medulloblastoma tumor resection in childhood. Childs Nerv Syst 22:132–138
Jones S, Kirollos RW, Van Hille PT (1996) Cerebellar mutism following posterior fossa tumour surgery. Br J Neurosurg 10:221–224
Kalelioglu M, Isik N, Isik N, Sarier M (1995) Mutism after total removal of medulloblastoma: case report. Turk Neurosurg 5:62–64
Kellogg WK Foundation (2004) Logic model development guide. In: Knowledge Centre, WK Kellogg Foundation. http://www.wkkf.org/knowledge-center/resources/2006/02/wk-kellogg-foundation-logic-model-development-guide.aspx Accessed 16 Dec 2012
Kingma A, Mooij JJA, Metzemaekers JDM, Leeuw JA (1994) Transient mutism and speech disorders after posterior fossa surgery in children with brain tumours. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 131:74–79
Kirk EA, Howard VC, Scott CA (1995) Description of posterior fossa syndrome in children after posterior fossa brain tumor surgery. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs 12:181–188
Kotíl K, Eras M, Akçetín M, Bílge T (2008) Cerebellar mutism following posterior fossa tumor resection in children. Turk Neurosurg 18:89–94
Law N, Greenberg N, Bouffet E, Taylor MD, Laughlin S, Strother D, Fryer C, McConnell D, Hukin J, Kaise C, Wang F, Mabbott DJ (2012) Clinical and neuroanatomical predictors of cerebellar mutism syndrome. Neuro Oncol 14:1294–1303
Levisohn L, Cronin-Golomb A, Schmahmann JD (2000) Neuropsychological consequences of cerebellar tumour resection in children: cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome in a paediatric population. Brain 123:1041–1050
Maffei M, Simonetti L, Agati R, Calbucci F, Leonardi M (2005) Cerebellar mutism after medulloblastoma resection: importance of MR features. Riv Neuroradiol 18:201–204
May L (2012) Posterior fossa syndrome. Childs Nerv Syst 28:1626
McMillan HJ, Keene DL, Matzinger MA, Vassilyadi M, Nzau M, Venureyra ECG (2009) Brainstem compression: a predictor of postoperative cerebellar mutism. Childs Nerv Syst 25:677–681
Mei C, Morgan AT (2011) Incidence of mutism, dysarthria and dysphagia associated with childhood posterior fossa tumour. Childs Nerv Syst 27:1129–1136
Miller NG, Reddick WE, Kocak M, Glass JO, Lobel U, Morris B, Gajjar A, Patay Z (2010) Cerebellocerebral diaschisis is the likely mechanism of postsurgical posterior fossa syndrome in pediatric patients with midline cerebellar tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:288–294
Moertel C, Passe TJ, Bobra S, Hargens L, Dahlheimer T, Finkelstein M (2007) Posterior fossa syndrome and atrophy in children with posterior fossa tumors. Neuro Oncol 9:172
Morgan AT, Liegois F, Liederkerke C, Vogel AP, Hayward R, Harkness W, Chong K, Vargha-Khadem F (2011) Role of cerebellum in fine speech control in childhood: persistent dysarthria after surgical treatment for posterior fossa syndrome. Brain Lang 117:69–76
Nagatani K, Waga S, Nakagawa Y (1991) Mutism after removal of a vermian medulloblastoma: cerebellar mutism. Surg Neurol 36:307–309
Ozgur BM, Berberian J, Aryan HE, Meltzer HS, Levy L (2006) The pathophysiologic mechanism of cerebellar mutism. Surg Neurol 66:18–25
Ozimek A, Richter S, Hein-Kropp C, Schoch B, Goriβen B, Kaiser O, Gizewiski E, Ziegler W, Timmann D (2004) Cerebellar mutism—report of four cases. J Neurol 251:963–972
Pearlman LS, McVittie A, Hunter K (2008) Discharge management of an adolescent female with posterior fossa syndrome: a case report. Can J Neurosci Nurs 30:14–21
Pollack IF (2001) Neurobehavioral abnormalities after posterior fossa surgery in children. Int Rev Psychiatr 13:302–312
Pollack IF (1997) Posterior fossa syndrome. Int Rev Neurobiol 41:411–432
Pollack IF, Polinko P, Albright L, Towbin R, Fitz C (1995) Mutism and pseudobulbar symptoms after resection of posterior fossa tumors in children: incidence and pathophysiology. Neurosurgery 37:885–893
Riva D, Giorgi C (2000) The cerebellum contributes to higher functions during development: evidence from a series of children surgically treated for posterior fossa tumours. Brain 123:1051–1061
Salvati M, Cervoni L, Santoro A (1996) Cerebellar mutism after posterior fossa surgery. J Neurosurg Sci 40:59–63
Servitzoglou M, Brock P, Hayward R, Gumley D, Phipps K, Levitt G (2007) Persisting posterior fossa syndrome morbidity in medulloblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 49:507–508
Siffert J, Allen J, Epstein F (1995) The posterior fossa syndrome following tumor resection: incidence, clinical features, and long-term outcome. Ann Neurol 38:553–553
Siffert J, Poussaint TY, Goumnerova LC, Scott RM, LaValley B, Tarbell NJ, Pomeroy SL (2000) Neurological dysfunction associated with postoperative cerebellar mutism. J Neurooncol 48:75–81
Soelva V, Abbushi A, Rueckriegel S, Bruhn H, Hernaiz P, Haberl EJ, Eisner W, Thomale UW (2010) Fronto-cerebellar fiber tractography after cerebellar tumor removal—correlation with clinical outcome. Neuro Oncol 12:ii33
Steinbok P, Cochrane DD, Perrin R, Price A (2003) Mutism after posterior fossa tumour resection in children: incomplete recovery on long-term follow-up. Pediatr Neurosurg 39:179–183
Trivedi M, O’Kane R, Picton S, Elliott M, Crimmins D, Tyagi A, Chumas P, Goodden J (2012) Ten years of paediatric posterior fossa tumours, the Leeds experience. Childs Nerv Syst 28:777
Turkel SB, Chen LS, Nelson MD, Hyder D, Gilles FH, Woodall L, Braslow K, Tavare CJ (2004) Case series: acute mood symptoms associated with posterior fossa lesions in children. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 16:443–445
Turkel SB, Krieger M, Chen L, Jubran R, Tavare CJ (2007) Progression of the posterior fossa syndrome. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 19:223
Turkel SB, Krieger MD, O’Neil S, Jubran R, Tavare CJ (2012) Symptoms before and after posterior fossa surgery in pediatric patients. Pediatr Neurosurg 48:21–25
Ugwu F, Kamaly-Asl I, Josan V (2012) Posterior fossa tumour surgery and perioperative course—a single institution experience. Childs Nerv Syst 28:777
Van Calenbergh F, Van de Laar A, Plets C, Goffin J, Casaer P (1995) Transient cerebellar mutism after posterior fossa surgery in children. Neurosurgery 37:894–898
Van Dongen HR, Catsman-Berrevoets CE, van Mourik M (1994) The syndrome of cerebellar mutism and subsequent dysarthria. Neurology 44:2040–2046
Van Mourik M, Catsman-Berrevoets CE, van Dongen HR, Neville BGR (1997) Complex orofacial movements and the disappearance of cerebellar mutism: report of five cases. Dev Med Child Neurol 39:686–690
Vandeinse D, Hornyak JE (1997) Linguistic and cognitive deficits associated with cerebellar mutism. Pediatr Rehabil 1:41–44
Volcan I, Cole GP, Johnston K (1986) A case of muteness of cerebellar origin. Arch Neurol 43:313–314
Wang YT, Kent RD, Duffy JR, Thomas JE, Fredericks GV (2006) Dysarthria following cerebellar mutism secondary to resection of a fourth ventricle medulloblastoma: a case study. J Med Speech Lang Pathol 14:109–122
Wolfe-Christensen C, Mullins LL, Scott JG, McNall-Knapp RY (2007) Persistent psychosocial problems in children who develop posterior fossa syndrome after medulloblastoma resection. Pediatr Blood Cancer 49:723–726
Anderson LM, Petticrew M, Rehfuess E, Armstrong R, Ueffing E, Baker P, Francis D, Tugwell P (2011) Using logic models to capture complexity in systematic reviews. Res Synth Methods 2:33–42
Mitchum R (2010) ASCO 2010: chasing waterfall plots. In: Science Life. The University of Chicago Medicine and Biological Sciences. http://sciencelife.uchospitals.edu/2010/06/08/asco-2010-chasing-waterfall-plots/ Accessed 10 Mar 2013
Nieto A, Gómez J (2010) Waterfall plots: a beautiful way of showing a whole picture of an interesting outcome. PhUSE (Association Programming Pharmaceutical Users Software Exchange Website) Wiki 2010. http://www.phusewiki.org/docs/2010/2010%20PAPERS/SP08%20Paper.pdf Accessed 10 Mar 2013
Brace N, Kemp R, Snelgar R (2012) Multiple regression. In: SPSS for Psychologists. http://www.palgrave.com/pdfs/0333734718.pdf Accessed 09 Aug 2013
De Leval MR, François K, Bull C, Brawn W, Spiegelhalter D (1994) Analysis of a cluster of surgical failures. Application to a series of neonatal arterial switch operations. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 107:914–924
Satz P (1993) Brain reserve capacity on symptom onset after brain injury: a formulation and review of evidence for threshold theory. Neuropsychology 7:273–295
Palmer SL, Glass JO, Li Y, Ogg R, Qaddoumi I, Armstrong GT, Wright K, Wetmore C, Broniscer A, Gajjar A, Reddick WE (2012) White matter integrity is associated with cognitive processing in patients treated for a posterior fossa tumor. Neuro Oncol 14:1185–1192
Williamson PR, Altman DG, Blazeby JM, Clarke M, Gargon E (2011) The COMET (core outcome measures in effectiveness trials) initiative. Trials 12:A70
Wefel JS, Vardy J, Ahles T, Schagen SB (2011) International cognition and cancer task force recommendations to harmonise studies of cognitive function in patients with cancer. Lancet Oncol 12:703–708
Haeusler GM, Phillips RS, Lehrnbecher T, Sung L, Ammann RA (2013) The reporting of outcomes in studies of fever and neutropenia in children with cancer: time for consensus. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60:1563–1564
Widemann BC, Balis FM, Kempf-Bielack B, Bielack S, Pratt CB, Ferrari S, Bacci G, Craft AW, Adamson PC (2004) High-dose methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer 100:2222–2232
Askie LM, Brocklehurst P, Darlow BA, Finer N, Schmidt B, Tarnow-Mordi W, for the NeOProM Collaborative Group (2011) NeOProM: Neonatal Oxygenation Prospective Meta-analysis Collaboration study protocol. BMC Pediatr 11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-11-6
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to give their full thanks to the candlelighters, Elizabeth Neilly and Jenny Makeham. Financial support was received from the Candlelighters charity.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reed-Berendt, R., Phillips, B., Picton, S. et al. Cause and outcome of cerebellar mutism: evidence from a systematic review. Childs Nerv Syst 30, 375–385 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2356-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2356-0