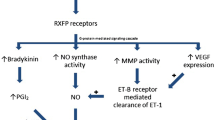
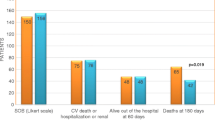
Abstract
Renal dysfunction is a frequent finding in patients with acute heart failure (AHF) and an important prognostic factor for adverse outcomes. Worsening of renal function occurs in 30–50 % of patients hospitalised for AHF, and is associated with increased mortality, prolonged hospital stay and increased risk of readmission. Likely mechanisms involved in the decrease in renal function include impaired haemodynamics and activation of neurohormonal factors, such as the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, the sympathetic nervous system and the arginine–vasopressin system. Additionally, many drugs currently used to treat AHF have a detrimental effect on renal function. Therefore, pharmacotherapy for AHF should carefully take into account any potential complications related to renal function. Serelaxin, currently in clinical development for the treatment of AHF is a recombinant form of human relaxin-2, identical in structure to the naturally occurring human relaxin-2 peptide hormone that mediates cardiac and renal adaptations during pregnancy. Data from both pre-clinical and clinical studies indicate a potentially beneficial effect of serelaxin on kidney function. In this review, we discuss the mechanisms and impact of impairment of renal function in AHF, and the potential benefits of new therapies, such as serelaxin, in this context.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heywood JT, Fonarow GC, Costanzo MR, Mathur VS, Wigneswaran JR, Wynne J (2007) High prevalence of renal dysfunction and its impact on outcome in 118,465 patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: a report from the ADHERE database. J Card Fail 13(6):422–430
Maggioni AP, Dahlstrom U, Filippatos G, Chioncel O, Crespo LM, Drozdz J, Fruhwald F, Gullestad L, Logeart D, Fabbri G, Urso R, Metra M, Parissis J, Persson H, Ponikowski P, Rauchhaus M, Voors AA, Nielsen OW, Zannad F, Tavazzi L (2013) EURObservational Research Programme: regional differences and 1-year follow-up results of the Heart Failure Pilot Survey (ESC-HF Pilot). Eur J Heart Fail 15(7):808–817
Smith GL, Lichtman JH, Bracken MB, Shlipak MG, Phillips CO, DiCapua P, Krumholz HM (2006) Renal impairment and outcomes in heart failure: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 47(10):1987–1996
Hillege HL, Girbes AR, de Kam PJ, Boomsma F, de Zeeuw D, Charlesworth A, Hampton JR, van Veldhuisen DJ (2000) Renal function, neurohormonal activation, and survival in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 102(2):203–210
Smilde TD, Hillege HL, Navis G, Boomsma F, de Zeeuw D, van Veldhuisen DJ (2004) Impaired renal function in patients with ischemic and nonischemic chronic heart failure: association with neurohormonal activation and survival. Am Heart J 148(1):165–172
Swindle J, Chan W, Johnson KW, Becker L, Blauer-Peterson C, Riedel A (2013) Renal impairment in acute heart failure: insights from a managed care database. Circulation 128:A12097
Forman DE, Butler J, Wang Y, Abraham WT, O’Connor CM, Gottlieb SS, Loh E, Massie BM, Rich MW, Stevenson LW, Young JB, Krumholz HM (2004) Incidence, predictors at admission, and impact of worsening renal function among patients hospitalized with heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 43(1):61–67
Nohria A, Hasselblad V, Stebbins A, Pauly DF, Fonarow GC, Shah M, Yancy CW, Califf RM, Stevenson LW, Hill JA (2008) Cardiorenal interactions: insights from the ESCAPE trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 51(13):1268–1274
Blair JE, Pang PS, Schrier RW, Metra M, Traver B, Cook T, Campia U, Ambrosy A, Burnett JC Jr, Grinfeld L, Maggioni AP, Swedberg K, Udelson JE, Zannad F, Konstam MA, Gheorghiade M (2011) Changes in renal function during hospitalization and soon after discharge in patients admitted for worsening heart failure in the placebo group of the EVEREST trial. Eur Heart J 32(20):2563–2572
Gheorghiade M, Pang PS (2009) Acute heart failure syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol 53(7):557–573
Carubelli V, Metra M, Lombardi C, Bettari L, Bugatti S, Lazzarini V, Dei CL (2012) Renal dysfunction in acute heart failure: epidemiology, mechanisms and assessment. Heart Fail Rev 17(2):271–282
Dupont M, Shrestha K, Singh D, Finucan M, Tang WH (2013) Lack of concordance in defining worsening renal function by rise in creatinine vs rise in cystatin C. Congest Heart Fail 19(4):E17–E21
Klein L, Massie BM, Leimberger JD, O’Connor CM, Pina IL, Adams KF Jr, Califf RM, Gheorghiade M (2008) Admission or changes in renal function during hospitalization for worsening heart failure predict postdischarge survival: results from the Outcomes of a Prospective Trial of Intravenous Milrinone for Exacerbations of Chronic Heart Failure (OPTIME-CHF). Circ Heart Fail 1(1):25–33
Damman K, Tang WH, Testani JM, McMurray JJ (2014) Terminology and definition of changes renal function in heart failure. Eur Heart J 35(48):3413–3416
Damman K, Valente MA, Voors AA, O’Connor CM, van Veldhuisen DJ, Hillege HL (2014) Renal impairment, worsening renal function, and outcome in patients with heart failure: an updated meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 35(7):455–469
Kociol RD, Greiner MA, Hammill BG, Phatak H, Fonarow GC, Curtis LH, Hernandez AF (2010) Long-term outcomes of medicare beneficiaries with worsening renal function during hospitalization for heart failure. Am J Cardiol 105(12):1786–1793
Testani JM, McCauley BD, Chen J, Shumski M, Shannon RP (2010) Worsening renal function defined as an absolute increase in serum creatinine is a biased metric for the study of cardio-renal interactions. Cardiology 116(3):206–212
Metra M, Cotter G, Davison BA, Felker GM, Filippatos G, Greenberg BH, Ponikowski P, Unemori E, Voors AA, Adams KF Jr, Dorobantu MI, Grinfeld L, Jondeau G, Marmor A, Masip J, Pang PS, Werdan K, Prescott MF, Edwards C, Teichman SL, Trapani A, Bush CA, Saini R, Schumacher C, Severin T, Teerlink JR (2013) Effect of serelaxin on cardiac, renal, and hepatic biomarkers in the Relaxin in Acute Heart Failure (RELAX-AHF) development program: correlation with outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol 61(2):196–206
Butler J, Forman DE, Abraham WT, Gottlieb SS, Loh E, Massie BM, O’Connor CM, Rich MW, Stevenson LW, Wang Y, Young JB, Krumholz HM (2004) Relationship between heart failure treatment and development of worsening renal function among hospitalized patients. Am Heart J 147(2):331–338
Llorens P, Miro O, Herrero P, Martin-Sanchez FJ, Jacob J, Valero A, Alonso H, Perez-Dura MJ, Noval A, Gil-Roman JJ, Zapater P, Llanos L, Gil V, Perello R (2014) Clinical effects and safety of different strategies for administering intravenous diuretics in acutely decompensated heart failure: a randomised clinical trial. Emerg Med J 31(9):706–713
Rossignol P, Dobre D, McMurray JJ, Swedberg K, Krum H, van Veldhuisen DJ, Shi H, Messig M, Vincent J, Girerd N, Bakris G, Pitt B, Zannad F (2014) Incidence, determinants, and prognostic significance of hyperkalemia and worsening renal function in patients with heart failure receiving the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist eplerenone or placebo in addition to optimal medical therapy: results from the Eplerenone in Mild Patients Hospitalization and Survival Study in Heart Failure (EMPHASIS-HF). Circ Heart Fail 7(1):51–58
Metra M, Davison B, Bettari L, Sun H, Edwards C, Lazzarini V, Piovanelli B, Carubelli V, Bugatti S, Lombardi C, Cotter G, Dei CL (2012) Is worsening renal function an ominous prognostic sign in patients with acute heart failure? The role of congestion and its interaction with renal function. Circ Heart Fail 5(1):54–62
Voors AA, Davison BA, Teerlink JR, Felker GM, Cotter G, Filippatos G, Greenberg BH, Pang PS, Levin B, Hua TA, Severin T, Ponikowski P, Metra M (2014) Diuretic response in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: characteristics and clinical outcome—an analysis from RELAX-AHF. Eur J Heart Fail 16(11):1230–1240
Ronco C, Haapio M, House AA, Anavekar N, Bellomo R (2008) Cardiorenal syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol 52(19):1527–1539
McCullough PA, Haapio M, Mankad S, Zamperetti N, Massie B, Bellomo R, Berl T, Anker SD, Anand I, Aspromonte N, Bagshaw SM, Bobek I, Cruz DN, Daliento L, Davenport A, Hillege H, House AA, Katz N, Maisel A, Mebazaa A, Palazzuoli A, Ponikowski P, Ronco F, Shaw A, Sheinfeld G, Soni S, Vescovo G, Zanco P, Ronco C, Berl T (2010) Prevention of cardio-renal syndromes: workgroup statements from the 7th ADQI consensus conference. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25(6):1777–1784
Cleland JG, Carubelli V, Castiello T, Yassin A, Pellicori P, Antony R (2012) Renal dysfunction in acute and chronic heart failure: prevalence, incidence and prognosis. Heart Fail Rev 17(2):133–149
House AA, Anand I, Bellomo R, Cruz D, Bobek I, Anker SD, Aspromonte N, Bagshaw S, Berl T, Daliento L, Davenport A, Haapio M, Hillege H, McCullough P, Katz N, Maisel A, Mankad S, Zanco P, Mebazaa A, Palazzuoli A, Ronco F, Shaw A, Sheinfeld G, Soni S, Vescovo G, Zamperetti N, Ponikowski P, Ronco C (2010) Definition and classification of cardio-renal syndromes: workgroup statements from the 7th ADQI consensus conference. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25(5):1416–1420
Bidani AK, Griffin KA, Epstein M (2012) Hypertension and chronic kidney disease progression: why the suboptimal outcomes? Am J Med 125(11):1057–1062
Tumlin JA, Costanzo MR, Chawla LS, Herzog CA, Kellum JA, McCullough PA, Ronco C (2013) Cardiorenal syndrome type 4: insights on clinical presentation and pathophysiology from the eleventh consensus conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI). Contrib Nephrol 182:158–173
Biolo A, Fisch M, Balog J, Chao T, Schulze PC, Ooi H, Siwik D, Colucci WS (2010) Episodes of acute heart failure syndrome are associated with increased levels of troponin and extracellular matrix markers. Circ Heart Fail 3(1):44–50
Tsutsui H, Kinugawa S, Matsushima S (2011) Oxidative stress and heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301(6):H2181–H2190
Guazzi M, Gatto P, Giusti G, Pizzamiglio F, Previtali I, Vignati C, Arena R (2013) Pathophysiology of cardiorenal syndrome in decompensated heart failure: role of lung–right heart–kidney interaction. Int J Cardiol 169(6):379–384
Damman K, Navis G, Smilde TD, Voors AA, van der Bij W, van Veldhuisen DJ, Hillege HL (2007) Decreased cardiac output, venous congestion and the association with renal impairment in patients with cardiac dysfunction. Eur J Heart Fail 9(9):872–878
Metra M, Cotter G, Gheorghiade M, Dei CL, Voors AA (2012) The role of the kidney in heart failure. Eur Heart J 33(17):2135–2142
Uthoff H, Breidthardt T, Klima T, Aschwanden M, Arenja N, Socrates T, Heinisch C, Noveanu M, Frischknecht B, Baumann U, Jaeger KA, Mueller C (2011) Central venous pressure and impaired renal function in patients with acute heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 13(4):432–439
Damman K, van Deursen VM, Navis G, Voors AA, van Veldhuisen DJ, Hillege HL (2009) Increased central venous pressure is associated with impaired renal function and mortality in a broad spectrum of patients with cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 53(7):582–588
Gheorghiade M, De LL, Fonarow GC, Filippatos G, Metra M, Francis GS (2005) Pathophysiologic targets in the early phase of acute heart failure syndromes. Am J Cardiol 96(6A):11G–17G
Dini FL, Demmer RT, Simioniuc A, Morrone D, Donati F, Guarini G, Orsini E, Caravelli P, Marzilli M, Colombo PC (2012) Right ventricular dysfunction is associated with chronic kidney disease and predicts survival in patients with chronic systolic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 14(3):287–294
Mullens W, Abrahams Z, Francis GS, Sokos G, Taylor DO, Starling RC, Young JB, Tang WH (2009) Importance of venous congestion for worsening of renal function in advanced decompensated heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 53(7):589–596
Shamseddin MK, Parfrey PS (2009) Mechanisms of the cardiorenal syndromes. Nat Rev Nephrol 5(11):641–649
Kanbay M, Segal M, Afsar B, Kang DH, Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Johnson RJ (2013) The role of uric acid in the pathogenesis of human cardiovascular disease. Heart 99(11):759–766
Lymperopoulos A (2013) Physiology and pharmacology of the cardiovascular adrenergic system. Front Physiol 4:240
Dzau VJ, Colucci WS, Hollenberg NK, Williams GH (1981) Relation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system to clinical state in congestive heart failure. Circulation 63(3):645–651
Shah BN, Greaves K (2010) The cardiorenal syndrome: a review. Int J Nephrol 2011:920195
McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Bohm M, Dickstein K, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fonseca C, Gomez-Sanchez MA, Jaarsma T, Kober L, Lip GY, Maggioni AP, Parkhomenko A, Pieske BM, Popescu BA, Ronnevik PK, Rutten FH, Schwitter J, Seferovic P, Stepinska J, Trindade PT, Voors AA, Zannad F, Zeiher A (2012) ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 33(14):1787–1847
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, Johnson MR, Kasper EK, Levy WC, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, McMurray JJ, Mitchell JE, Peterson PN, Riegel B, Sam F, Stevenson LW, Tang WH, Tsai EJ, Wilkoff BL (2013) 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation 128(16):e240–e327
O’Connor CM, Starling RC, Hernandez AF, Armstrong PW, Dickstein K, Hasselblad V, Heizer GM, Komajda M, Massie BM, McMurray JJ, Nieminen MS, Reist CJ, Rouleau JL, Swedberg K, Adams KF Jr, Anker SD, Atar D, Battler A, Botero R, Bohidar NR, Butler J, Clausell N, Corbalan R, Costanzo MR, Dahlstrom U, Deckelbaum LI, Diaz R, Dunlap ME, Ezekowitz JA, Feldman D, Felker GM, Fonarow GC, Gennevois D, Gottlieb SS, Hill JA, Hollander JE, Howlett JG, Hudson MP, Kociol RD, Krum H, Laucevicius A, Levy WC, Mendez GF, Metra M, Mittal S, Oh BH, Pereira NL, Ponikowski P, Tang WH, Tanomsup S, Teerlink JR, Triposkiadis F, Troughton RW, Voors AA, Whellan DJ, Zannad F, Califf RM (2011) Effect of nesiritide in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. N Engl J Med 365(1):32–43
Sackner-Bernstein JD, Skopicki HA, Aaronson KD (2005) Risk of worsening renal function with nesiritide in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure. Circulation 111(12):1487–1491
van Deursen V, Hernandez AF, Stebbins A, Hasselblad V, Ezekowitz JA, Califf RM, Gottlieb SS, O’Connor CM, Starling RC, Tang WH, McMurray JJ, Dickstein K, Voors AA (2014) Nesiritide, renal function, and associated outcomes during hospitalization for acute decompensated heart failure: results from the Acute Study of Clinical Effectiveness of Nesiritide and Decompensated Heart Failure (ASCEND-HF). Circulation 130(12):958–965
O’Connor CM, Gattis WA, Uretsky BF, Adams KF Jr, McNulty SE, Grossman SH, McKenna WJ, Zannad F, Swedberg K, Gheorghiade M, Califf RM (1999) Continuous intravenous dobutamine is associated with an increased risk of death in patients with advanced heart failure: insights from the Flolan International Randomized Survival Trial (FIRST). Am Heart J 138(1 Pt 1):78–86
Tacon CL, McCaffrey J, Delaney A (2012) Dobutamine for patients with severe heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Intensive Care Med 38(3):359–367
Fedele F, Bruno N, Brasolin B, Caira C, D’Ambrosi A, Mancone M (2014) Levosimendan improves renal function in acute decompensated heart failure: possible underlying mechanisms. Eur J Heart Fail 16(3):281–288
Yilmaz MB, Yalta K, Yontar C, Karadas F, Erdem A, Turgut OO, Yilmaz A, Tandogan I (2007) Levosimendan improves renal function in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: comparison with dobutamine. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 21(6):431–435
Bart BA, Goldsmith SR, Lee KL, Givertz MM, O’Connor CM, Bull DA, Redfield MM, Deswal A, Rouleau JL, LeWinter MM, Ofili EO, Stevenson LW, Semigran MJ, Felker GM, Chen HH, Hernandez AF, Anstrom KJ, McNulty SE, Velazquez EJ, Ibarra JC, Mascette AM, Braunwald E (2012) Ultrafiltration in decompensated heart failure with cardiorenal syndrome. N Engl J Med 367(24):2296–2304
Krishnamoorthy A, Greiner MA, Sharma PP, DeVore AD, Johnson KW, Fonarow GC, Curtis LH, Hernandez AF (2014) Transient and persistent worsening renal function during hospitalization for acute heart failure. Am Heart J 168(6):891–900
Palmer JB, Friedman HS, Waltman Johnson K, Navaratnam P, Gottlieb SS (2014) Association of worsening renal function with length of stay and costs in patients hospitalized with acute heart failure. J Card Fail 20(Suppl.):S50–S51
Teichman SL, Unemori E, Dschietzig T, Conrad K, Voors AA, Teerlink JR, Felker GM, Metra M, Cotter G (2009) Relaxin, a pleiotropic vasodilator for the treatment of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev 14(4):321–329
Hsu SY, Nakabayashi K, Nishi S, Kumagai J, Kudo M, Sherwood OD, Hsueh AJ (2002) Activation of orphan receptors by the hormone relaxin. Science 295(5555):671–674
Kohsaka T, Min G, Lukas G, Trupin S, Campbell ET, Sherwood OD (1998) Identification of specific relaxin-binding cells in the human female. Biol Reprod 59(4):991–999
Novak J, Parry LJ, Matthews JE, Kerchner LJ, Indovina K, Hanley-Yanez K, Doty KD, Debrah DO, Shroff SG, Conrad KP (2006) Evidence for local relaxin ligand-receptor expression and function in arteries. FASEB J 20(13):2352–2362
Díez J (2014) Serelaxin: a novel therapy for acute heart failure with a range of hemodynamic and non-hemodynamic actions. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 14:275–285
Jelinic M, Leo CH, Post Uiterweer ED, Sandow SL, Gooi JH, Wlodek ME, Conrad KP, Parkington H, Tare M, Parry LJ (2014) Localization of relaxin receptors in arteries and veins, and region-specific increases in compliance and bradykinin-mediated relaxation after in vivo serelaxin treatment. FASEB J 28(1):275–287
McGuane JT, Debrah JE, Sautina L, Jarajapu YP, Novak J, Rubin JP, Grant MB, Segal M, Conrad KP (2011) Relaxin induces rapid dilation of rodent small renal and human subcutaneous arteries via PI3 kinase and nitric oxide. Endocrinology 152(7):2786–2796
Du XJ, Bathgate RA, Samuel CS, Dart AM, Summers RJ (2010) Cardiovascular effects of relaxin: from basic science to clinical therapy. Nat Rev Cardiol 7(1):48–58
Teichman SL, Unemori E, Teerlink JR, Cotter G, Metra M (2010) Relaxin: review of biology and potential role in treating heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep 7(2):75–82
Danielson LA, Kercher LJ, Conrad KP (2000) Impact of gender and endothelin on renal vasodilation and hyperfiltration induced by relaxin in conscious rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279(4):R1298–R1304
Boehnert MU, Hilbig H, Armbruster FP (2005) Relaxin as an additional protective substance in preserving and reperfusion solution for liver transplantation, shown in a model of isolated perfused rat liver. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1041:434–440
Boehnert MU, Armbruster FP, Hilbig H (2009) Relaxin as a protective substance in the preserving solution for liver transplantation: spectrophotometric in vivo imaging of local oxygen supply in an isolated perfused rat liver model. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1160:320–321
Collino M, Rogazzo M, Pini A, Benetti E, Rosa AC, Chiazza F, Fantozzi R, Bani D, Masini E (2013) Acute treatment with relaxin protects the kidney against ischaemia/reperfusion injury. J Cell Mol Med 17(11):1494–1505
Samuel CS, Zhao C, Bathgate RA, Du XJ, Summers RJ, Amento EP, Walker LL, McBurnie M, Zhao L, Tregear GW (2005) The relaxin gene-knockout mouse: a model of progressive fibrosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1041:173–181
Samuel CS, Cendrawan S, Gao XM, Ming Z, Zhao C, Kiriazis H, Xu Q, Tregear GW, Bathgate RA, Du XJ (2011) Relaxin remodels fibrotic healing following myocardial infarction. Lab Invest 91(5):675–690
Sasser JM, Molnar M, Baylis C (2011) Relaxin ameliorates hypertension and increases nitric oxide metabolite excretion in angiotensin II but not N(omega)-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester hypertensive rats. Hypertension 58(2):197–204
Segal MS, Sautina L, Li S, Diao Y, Agoulnik AI, Kielczewski J, McGuane JT, Grant MB, Conrad KP (2012) Relaxin increases human endothelial progenitor cell NO and migration and vasculogenesis in mice. Blood 119(2):629–636
Danielson LA, Sherwood OD, Conrad KP (1999) Relaxin is a potent renal vasodilator in conscious rats. J Clin Invest 103(4):525–533
Danielson LA, Welford A, Harris A (2006) Relaxin improves renal function and histology in aging Munich Wistar rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(5):1325–1333
Smith MC, Danielson LA, Conrad KP, Davison JM (2006) Influence of recombinant human relaxin on renal hemodynamics in healthy volunteers. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(11):3192–3197
Voors AA, Dahlke M, Meyer S, Stepinska J, Gottlieb SS, Jones A, Zhang Y, Laurent D, Slart RH, Navis GJ (2014) Renal hemodynamic effects of serelaxin in patients with chronic heart failure: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Circ Heart Fail 7:994–1002
Conrad KP, Shroff SG (2011) Effects of relaxin on arterial dilation, remodeling, and mechanical properties. Curr Hypertens Rep 13(6):409–420
Dschietzig T, Teichman S, Unemori E, Wood S, Boehmer J, Richter C, Baumann G, Stangl K (2009) Intravenous recombinant human relaxin in compensated heart failure: a safety, tolerability, and pharmacodynamic trial. J Card Fail 15(3):182–190
Ponikowski P, Mitrovic V, Ruda M, Fernandez A, Voors AA, Vishnevsky A, Cotter G, Milo O, Laessing U, Zhang Y, Dahlke M, Zymlinski R, Metra M (2014) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study to assess haemodynamic effects of serelaxin in patients with acute heart failure. Eur Heart J 35(7):431–441
Teerlink JR, Cotter G, Davison BA, Felker GM, Filippatos G, Greenberg BH, Ponikowski P, Unemori E, Voors AA, Adams KF Jr, Dorobantu MI, Grinfeld LR, Jondeau G, Marmor A, Masip J, Pang PS, Werdan K, Teichman SL, Trapani A, Bush CA, Saini R, Schumacher C, Severin TM, Metra M (2013) Serelaxin, recombinant human relaxin-2, for treatment of acute heart failure (RELAX-AHF): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 381(9860):29–39
Metra M, Ponikowski P, Cotter G, Davison BA, Felker GM, Filippatos G, Greenberg BH, Hua TA, Severin T, Unemori E, Voors AA, Teerlink JR (2013) Effects of serelaxin in subgroups of patients with acute heart failure: results from RELAX-AHF. Eur Heart J 34(40):3128–3136
Novartis Pharmaceuticals (2015). http://www.novartis.com/downloads/newsroom/corporate-fact-sheet/2a_Pharmaceuticals_EN.pdf. Accessed 19 Feb 2015
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT01870778 (2015) Efficacy, safety and tolerability of serelaxin when added to standard therapy in AHF. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01870778. Accessed 19 Feb 2015
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02064868 (2014) Effect of serelaxin versus standard of care in acute heart failure (AHF) patients (RELAX-AHF-EU) http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02064868?term=NCT02064868&rank=1. Accessed 19 Feb 2015
Clinicaltrials.gov. NCT02007720 (2014) Efficacy, Safety and tolerability of sexelaxin when added to standard therapy in AHF. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02007720?term=NCT02007720&rank=1. Accessed 19 Feb 2015
Acknowledgments
We thank Minal Kotecha of CircleScience, an Ashfield Company, part of UDG Healthcare plc, for providing writing assistance, which was funded by Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland. The authors did not receive any funding grants to support the development of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Roland E Schmieder: Received Speakers Bureau honoraria and is an advisory board member for Novartis. His University Hospital has also received grants from Novartis. Veselin Mitrovic: Employed by Kerckhoff-Klinik Forschungsgesellschaft mbH, has received grant/research support from Bayer and Novartis; honoraria from Bayer, Novartis and GlaxoSmithKline and is a consultant for Cardiorentis and a Board Member for Daichi Sankyo. Christian Hengstenberg: Received speakers bureau honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Edwards, Novartis, and Symetis; Advisory Board member for Novartis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmieder, R.E., Mitrovic, V. & Hengstenberg, C. Renal impairment and worsening of renal function in acute heart failure: can new therapies help? The potential role of serelaxin. Clin Res Cardiol 104, 621–631 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-015-0839-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-015-0839-y