Abstract
Purpose
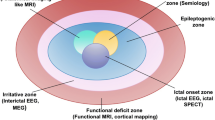
In order to presurgically define the anatomical location of the epileptogenic zone (EZ) and its proximity to possible cortical and subcortical eloquent areas in pediatric patients with medically intractable focal epilepsy, an array of noninvasive tools are available: recorded seizure semiology, scalp electroencephalographic (EEG) recordings (ictal and interictal epileptic patterns), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), ictal single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), neuropsychological testing, and/or magnetoencephalography. When the noninvasive tools fail or are insufficient in precisely localizing the EZ and its functional and anatomical interphase with potential eloquent cortical areas, invasive extra-operative monitoring procedures might be needed.
Discussion
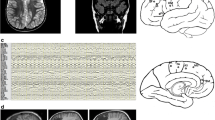
In this chapter, we will discuss the main goals of extra-operative invasive evaluation for children with medically intractable epilepsy in whom cortical dysplasia is a possible etiology. We will specifically discuss the possible indications, surgical strategies, results, and morbidity associated with the placement of subdural and stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) electrodes. The rationale behind the choice of each one of the above techniques will also be discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelson PD, O'Rourke DK, Albright AL (1995) Chronic invasive monitoring for identifying seizure foci in children. Neurosurg Clin N Am 6(3):491–504
Almeida AN, Martinez V, Feindel W (2005) The first case of invasive EEG monitoring for the surgical treatment of epilepsy: historical significance and context. Epilepsia 46(7):1082–1085
Avanzini GG (1994) Discussion of stereoelectroencephalography. Acta Neurol Scand 152:70–73
Bancaud J, Angelergues R, Bernouilli C (1970) Functional stereotaxic exploration (SEEG) of epilepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 28(1):85–86
Battaglia G, Chiapparini L, Franceschetti S et al (2006) Periventricular nodular heterotopia: classification, epileptic history, and genesis of epileptic discharges. Epilepsia 47(1):86–97
Bulacio JC, Jehi L, Wong C et al (2012) Long-term seizure outcome after resective surgery in patients evaluated with intracranial electrodes. Epilepsia 53(10):1722–1730
Chabardès S, Minotti L, Hamelin S et al (2008) Temporal disconnection as an alternative treatment for intractable temporal lobe epilepsy: techniques, complications and results. Neuro-Chirurgie 54(3):297–302
Cossu M, Cardinale F, Castana L et al (2005) Stereoelectroencephalography in the presurgical evaluation of focal epilepsy: a retrospective analysis of 215 procedures. Neurosurgery 57(4):706–718
Cossu M, Cardinale F, Castana L et al (2006) Stereo-EEG in children. Childs Nerv Syst 22(8):766–778
Cossu M, Chabardès S, Hoffmann D, LoRusso G (2008) Presurgical evaluation of intractable epilepsy using stereo-electro-encephalography methodology: principles, technique and morbidity. Neuro-Chirurgie 54(3):367–373
Devaux B, Chassoux F, Guenot M et al (2008) Epilepsy surgery in France. Neuro-Chirurgie 54(3):453–465
Dinner DS, Lüders HO, Klem G (1998) Chronic electrocorticography: Cleveland clinic experience. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 48:58–69
Gonzalez Martinez J, Bulacio J, Alexopoulos A, Jehi L, Bingaman W, Najm I (2012) Stereoelectroencephalography in the “difficult to localize” refractory focal epilepsy: early experience from a North American Epilepsy Center. Epilepsia 54(2):323–330
Guénot M, Isnard J (2008) Epilepsy and insula. Neuro-Chirurgie 54(3):374–381
Jayakar P, Duchowny M, Resnick TJ (1994) Subdural monitoring in the evaluation of children for epilepsy surgery. J Child Neurol 9(2_suppl):261–266
Jeha LE, Najm I, Bingaman W, Dinner D, Widdess-Walsh P, Luders H (2007) Surgical outcome and prognostic factors of frontal lobe epilepsy surgery. Brain 130(Pt 2):574–584
Kellinghaus C, Moddel G, Shigeto H et al (2007) Dissociation between in vitro and in vivo epileptogenicity in a rat model of cortical dysplasia. Epileptic Disord 9(1):11–19
Lee WS, Lee JK, Lee SA, Kang JK, Ko TS (2000) Complications and results of subdural grid electrode implantation in epilepsy surgery. Surg Neurol 54(5):346–351
Marnet D, Devaux B, Chassoux F et al (2008) Surgical resection of focal cortical dysplasias in the central region. Neuro-Chirurgie 54(3):399–408
Marusic P, Najm IM, Ying Z et al (2002) Focal cortical dysplasias in eloquent cortex: functional characteristics and correlation with MRI and histopathologic changes. Epilepsia 43(1):27–32
Nair DR, Burgess R, McIntyre CC, Luders H (2008) Chronic subdural electrodes in the management of epilepsy. Clin Neurophysiol Off J Int Fed Clin Neurophysiol 119(1):11–28
Najm IM, Bingaman WE, Lüders HO (2002) The use of subdural grids in the management of focal malformations due to abnormal cortical development. Neurosurg Clin N Am 13(1):87–92, viii–ix
Onal C, Otsubo H, Araki T et al (2003) Complications of invasive subdural grid monitoring in children with epilepsy. J Neurosurg 98(5):1017–1026
Rosenow F, Lüders H (2001) Presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Brain 124(Pt 9):1683–1700
Russo GL, Tassi L, Cossu M et al (2003) Focal cortical resection in malformations of cortical development. Epileptic Disord 5(Suppl 2):47–51
Rydenhag B, Silander HC (2001) Complications of epilepsy surgery after 654 procedures in Sweden, September 1990-1995: a multicenter study based on the Swedish National Epilepsy Surgery Register. Neurosurgery 49(1):51–56
Siegel AM (2004) Presurgical evaluation and surgical treatment of medically refractory epilepsy. Neurosurg Rev 27(1):1–18, discussion 19–21
Simon SL, Telfeian A, Duhaime AC (2003) Complications of invasive monitoring used in intractable pediatric epilepsy. Pediatr Neurosurg 38(1):47–52
Talairach J, Bancaud J, Bonis A et al (1992) Surgical therapy for frontal epilepsies. Adv Neurol 57:707–732
Vadera S, Mullin J, Bulacio J, Najm I, Bingaman W, Gonzalez-Martinez J (2013) SEEG following subdural grid placement for difficult to localize epilepsy. Neurosurgery 72(5):723–729
Widdess-Walsh P, Jeha L, Nair D, Kotagal P, Bingaman W, Najm I (2007) Subdural electrode analysis in focal cortical dysplasia: predictors of surgical outcome. Neurology 69(7):660–667
Wieser HG (1996) Epilepsy surgery. Baillière Clin Neurol 5(4):849–875
Wyler AR, Walker G, Somes G (1991) The morbidity of long-term seizure monitoring using subdural strip electrodes. J Neurosurg 74(5):734–737
Wyllie E, Cascino GD, Gidal BE, Goddkin HP (eds) (2010) Wyllie’s treatment of epilepsy: principles and practice (Wyllie, Treatment of Epilepsy) Fifth. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Ying Z, Najm IM (2002) Mechanisms of epileptogenicity in focal malformations caused by abnormal cortical development. Neurosurg Clin N Am 13(1):27–33, vii
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonzalez-Martinez, J., Najm, I.M. Indications and selection criteria for invasive monitoring in children with cortical dysplasia. Childs Nerv Syst 30, 1823–1829 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2497-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2497-1