Abstract
Purpose
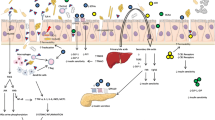
Increasing evidence suggests that the intestinal microbiome (IM) and bacterial metabolites may influence glucose homeostasis, energy expenditure and the intestinal barrier integrity and lead to the presence of systemic low-grade inflammation, all of which can contribute to insulin resistance (IR) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). The purpose of this review is to explore the role of the IM and bacterial metabolites in the pathogenesis and treatment of these conditions.
Results
This review summarizes research focused on how to modulate the IM through diet, prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics and fecal microbiota transplant in order to treat IR and T2D.
Conclusion
There is an abundance of evidence suggesting a role for IM in the pathogenesis of IR and T2D based on reviewed studies using various methods to modulate IM and metabolites. However, the results are inconsistent. Future research should further assess this relationship.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Organization WH (2018) The top 10 causes of death. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death. Accessed 19 August 2020
Organization WH (2016) Global report on diabetes. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565257
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA, Ogurtsova K, Shaw JE, Bright D, Williams R, Committee IDFDA (2019) Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 157:107843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
Pulgaron ER, Delamater AM (2014) Obesity and type 2 diabetes in children: epidemiology and treatment. Curr Diab Rep 14(8):508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-014-0508-y
Lee JM, Okumura MJ, Davis MM, Herman WH, Gurney JG (2006) Prevalence and determinants of insulin resistance among U.S. adolescents: a population-based study. Diabetes Care 29(11):2427–2432. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc06-0709
Freeman AM, Pennings N (2020) Insulin Resistance. StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL)
Skyler JS, Bakris GL, Bonifacio E, Darsow T, Eckel RH, Groop L, Groop PH, Handelsman Y, Insel RA, Mathieu C, McElvaine AT, Palmer JP, Pugliese A, Schatz DA, Sosenko JM, Wilding JP, Ratner RE (2017) Differentiation of diabetes by pathophysiology, natural history, and prognosis. Diabetes 66(2):241–255. https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-0806
Sun X, Yu W, Hu C (2014) Genetics of type 2 diabetes: insights into the pathogenesis and its clinical application. Biomed Res Int 2014:926713. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/926713
Rung J, Cauchi S, Albrechtsen A, Shen L, Rocheleau G, Cavalcanti-Proenca C, Bacot F, Balkau B, Belisle A, Borch-Johnsen K, Charpentier G, Dina C, Durand E, Elliott P, Hadjadj S, Jarvelin MR, Laitinen J, Lauritzen T, Marre M, Mazur A, Meyre D, Montpetit A, Pisinger C, Posner B, Poulsen P, Pouta A, Prentki M, Ribel-Madsen R, Ruokonen A, Sandbaek A, Serre D, Tichet J, Vaxillaire M, Wojtaszewski JF, Vaag A, Hansen T, Polychronakos C, Pedersen O, Froguel P, Sladek R (2009) Genetic variant near IRS1 is associated with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. Nat Genet 41(10):1110–1115. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.443
Marin-Penalver JJ, Martin-Timon I, Sevillano-Collantes C, Del Canizo-Gomez FJ (2016) Update on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 7(17):354–395. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i17.354
Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, Wolski K, Aminian A, Brethauer SA, Navaneethan SD, Singh RP, Pothier CE, Nissen SE, Kashyap SR, Investigators S (2017) Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes - 5-year outcomes. N Engl J Med 376(7):641–651. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1600869
Caricilli AM, Saad MJ (2013) The role of gut microbiota on insulin resistance. Nutrients 5(3):829–851. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5030829
Wilcox G (2005) Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin Biochem Rev 26(2):19–39
Smith U (2002) Impaired ('diabetic’) insulin signaling and action occur in fat cells long before glucose intolerance–is insulin resistance initiated in the adipose tissue? Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 26(7):897–904. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802028
Hunter SJ, Garvey WT (1998) Insulin action and insulin resistance: diseases involving defects in insulin receptors, signal transduction, and the glucose transport effector system. Am J Med 105(4):331–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9343(98)00300-3
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR (2004) Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 27(6):1487–1495. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.6.1487
Sumner AE, Cowie CC (2008) Ethnic differences in the ability of triglyceride levels to identify insulin resistance. Atherosclerosis 196(2):696–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.12.018
Gayoso-Diz P, Otero-Gonzalez A, Rodriguez-Alvarez MX, Gude F, Garcia F, De Francisco A, Quintela AG (2013) Insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) cut-off values and the metabolic syndrome in a general adult population: effect of gender and age: EPIRCE cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord 13:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6823-13-47
Cantley J, Ashcroft FM (2015) Q&A: insulin secretion and type 2 diabetes: why do beta-cells fail? BMC Biol 13:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-015-0140-6
Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, Bailey CJ, Ceriello A, Delgado V, Federici M, Filippatos G, Grobbee DE, Hansen TB, Huikuri HV, Johansson I, Juni P, Lettino M, Marx N, Mellbin LG, Ostgren CJ, Rocca B, Roffi M, Sattar N, Seferovic PM, Sousa-Uva M, Valensi P, Wheeler DC, Group ESCSD (2020) 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J 41(2):255–323. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz486
American Diabetes A (2019) 2 Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 42(Suppl 1):S13–S28. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-S002
Dedoussis GV, Kaliora AC, Panagiotakos DB (2007) Genes, diet and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review. Rev Diabet Stud 4(1):13–24. https://doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2007.4.13
Belkina AC, Denis GV (2010) Obesity genes and insulin resistance. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 17(5):472–477. https://doi.org/10.1097/MED.0b013e32833c5c48
Wu H, Ballantyne CM (2020) Metabolic inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity. Circ Res 126(11):1549–1564. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315896
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444(7121):840–846. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05482
Statovci D, Aguilera M, MacSharry J, Melgar S (2017) The impact of western diet and nutrients on the microbiota and immune response at mucosal interfaces. Front Immunol 8:838. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00838
Rosenheck R (2008) Fast food consumption and increased caloric intake: a systematic review of a trajectory towards weight gain and obesity risk. Obes Rev 9(6):535–547. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2008.00477.x
Brons C, Jensen CB, Storgaard H, Hiscock NJ, White A, Appel JS, Jacobsen S, Nilsson E, Larsen CM, Astrup A, Quistorff B, Vaag A (2009) Impact of short-term high-fat feeding on glucose and insulin metabolism in young healthy men. J Physiol 587(Pt 10):2387–2397. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2009.169078
Bisschop PH, de Metz J, Ackermans MT, Endert E, Pijl H, Kuipers F, Meijer AJ, Sauerwein HP, Romijn JA (2001) Dietary fat content alters insulin-mediated glucose metabolism in healthy men. Am J Clin Nutr 73(3):554–559. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/73.3.554
Montell E, Turini M, Marotta M, Roberts M, Noe V, Ciudad CJ, Mace K, Gomez-Foix AM (2001) DAG accumulation from saturated fatty acids desensitizes insulin stimulation of glucose uptake in muscle cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280(2):E229-237. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.2001.280.2.E229
Finck BN, Hall AM (2015) Does diacylglycerol accumulation in fatty liver disease cause hepatic insulin resistance? Biomed Res Int 2015:104132. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/104132
Ertunc ME, Hotamisligil GS (2016) Lipid signaling and lipotoxicity in metaflammation: indications for metabolic disease pathogenesis and treatment. J Lipid Res 57(12):2099–2114. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R066514
Kolczynska K, Loza-Valdes A, Hawro I, Sumara G (2020) Diacylglycerol-evoked activation of PKC and PKD isoforms in regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism: a review. Lipids Health Dis 19(1):113. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-020-01286-8
Ghemrawi R, Battaglia-Hsu SF, Arnold C (2018) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic disorders. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7060063
Ho N, Xu C, Thibault G (2018) From the unfolded protein response to metabolic diseases: lipids under the spotlight. J Cell Sci. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.199307
Oh YS, Bae GD, Baek DJ, Park EY, Jun HS (2018) Fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta-cells during development of type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:384. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00384
Yi X, Cai X, Wang S, Xiao Y (2020) Mechanisms of impaired pancreatic betacell function in highfat dietinduced obese mice: the role of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Med Rep 21(5):2041–2050. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11013
Preston AM, Gurisik E, Bartley C, Laybutt DR, Biden TJ (2009) Reduced endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi protein trafficking contributes to ER stress in lipotoxic mouse beta cells by promoting protein overload. Diabetologia 52(11):2369–2373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-009-1506-5
Beigrezaei S, Ghiasvand R, Feizi A, Iraj B (2019) Relationship between dietary patterns and incidence of type 2 diabetes. Int J Prev Med 10:122. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_206_17
Cnop M, Abdulkarim B, Bottu G, Cunha DA, Igoillo-Esteve M, Masini M, Turatsinze JV, Griebel T, Villate O, Santin I, Bugliani M, Ladriere L, Marselli L, McCarthy MI, Marchetti P, Sammeth M, Eizirik DL (2014) RNA sequencing identifies dysregulation of the human pancreatic islet transcriptome by the saturated fatty acid palmitate. Diabetes 63(6):1978–1993. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-1383
Brown AE, Walker M (2016) Genetics of insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. Curr Cardiol Rep 18(8):75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-016-0755-4
Repaske DR (2016) Medication-induced diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes 17(6):392–397. https://doi.org/10.1111/pedi.12406
Mi D, Fang H, Zhao Y, Zhong L (2017) Birth weight and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med 14(6):5313–5320. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5234
Schippa S, Conte MP (2014) Dysbiotic events in gut microbiota: impact on human health. Nutrients 6(12):5786–5805. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6125786
Deng F, Li Y, Zhao J (2019) The gut microbiome of healthy long-living people. Aging (Albany NY) 11(2):289–290. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101771
Le Chatelier E, Nielsen T, Qin J, Prifti E, Hildebrand F, Falony G, Almeida M, Arumugam M, Batto JM, Kennedy S, Leonard P, Li J, Burgdorf K, Grarup N, Jorgensen T, Brandslund I, Nielsen HB, Juncker AS, Bertalan M, Levenez F, Pons N, Rasmussen S, Sunagawa S, Tap J, Tims S, Zoetendal EG, Brunak S, Clement K, Dore J, Kleerebezem M, Kristiansen K, Renault P, Sicheritz-Ponten T, de Vos WM, Zucker JD, Raes J, Hansen T, Meta HITc, Bork P, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Pedersen O (2013) Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 500(7464):541–546. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12506
Wang B, Jiang X, Cao M, Ge J, Bao Q, Tang L, Chen Y, Li L (2016) Altered fecal microbiota correlates with liver biochemistry in nonobese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep 6:32002. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32002
Gong D, Gong X, Wang L, Yu X, Dong Q (2016) Involvement of reduced microbial diversity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2016:6951091. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6951091
Pascal V, Pozuelo M, Borruel N, Casellas F, Campos D, Santiago A, Martinez X, Varela E, Sarrabayrouse G, Machiels K, Vermeire S, Sokol H, Guarner F, Manichanh C (2017) A microbial signature for Crohn’s disease. Gut 66(5):813–822. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313235
Mosca A, Leclerc M, Hugot JP (2016) Gut microbiota diversity and human diseases: should we reintroduce key predators in our ecosystem? Front Microbiol 7:455. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00455
Li Q, Chang Y, Zhang K, Chen H, Tao S, Zhang Z (2020) Implication of the gut microbiome composition of type 2 diabetic patients from northern China. Sci Rep 10(1):5450. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62224-3
Doumatey AP, Adeyemo A, Zhou J, Lei L, Adebamowo SN, Adebamowo C, Rotimi CN (2020) Gut microbiome profiles are associated with type 2 diabetes in urban africans. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:63. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00063
Sun L, Xie C, Wang G, Wu Y, Wu Q, Wang X, Liu J, Deng Y, Xia J, Chen B, Zhang S, Yun C, Lian G, Zhang X, Zhang H, Bisson WH, Shi J, Gao X, Ge P, Liu C, Krausz KW, Nichols RG, Cai J, Rimal B, Patterson AD, Wang X, Gonzalez FJ, Jiang C (2018) Gut microbiota and intestinal FXR mediate the clinical benefits of metformin. Nat Med 24(12):1919–1929. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0222-4
Larsen N, Vogensen FK, van den Berg FW, Nielsen DS, Andreasen AS, Pedersen BK, Al-Soud WA, Sorensen SJ, Hansen LH, Jakobsen M (2010) Gut microbiota in human adults with type 2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults. PLoS ONE 5(2):e9085. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009085
Gaike AH, Paul D, Bhute S, Dhotre DP, Pande P, Upadhyaya S, Reddy Y, Sampath R, Ghosh D, Chandraprabha D, Acharya J, Banerjee G, Sinkar VP, Ghaskadbi SS, Shouche YS (2020) The gut microbial diversity of newly diagnosed diabetics but not of prediabetics is significantly different from that of healthy nondiabetics. mSystems. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00578-19
Ahmad A, Yang W, Chen G, Shafiq M, Javed S, Ali Zaidi SS, Shahid R, Liu C, Bokhari H (2019) Analysis of gut microbiota of obese individuals with type 2 diabetes and healthy individuals. PLoS ONE 14(12):e0226372. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0226372
Zhang X, Shen D, Fang Z, Jie Z, Qiu X, Zhang C, Chen Y, Ji L (2013) Human gut microbiota changes reveal the progression of glucose intolerance. PLoS ONE 8(8):e71108. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071108
Tilg H, Kaser A (2011) Gut microbiome, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction. J Clin Invest 121(6):2126–2132. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI58109
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D, Peng Y, Zhang D, Jie Z, Wu W, Qin Y, Xue W, Li J, Han L, Lu D, Wu P, Dai Y, Sun X, Li Z, Tang A, Zhong S, Li X, Chen W, Xu R, Wang M, Feng Q, Gong M, Yu J, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Hansen T, Sanchez G, Raes J, Falony G, Okuda S, Almeida M, LeChatelier E, Renault P, Pons N, Batto JM, Zhang Z, Chen H, Yang R, Zheng W, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Nielsen R, Pedersen O, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2012) A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 490(7418):55–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11450
Gurung M, Li Z, You H, Rodrigues R, Jump DB, Morgun A, Shulzhenko N (2020) Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine 51:102590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.051
Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Nilsson A, Akrami R, Lee YS, De Vadder F, Arora T, Hallen A, Martens E, Bjorck I, Backhed F (2015) Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of prevotella. Cell Metab 22(6):971–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.001
Sedighi M, Razavi S, Navab-Moghadam F, Khamseh ME, Alaei-Shahmiri F, Mehrtash A, Amirmozafari N (2017) Comparison of gut microbiota in adult patients with type 2 diabetes and healthy individuals. Microb Pathog 111:362–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.08.038
Wu X, Ma C, Han L, Nawaz M, Gao F, Zhang X, Yu P, Zhao C, Li L, Zhou A, Wang J, Moore JE, Millar BC, Xu J (2010) Molecular characterisation of the faecal microbiota in patients with type II diabetes. Curr Microbiol 61(1):69–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9582-9
Gao R, Zhu C, Li H, Yin M, Pan C, Huang L, Kong C, Wang X, Zhang Y, Qu S, Qin H (2018) Dysbiosis signatures of gut microbiota along the sequence from healthy, young patients to those with overweight and obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 26(2):351–361. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22088
Sasaki M, Ogasawara N, Funaki Y, Mizuno M, Iida A, Goto C, Koikeda S, Kasugai K, Joh T (2013) Transglucosidase improves the gut microbiota profile of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. BMC Gastroenterol 13:81. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-13-81
Karlsson FH, Tremaroli V, Nookaew I, Bergstrom G, Behre CJ, Fagerberg B, Nielsen J, Backhed F (2013) Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature 498(7452):99–103. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12198
Graessler J, Qin Y, Zhong H, Zhang J, Licinio J, Wong ML, Xu A, Chavakis T, Bornstein AB, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Lamounier-Zepter V, Lohmann T, Wolf T, Bornstein SR (2013) Metagenomic sequencing of the human gut microbiome before and after bariatric surgery in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: correlation with inflammatory and metabolic parameters. Pharmacogenomics J 13(6):514–522. https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2012.43
Forslund K, Hildebrand F, Nielsen T, Falony G, Le Chatelier E, Sunagawa S, Prifti E, Vieira-Silva S, Gudmundsdottir V, Pedersen HK, Arumugam M, Kristiansen K, Voigt AY, Vestergaard H, Hercog R, Costea PI, Kultima JR, Li J, Jorgensen T, Levenez F, Dore J, Meta HITc, Nielsen HB, Brunak S, Raes J, Hansen T, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Bork P, Pedersen O (2015) Disentangling type 2 diabetes and metformin treatment signatures in the human gut microbiota. Nature 528(7581):262–266. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15766
Aydin O, Nieuwdorp M, Gerdes V (2018) The gut microbiome as a target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 18(8):55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-018-1020-6
Vrieze A, Van Nood E, Holleman F, Salojarvi J, Kootte RS, Bartelsman JF, Dallinga-Thie GM, Ackermans MT, Serlie MJ, Oozeer R, Derrien M, Druesne A, Van Hylckama Vlieg JE, Bloks VW, Groen AK, Heilig HG, Zoetendal EG, Stroes ES, de Vos WM, Hoekstra JB, Nieuwdorp M (2012) Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Gastroenterology 143(4):913-916 e917. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.031
Salamon D, Sroka-Oleksiak A, Kapusta P, Szopa M, Mrozinska S, Ludwig-Slomczynska AH, Wolkow PP, Bulanda M, Klupa T, Malecki MT, Gosiewski T (2018) Characteristics of gut microbiota in adult patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes based on nextgeneration sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene fragment. Pol Arch Intern Med 128(6):336–343. https://doi.org/10.20452/pamw.4246
Remely M, Aumueller E, Merold C, Dworzak S, Hippe B, Zanner J, Pointner A, Brath H, Haslberger AG (2014) Effects of short chain fatty acid producing bacteria on epigenetic regulation of FFAR3 in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Gene 537(1):85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.11.081
Furet JP, Kong LC, Tap J, Poitou C, Basdevant A, Bouillot JL, Mariat D, Corthier G, Dore J, Henegar C, Rizkalla S, Clement K (2010) Differential adaptation of human gut microbiota to bariatric surgery-induced weight loss: links with metabolic and low-grade inflammation markers. Diabetes 59(12):3049–3057. https://doi.org/10.2337/db10-0253
Hermes GDA, Reijnders D, Kootte RS, Goossens GH, Smidt H, Nieuwdorp M, Blaak EE, Zoetendal EG (2020) Individual and cohort-specific gut microbiota patterns associated with tissue-specific insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese males. Sci Rep 10(1):7523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64574-4
Greer RL, Dong X, Moraes AC, Zielke RA, Fernandes GR, Peremyslova E, Vasquez-Perez S, Schoenborn AA, Gomes EP, Pereira AC, Ferreira SR, Yao M, Fuss IJ, Strober W, Sikora AE, Taylor GA, Gulati AS, Morgun A, Shulzhenko N (2016) Akkermansia muciniphila mediates negative effects of IFNgamma on glucose metabolism. Nat Commun 7:13329. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13329
Allin KH, Tremaroli V, Caesar R, Jensen BAH, Damgaard MTF, Bahl MI, Licht TR, Hansen TH, Nielsen T, Dantoft TM, Linneberg A, Jorgensen T, Vestergaard H, Kristiansen K, Franks PW, Hansen T, Backhed F, Pedersen O, consortium I-D (2018) Aberrant intestinal microbiota in individuals with prediabetes. Diabetologia 61(4):810–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4550-1
Everard A, Belzer C, Geurts L, Ouwerkerk JP, Druart C, Bindels LB, Guiot Y, Derrien M, Muccioli GG, Delzenne NM, de Vos WM, Cani PD (2013) Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(22):9066–9071. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219451110
de la Cuesta-Zuluaga J, Mueller NT, Corrales-Agudelo V, Velasquez-Mejia EP, Carmona JA, Abad JM, Escobar JS (2017) Metformin is associated with higher relative abundance of mucin-degrading akkermansia muciniphila and several short-chain fatty acid-producing microbiota in the gut. Diabetes Care 40(1):54–62. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc16-1324
Larsen JM (2017) The immune response to Prevotella bacteria in chronic inflammatory disease. Immunology 151(4):363–374. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12760
Iljazovic A, Roy U, Galvez EJC, Lesker TR, Zhao B, Gronow A, Amend L, Will SE, Hofmann JD, Pils MC, Schmidt-Hohagen K, Neumann-Schaal M, Strowig T (2021) Perturbation of the gut microbiome by Prevotella spp. enhances host susceptibility to mucosal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 14(1):113–124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41385-020-0296-4
Hippe B, Remely M, Aumueller E, Pointner A, Magnet U, Haslberger AG (2016) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii phylotypes in type two diabetic, obese, and lean control subjects. Benef Microbes 7(4):511–517. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2015.0075
Plovier H, Everard A, Druart C, Depommier C, Van Hul M, Geurts L, Chilloux J, Ottman N, Duparc T, Lichtenstein L, Myridakis A, Delzenne NM, Klievink J, Bhattacharjee A, van der Ark KC, Aalvink S, Martinez LO, Dumas ME, Maiter D, Loumaye A, Hermans MP, Thissen JP, Belzer C, de Vos WM, Cani PD (2017) A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat Med 23(1):107–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4236
Kang JH, Yun SI, Park MH, Park JH, Jeong SY, Park HO (2013) Anti-obesity effect of Lactobacillus gasseri BNR17 in high-sucrose diet-induced obese mice. PLoS ONE 8(1):e54617. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054617
Li X, Wang N, Yin B, Fang D, Jiang T, Fang S, Zhao J, Zhang H, Wang G, Chen W (2016) Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum CCFM0236 on hyperglycaemia and insulin resistance in high-fat and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice. J Appl Microbiol 121(6):1727–1736. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13276
Chen P, Zhang Q, Dang H, Liu X, Tian F, Zhao J, Chen Y, Zhang H, Chen W (2014) Antidiabetic effect of Lactobacillus casei CCFM0412 on mice with type 2 diabetes induced by a high-fat diet and streptozotocin. Nutrition 30(9):1061–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2014.03.022
Wang G, Li X, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W (2017) Lactobacillus casei CCFM419 attenuates type 2 diabetes via a gut microbiota dependent mechanism. Food Funct 8(9):3155–3164. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7fo00593h
Tian P, Li B, He C, Song W, Hou A, Tian S, Meng X, Li K, Shan Y (2016) Antidiabetic (type 2) effects of Lactobacillus G15 and Q14 in rats through regulation of intestinal permeability and microbiota. Food Funct 7(9):3789–3797. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6fo00831c
Zhang L, Qin Q, Liu M, Zhang X, He F, Wang G (2018) Akkermansia muciniphila can reduce the damage of gluco/lipotoxicity, oxidative stress and inflammation, and normalize intestine microbiota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pathog Dis. https://doi.org/10.1093/femspd/fty028
Yang JY, Lee YS, Kim Y, Lee SH, Ryu S, Fukuda S, Hase K, Yang CS, Lim HS, Kim MS, Kim HM, Ahn SH, Kwon BE, Ko HJ, Kweon MN (2017) Gut commensal Bacteroides acidifaciens prevents obesity and improves insulin sensitivity in mice. Mucosal Immunol 10(1):104–116. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2016.42
Dang F, Jiang Y, Pan R, Zhou Y, Wu S, Wang R, Zhuang K, Zhang W, Li T, Man C (2018) Administration of Lactobacillus paracasei ameliorates type 2 diabetes in mice. Food Funct 9(7):3630–3639. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo00081f
Rooks MG, Garrett WS (2016) Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 16(6):341–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.42
Alexander C, Swanson KS, Fahey GC, Garleb KA (2019) Perspective: physiologic importance of short-chain fatty acids from nondigestible carbohydrate fermentation. Adv Nutr 10(4):576–589. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmz004
Gerard C, Vidal H (2019) Impact of gut microbiota on host glycemic control. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10:29. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00029
Chambers ES, Morrison DJ, Frost G (2015) Control of appetite and energy intake by SCFA: what are the potential underlying mechanisms? Proc Nutr Soc 74(3):328–336. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665114001657
Frost G, Sleeth ML, Sahuri-Arisoylu M, Lizarbe B, Cerdan S, Brody L, Anastasovska J, Ghourab S, Hankir M, Zhang S, Carling D, Swann JR, Gibson G, Viardot A, Morrison D, Louise Thomas E, Bell JD (2014) The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism. Nat Commun 5:3611. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4611
Canfora EE, Jocken JW, Blaak EE (2015) Short-chain fatty acids in control of body weight and insulin sensitivity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 11(10):577–591. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2015.128
Silva YP, Bernardi A, Frozza RL (2020) The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in gut-brain communication. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:25. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00025
Tolhurst G, Heffron H, Lam YS, Parker HE, Habib AM, Diakogiannaki E, Cameron J, Grosse J, Reimann F, Gribble FM (2012) Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 61(2):364–371. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-1019
Batterham RL, Cowley MA, Small CJ, Herzog H, Cohen MA, Dakin CL, Wren AM, Brynes AE, Low MJ, Ghatei MA, Cone RD, Bloom SR (2002) Gut hormone PYY(3–36) physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature 418(6898):650–654. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00887
Verdich C, Flint A, Gutzwiller JP, Naslund E, Beglinger C, Hellstrom PM, Long SJ, Morgan LM, Holst JJ, Astrup A (2001) A meta-analysis of the effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide on ad libitum energy intake in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(9):4382–4389. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.86.9.7877
Nadkarni P, Chepurny OG, Holz GG (2014) Regulation of glucose homeostasis by GLP-1. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 121:23–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800101-1.00002-8
Puddu A, Sanguineti R, Montecucco F, Viviani GL (2014) Evidence for the gut microbiota short-chain fatty acids as key pathophysiological molecules improving diabetes. Mediat Inflamm 2014:162021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/162021
Roelofsen H, Priebe MG, Vonk RJ (2010) The interaction of short-chain fatty acids with adipose tissue: relevance for prevention of type 2 diabetes. Benef Microbes 1(4):433–437. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2010.0028
Ma N, Wu Y, Xie F, Du K, Wang Y, Shi L, Ji L, Liu T, Ma X (2017) Dimethyl fumarate reduces the risk of mycotoxins via improving intestinal barrier and microbiota. Oncotarget 8(27):44625–44638. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17886
Zheng L, Kelly CJ, Battista KD, Schaefer R, Lanis JM, Alexeev EE, Wang RX, Onyiah JC, Kominsky DJ, Colgan SP (2017) Microbial-derived butyrate promotes epithelial barrier function through IL-10 receptor-dependent repression of claudin-2. J Immunol 199(8):2976–2984. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1700105
Ploger S, Stumpff F, Penner GB, Schulzke JD, Gabel G, Martens H, Shen Z, Gunzel D, Aschenbach JR (2012) Microbial butyrate and its role for barrier function in the gastrointestinal tract. Ann NY Acad Sci 1258:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06553.x
Wang HB, Wang PY, Wang X, Wan YL, Liu YC (2012) Butyrate enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function via up-regulation of tight junction protein Claudin-1 transcription. Dig Dis Sci 57(12):3126–3135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-012-2259-4
Liu H, Wang J, He T, Becker S, Zhang G, Li D, Ma X (2018) Butyrate: A double-edged sword for health? Adv Nutr 9(1):21–29. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmx009
Ma X, Fan PX, Li LS, Qiao SY, Zhang GL, Li DF (2012) Butyrate promotes the recovering of intestinal wound healing through its positive effect on the tight junctions. J Anim Sci 90(Suppl 4):266–268. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.50965
Yan H, Ajuwon KM (2017) Butyrate modifies intestinal barrier function in IPEC-J2 cells through a selective upregulation of tight junction proteins and activation of the Akt signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 12(6):e0179586. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179586
Lewis K, Lutgendorff F, Phan V, Soderholm JD, Sherman PM, McKay DM (2010) Enhanced translocation of bacteria across metabolically stressed epithelia is reduced by butyrate. Inflamm Bowel Dis 16(7):1138–1148. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.21177
Harsch IA, Konturek PC (2018) The role of gut microbiota in obesity and type 2 and type 1 diabetes mellitus: new insights into “Old” diseases. Med Sci (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci6020032
Sakai J, Cammarota E, Wright JA, Cicuta P, Gottschalk RA, Li N, Fraser IDC, Bryant CE (2017) Lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB nuclear translocation is primarily dependent on MyD88, but TNFalpha expression requires TRIF and MyD88. Sci Rep 7(1):1428. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01600-y
Backhed F, Normark S, Schweda EK, Oscarson S, Richter-Dahlfors A (2003) Structural requirements for TLR4-mediated LPS signalling: a biological role for LPS modifications. Microbes Infect 5(12):1057–1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1286-4579(03)00207-7
Devaraj S, Tobias P, Jialal I (2011) Knockout of toll-like receptor-4 attenuates the pro-inflammatory state of diabetes. Cytokine 55(3):441–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2011.03.023
Bours V, Bonizzi G, Bentires-Alj M, Bureau F, Piette J, Lekeux P, Merville M (2000) NF-kappaB activation in response to toxical and therapeutical agents: role in inflammation and cancer treatment. Toxicology 153(1–3):27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-483x(00)00302-4
Chen L, Chen R, Wang H, Liang F (2015) Mechanisms Linking Inflammation to Insulin Resistance. Int J Endocrinol 2015:508409. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/508409
Salguero MV, Al-Obaide MAI, Singh R, Siepmann T, Vasylyeva TL (2019) Dysbiosis of Gram-negative gut microbiota and the associated serum lipopolysaccharide exacerbates inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Exp Ther Med 18(5):3461–3469. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7943
Cani PD, Delzenne NM (2011) The gut microbiome as therapeutic target. Pharmacol Ther 130(2):202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.01.012
Palau-Rodriguez M, Tulipani S, Isabel Queipo-Ortuno M, Urpi-Sarda M, Tinahones FJ, Andres-Lacueva C (2015) Metabolomic insights into the intricate gut microbial-host interaction in the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Front Microbiol 6:1151. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01151
Quevrain E, Maubert MA, Michon C, Chain F, Marquant R, Tailhades J, Miquel S, Carlier L, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Pigneur B, Lequin O, Kharrat P, Thomas G, Rainteau D, Aubry C, Breyner N, Afonso C, Lavielle S, Grill JP, Chassaing G, Chatel JM, Trugnan G, Xavier R, Langella P, Sokol H, Seksik P (2016) Identification of an anti-inflammatory protein from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, a commensal bacterium deficient in Crohn’s disease. Gut 65(3):415–425. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307649
Sokol H, Pigneur B, Watterlot L, Lakhdari O, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Gratadoux JJ, Blugeon S, Bridonneau C, Furet JP, Corthier G, Grangette C, Vasquez N, Pochart P, Trugnan G, Thomas G, Blottiere HM, Dore J, Marteau P, Seksik P, Langella P (2008) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(43):16731–16736. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0804812105
Breyner NM, Michon C, de Sousa CS, Vilas Boas PB, Chain F, Azevedo VA, Langella P, Chatel JM (2017) Microbial anti-inflammatory molecule (MAM) from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii shows a protective effect on DNBS and DSS-induced colitis model in mice through inhibition of NF-kappaB pathway. Front Microbiol 8:114. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00114
Xu J, Liang R, Zhang W, Tian K, Li J, Chen X, Yu T, Chen Q (2020) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii-derived microbial anti-inflammatory molecule regulates intestinal integrity in diabetes mellitus mice via modulating tight junction protein expression. J Diabetes 12(3):224–236. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.12986
Abildgaard A, Elfving B, Hokland M, Wegener G, Lund S (2018) The microbial metabolite indole-3-propionic acid improves glucose metabolism in rats, but does not affect behaviour. Arch Physiol Biochem 124(4):306–312. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2017.1398262
Chimerel C, Emery E, Summers DK, Keyser U, Gribble FM, Reimann F (2014) Bacterial metabolite indole modulates incretin secretion from intestinal enteroendocrine L cells. Cell Rep 9(4):1202–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.10.032
de Mello VD, Paananen J, Lindstrom J, Lankinen MA, Shi L, Kuusisto J, Pihlajamaki J, Auriola S, Lehtonen M, Rolandsson O, Bergdahl IA, Nordin E, Ilanne-Parikka P, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S, Landberg R, Eriksson JG, Tuomilehto J, Hanhineva K, Uusitupa M (2017) Indolepropionic acid and novel lipid metabolites are associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes in the finnish diabetes prevention study. Sci Rep 7:46337. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46337
Karamanos B, Thanopoulou A, Angelico F, Assaad-Khalil S, Barbato A, Del Ben M, Dimitrijevic-Sreckovic V, Djordjevic P, Gallotti C, Katsilambros N, Migdalis I, Mrabet M, Petkova M, Roussi D, Tenconi MT (2002) Nutritional habits in the Mediterranean Basin. The macronutrient composition of diet and its relation with the traditional Mediterranean diet. Multi-centre study of the Mediterranean Group for the Study of Diabetes (MGSD). Eur J Clin Nutr 56(10):983–991. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601413
Aktas AB, Ozen B, Tokatli F, Sen I (2014) Phenolics profile of a naturally debittering olive in comparison to regular olive varieties. J Sci Food Agric 94(4):691–698. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6308
Lacatusu CM, Grigorescu ED, Floria M, Onofriescu A, Mihai BM (2019) The Mediterranean diet: from an environment-driven food culture to an emerging medical prescription. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16060942
Sleiman D, Al-Badri MR, Azar ST (2015) Effect of mediterranean diet in diabetes control and cardiovascular risk modification: a systematic review. Front Public Health 3:69. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2015.00069
Milanski M, Degasperi G, Coope A, Morari J, Denis R, Cintra DE, Tsukumo DM, Anhe G, Amaral ME, Takahashi HK, Curi R, Oliveira HC, Carvalheira JB, Bordin S, Saad MJ, Velloso LA (2009) Saturated fatty acids produce an inflammatory response predominantly through the activation of TLR4 signaling in hypothalamus: implications for the pathogenesis of obesity. J Neurosci 29(2):359–370. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2760-08.2009
Casas R, Sacanella E, Estruch R (2014) The immune protective effect of the Mediterranean diet against chronic low-grade inflammatory diseases. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 14(4):245–254. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530314666140922153350
Telle-Hansen VH, Gaundal L, Myhrstad MCW (2019) Polyunsaturated fatty acids and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051067
Silva FM, Kramer CK, de Almeida JC, Steemburgo T, Gross JL, Azevedo MJ (2013) Fiber intake and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev 71(12):790–801. https://doi.org/10.1111/nure.12076
Bozzetto L, Costabile G, Della Pepa G, Ciciola P, Vetrani C, Vitale M, Rivellese AA, Annuzzi G (2018) Dietary fibre as a unifying remedy for the whole spectrum of obesity-associated cardiovascular risk. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070943
Jardine M (2016) Nutrition considerations for microbiota health in diabetes. Diabetes Spectr 29(4):238–244. https://doi.org/10.2337/ds16-0003
Salas-Salvado J, Diaz-Lopez A, Ruiz-Canela M, Basora J, Fito M, Corella D, Serra-Majem L, Warnberg J, Romaguera D, Estruch R, Vidal J, Martinez JA, Aros F, Vazquez C, Ros E, Vioque J, Lopez-Miranda J, Bueno-Cavanillas A, Tur JA, Tinahones FJ, Martin V, Lapetra J, Pinto X, Daimiel L, Delgado-Rodriguez M, Matia P, Gomez-Gracia E, Diez-Espino J, Babio N, Castaner O, Sorli JV, Fiol M, Zulet MA, Bullo M, Goday A, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Investigators PR-P (2019) Effect of a lifestyle intervention program with energy-restricted mediterranean diet and exercise on weight loss and cardiovascular risk factors: one-year results of the PREDIMED-Plus Trial. Diabetes Care 42(5):777–788. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-0836
Toobert DJ, Glasgow RE, Strycker LA, Barrera M Jr, Radcliffe JL, Wander RC, Bagdade JD (2003) Biologic and quality-of-life outcomes from the Mediterranean Lifestyle Program: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care 26(8):2288–2293. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.8.2288
Itsiopoulos C, Brazionis L, Kaimakamis M, Cameron M, Best JD, O’Dea K, Rowley K (2011) Can the Mediterranean diet lower HbA1c in type 2 diabetes? Results from a randomized cross-over study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 21(9):740–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2010.03.005
Elhayany A, Lustman A, Abel R, Attal-Singer J, Vinker S (2010) A low carbohydrate Mediterranean diet improves cardiovascular risk factors and diabetes control among overweight patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 1-year prospective randomized intervention study. Diabetes Obes Metab 12(3):204–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01151.x
Esposito K, Maiorino MI, Ciotola M, Di Palo C, Scognamiglio P, Gicchino M, Petrizzo M, Saccomanno F, Beneduce F, Ceriello A, Giugliano D (2009) Effects of a Mediterranean-style diet on the need for antihyperglycemic drug therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 151(5):306–314. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-151-5-200909010-00004
Garcia-Mantrana I, Selma-Royo M, Alcantara C, Collado MC (2018) Shifts on gut microbiota associated to mediterranean diet adherence and specific dietary intakes on general adult population. Front Microbiol 9:890. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00890
Gutierrez-Diaz I, Fernandez-Navarro T, Sanchez B, Margolles A, Gonzalez S (2016) Mediterranean diet and faecal microbiota: a transversal study. Food Funct 7(5):2347–2356. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6fo00105j
Haro C, Montes-Borrego M, Rangel-Zuniga OA, Alcala-Diaz JF, Gomez-Delgado F, Perez-Martinez P, Delgado-Lista J, Quintana-Navarro GM, Tinahones FJ, Landa BB, Lopez-Miranda J, Camargo A, Perez-Jimenez F (2016) Two healthy diets modulate gut microbial community improving insulin sensitivity in a human obese population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101(1):233–242. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-3351
Balfego M, Canivell S, Hanzu FA, Sala-Vila A, Martinez-Medina M, Murillo S, Mur T, Ruano EG, Linares F, Porras N, Valladares S, Fontalba M, Roura E, Novials A, Hernandez C, Aranda G, Siso-Almirall A, Rojo-Martinez G, Simo R, Gomis R (2016) Effects of sardine-enriched diet on metabolic control, inflammation and gut microbiota in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a pilot randomized trial. Lipids Health Dis 15:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-016-0245-0
Meslier V, Laiola M, Roager HM, De Filippis F, Roume H, Quinquis B, Giacco R, Mennella I, Ferracane R, Pons N, Pasolli E, Rivellese A, Dragsted LO, Vitaglione P, Ehrlich SD, Ercolini D (2020) Mediterranean diet intervention in overweight and obese subjects lowers plasma cholesterol and causes changes in the gut microbiome and metabolome independently of energy intake. Gut 69(7):1258–1268. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-320438
Kahleova H, Matoulek M, Malinska H, Oliyarnik O, Kazdova L, Neskudla T, Skoch A, Hajek M, Hill M, Kahle M, Pelikanova T (2011) Vegetarian diet improves insulin resistance and oxidative stress markers more than conventional diet in subjects with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 28(5):549–559. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.03209.x
Clarys P, Deliens T, Huybrechts I, Deriemaeker P, Vanaelst B, De Keyzer W, Hebbelinck M, Mullie P (2014) Comparison of nutritional quality of the vegan, vegetarian, semi-vegetarian, pesco-vegetarian and omnivorous diet. Nutrients 6(3):1318–1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6031318
Kahleova H, Dort S, Holubkov R, Barnard ND (2018) A plant-based high-carbohydrate, low-fat diet in overweight individuals in a 16-week randomized clinical trial: the role of carbohydrates. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091302
Barnard ND, Cohen J, Jenkins DJ, Turner-McGrievy G, Gloede L, Green A, Ferdowsian H (2009) A low-fat vegan diet and a conventional diabetes diet in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled, 74-wk clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr 89(5):1588S-1596S. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.26736H
Jain A, Li XH, Chen WN (2018) Similarities and differences in gut microbiome composition correlate with dietary patterns of Indian and Chinese adults. AMB Express 8(1):104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0632-1
De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Di Paola M, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P (2010) Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(33):14691–14696. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1005963107
Ruengsomwong S, La-Ongkham O, Jiang J, Wannissorn B, Nakayama J, Nitisinprasert S (2016) Microbial Community of healthy thai vegetarians and non-vegetarians, their core gut microbiota, and pathogen risk. J Microbiol Biotechnol 26(10):1723–1735. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1603.03057
Jeffery IB, O’Toole PW (2013) Diet-microbiota interactions and their implications for healthy living. Nutrients 5(1):234–252. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5010234
Matijasic BB, Obermajer T, Lipoglavsek L, Grabnar I, Avgustin G, Rogelj I (2014) Association of dietary type with fecal microbiota in vegetarians and omnivores in Slovenia. Eur J Nutr 53(4):1051–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-013-0607-6
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y, Fischbach MA, Biddinger SB, Dutton RJ, Turnbaugh PJ (2014) Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 505(7484):559–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12820
Kim MS, Hwang SS, Park EJ, Bae JW (2013) Strict vegetarian diet improves the risk factors associated with metabolic diseases by modulating gut microbiota and reducing intestinal inflammation. Environ Microbiol Rep 5(5):765–775. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12079
Brooks AW, Priya S, Blekhman R, Bordenstein SR (2018) Gut microbiota diversity across ethnicities in the United States. PLoS Biol 16(12):e2006842. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2006842
Gibson G, Scott K, Rastall R, Tuohy K, Hotchkiss A, Dubert-Ferrandon A, Gareau MG, Murphy EF, Saulnier D, Loh G, Macfarlane S, Delzenne N, Ringel Y, Kozianowski G, Dickmann RS, Lenoir-Wijnkoop I, Walker C, Buddington R (2010) Dietary prebiotics: current status and new definition. Food Sci Technol Bull Funct Food 7:1–19
He M, Shi B (2017) Gut microbiota as a potential target of metabolic syndrome: the role of probiotics and prebiotics. Cell Biosci 7:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-017-0183-1
Swanson KS, de Vos WM, Martens EC, Gilbert JA, Menon RS, Soto-Vaca A, Hautvast J, Meyer PD, Borewicz K, Vaughan EE, Slavin JL (2020) Effect of fructans, prebiotics and fibres on the human gut microbiome assessed by 16S rRNA-based approaches: a review. Benef Microbes 11(2):101–129. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2019.0082
Holscher HD, Caporaso JG, Hooda S, Brulc JM, Fahey GC Jr, Swanson KS (2015) Fiber supplementation influences phylogenetic structure and functional capacity of the human intestinal microbiome: follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 101(1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.114.092064
Cani PD, Joly E, Horsmans Y, Delzenne NM (2006) Oligofructose promotes satiety in healthy human: a pilot study. Eur J Clin Nutr 60(5):567–572. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602350
Dehghan P, Gargari BP, Jafar-Abadi MA, Aliasgharzadeh A (2014) Inulin controls inflammation and metabolic endotoxemia in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized-controlled clinical trial. Int J Food Sci Nutr 65(1):117–123. https://doi.org/10.3109/09637486.2013.836738
Pourghassem Gargari B, Dehghan P, Aliasgharzadeh A, Asghari Jafar-Abadi M (2013) Effects of high performance inulin supplementation on glycemic control and antioxidant status in women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab J 37(2):140–148. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.2.140
Russo F, Riezzo G, Chiloiro M, De Michele G, Chimienti G, Marconi E, D’Attoma B, Linsalata M, Clemente C (2010) Metabolic effects of a diet with inulin-enriched pasta in healthy young volunteers. Curr Pharm Des 16(7):825–831. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161210790883570
Kellow NJ, Coughlan MT, Reid CM (2014) Metabolic benefits of dietary prebiotics in human subjects: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr 111(7):1147–1161. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114513003607
Gomes AC, Bueno AA, de Souza RG, Mota JF (2014) Gut microbiota, probiotics and diabetes. Nutr J 13:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-13-60
Vulevic J, Juric A, Tzortzis G, Gibson GR (2013) A mixture of trans-galactooligosaccharides reduces markers of metabolic syndrome and modulates the fecal microbiota and immune function of overweight adults. J Nutr 143(3):324–331. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.112.166132
Canfora EE, van der Beek CM, Hermes GDA, Goossens GH, Jocken JWE, Holst JJ, van Eijk HM, Venema K, Smidt H, Zoetendal EG, Dejong CHC, Lenaerts K, Blaak EE (2017) Supplementation of diet with galacto-oligosaccharides increases bifidobacteria, but not insulin sensitivity, in obese prediabetic individuals. Gastroenterology 153(1):87-97e83. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.051
Costabile A, Klinder A, Fava F, Napolitano A, Fogliano V, Leonard C, Gibson GR, Tuohy KM (2008) Whole-grain wheat breakfast cereal has a prebiotic effect on the human gut microbiota: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Br J Nutr 99(1):110–120. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114507793923
Nicolucci AC, Hume MP, Martinez I, Mayengbam S, Walter J, Reimer RA (2017) Prebiotics reduce body fat and alter intestinal microbiota in children who are overweight or with obesity. Gastroenterology 153(3):711–722. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.055
Chambers ES, Byrne CS, Morrison DJ, Murphy KG, Preston T, Tedford C, Garcia-Perez I, Fountana S, Serrano-Contreras JI, Holmes E, Reynolds CJ, Roberts JF, Boyton RJ, Altmann DM, McDonald JAK, Marchesi JR, Akbar AN, Riddell NE, Wallis GA, Frost GS (2019) Dietary supplementation with inulin-propionate ester or inulin improves insulin sensitivity in adults with overweight and obesity with distinct effects on the gut microbiota, plasma metabolome and systemic inflammatory responses: a randomised cross-over trial. Gut 68(8):1430–1438. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318424
Rebello CJ, Burton J, Heiman M, Greenway FL (2015) Gastrointestinal microbiome modulator improves glucose tolerance in overweight and obese subjects: a randomized controlled pilot trial. J Diabetes Complicat 29(8):1272–1276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.08.023
Schutte S, Esser D, Hoevenaars FPM, Hooiveld G, Priebe MG, Vonk RJ, Wopereis S, Afman LA (2018) A 12-wk whole-grain wheat intervention protects against hepatic fat: the Graandioos study, a randomized trial in overweight subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 108(6):1264–1274. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqy204
Bomhof MR, Parnell JA, Ramay HR, Crotty P, Rioux KP, Probert CS, Jayakumar S, Raman M, Reimer RA (2019) Histological improvement of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with a prebiotic: a pilot clinical trial. Eur J Nutr 58(4):1735–1745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1721-2
Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR, Merenstein DJ, Pot B, Morelli L, Canani RB, Flint HJ, Salminen S, Calder PC, Sanders ME (2014) Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(8):506–514. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66
Soleimani A, Zarrati Mojarrad M, Bahmani F, Taghizadeh M, Ramezani M, Tajabadi-Ebrahimi M, Jafari P, Esmaillzadeh A, Asemi Z (2017) Probiotic supplementation in diabetic hemodialysis patients has beneficial metabolic effects. Kidney Int 91(2):435–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2016.09.040
Tonucci LB, Olbrich Dos Santos KM, Licursi de Oliveira L, Rocha Ribeiro SM, Duarte Martino HS (2017) Clinical application of probiotics in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin Nutr 36(1):85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2015.11.011
Bjerg AT, Kristensen M, Ritz C, Stark KD, Holst JJ, Leser TD, Wellejus A, Astrup A (2015) Four weeks supplementation with Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei L. casei W8(R) shows modest effect on triacylglycerol in young healthy adults. Benef Microbes 6(1):29–39. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2014.0058
Bjerg AT, Kristensen M, Ritz C, Holst JJ, Rasmussen C, Leser TD, Wellejus A, Astrup A (2014) Lactobacillus paracasei subsp paracasei L. casei W8 suppresses energy intake acutely. Appetite 82:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2014.07.016
Yao K, Zeng L, He Q, Wang W, Lei J, Zou X (2017) Effect of probiotics on glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials. Med Sci Monit 23:3044–3053. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.902600
Tao YW, Gu YL, Mao XQ, Zhang L, Pei YF (2020) Effects of probiotics on type II diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. J Transl Med 18(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-020-02213-2
Wang J, Tang H, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Derrien M, Rocher E, van Hylckama Vlieg JE, Strissel K, Zhao L, Obin M, Shen J (2015) Modulation of gut microbiota during probiotic-mediated attenuation of metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice. ISME J 9(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.99
Firouzi S, Majid HA, Ismail A, Kamaruddin NA, Barakatun-Nisak MY (2017) Effect of multi-strain probiotics (multi-strain microbial cell preparation) on glycemic control and other diabetes-related outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Nutr 56(4):1535–1550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1199-8
Jones RB, Alderete TL, Martin AA, Geary BA, Hwang DH, Palmer SL, Goran MI (2018) Probiotic supplementation increases obesity with no detectable effects on liver fat or gut microbiota in obese Hispanic adolescents: a 16-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatr Obes 13(11):705–714. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijpo.12273
Simon MC, Strassburger K, Nowotny B, Kolb H, Nowotny P, Burkart V, Zivehe F, Hwang JH, Stehle P, Pacini G, Hartmann B, Holst JJ, MacKenzie C, Bindels LB, Martinez I, Walter J, Henrich B, Schloot NC, Roden M (2015) Intake of Lactobacillus reuteri improves incretin and insulin secretion in glucose-tolerant humans: a proof of concept. Diabetes Care 38(10):1827–1834. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-2690
Sato J, Kanazawa A, Azuma K, Ikeda F, Goto H, Komiya K, Kanno R, Tamura Y, Asahara T, Takahashi T, Nomoto K, Yamashiro Y, Watada H (2017) Probiotic reduces bacterial translocation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomised controlled study. Sci Rep 7(1):12115. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12535-9
Hsieh MC, Tsai WH, Jheng YP, Su SL, Wang SY, Lin CC, Chen YH, Chang WW (2018) The beneficial effects of Lactobacillus reuteri ADR-1 or ADR-3 consumption on type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Sci Rep 8(1):16791. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35014-1
Gobel RJ, Larsen N, Jakobsen M, Molgaard C, Michaelsen KF (2012) Probiotics to adolescents with obesity: effects on inflammation and metabolic syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 55(6):673–678. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e318263066c
Brahe LK, Le Chatelier E, Prifti E, Pons N, Kennedy S, Blaedel T, Hakansson J, Dalsgaard TK, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Astrup A, Ehrlich SD, Larsen LH (2015) Dietary modulation of the gut microbiota–a randomised controlled trial in obese postmenopausal women. Br J Nutr 114(3):406–417. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114515001786
Pandey KR, Naik SR, Vakil BV (2015) Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics: a review. J Food Sci Technol 52(12):7577–7587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1921-1
Soleimani A, Motamedzadeh A, Zarrati Mojarrad M, Bahmani F, Amirani E, Ostadmohammadi V, Tajabadi-Ebrahimi M, Asemi Z (2019) The effects of synbiotic supplementation on metabolic status in diabetic patients undergoing hemodialysis: a randomized, double-blinded. Placebo-Controlled Trial Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 11(4):1248–1256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9499-3
Moroti C, Souza Magri LF, de Rezende CM, Cavallini DC, Sivieri K (2012) Effect of the consumption of a new symbiotic shake on glycemia and cholesterol levels in elderly people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lipids Health Dis 11:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-11-29
Ebrahimi ZS, Nasli-Esfahani E, Nadjarzade A, Mozaffari-Khosravi H (2017) Effect of symbiotic supplementation on glycemic control, lipid profiles and microalbuminuria in patients with non-obese type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord 16:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40200-017-0304-8
Asemi Z, Khorrami-Rad A, Alizadeh SA, Shakeri H, Esmaillzadeh A (2014) Effects of synbiotic food consumption on metabolic status of diabetic patients: a double-blind randomized cross-over controlled clinical trial. Clin Nutr 33(2):198–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2013.05.015
Mahboobi S, Rahimi F, Jafarnejad S (2018) Effects of prebiotic and synbiotic supplementation on glycaemia and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Adv Pharm Bull 8(4):565–574. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2018.065
Angelino D, Martina A, Rosi A, Veronesi L, Antonini M, Mennella I, Vitaglione P, Grioni S, Brighenti F, Zavaroni I, Fares C, Torriani S, Pellegrini N (2019) Glucose- and lipid-related biomarkers are affected in healthy obese or hyperglycemic adults consuming a whole-grain pasta enriched in prebiotics and probiotics: a 12-week randomized controlled trial. J Nutr 149(10):1714–1723. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxz071
Horvath A, Leber B, Feldbacher N, Tripolt N, Rainer F, Blesl A, Trieb M, Marsche G, Sourij H, Stadlbauer V (2020) Effects of a multispecies synbiotic on glucose metabolism, lipid marker, gut microbiome composition, gut permeability, and quality of life in diabesity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Eur J Nutr 59(7):2969–2983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02135-w
Kim KO, Gluck M (2019) Fecal microbiota transplantation: an update on clinical practice. Clin Endosc 52(2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.009
Kootte RS, Levin E, Salojarvi J, Smits LP, Hartstra AV, Udayappan SD, Hermes G, Bouter KE, Koopen AM, Holst JJ, Knop FK, Blaak EE, Zhao J, Smidt H, Harms AC, Hankemeijer T, Bergman J, Romijn HA, Schaap FG, Olde Damink SWM, Ackermans MT, Dallinga-Thie GM, Zoetendal E, de Vos WM, Serlie MJ, Stroes ESG, Groen AK, Nieuwdorp M (2017) Improvement of insulin sensitivity after lean donor feces in metabolic syndrome is driven by baseline intestinal microbiota composition. Cell Metab 26(4):611–619616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.008
Smits LP, Kootte RS, Levin E, Prodan A, Fuentes S, Zoetendal EG, Wang Z, Levison BS, Cleophas MCP, Kemper EM, Dallinga-Thie GM, Groen AK, Joosten LAB, Netea MG, Stroes ESG, de Vos WM, Hazen SL, Nieuwdorp M (2018) Effect of vegan fecal microbiota transplantation on carnitine- and choline-derived trimethylamine-N-oxide production and vascular inflammation in patients with metabolic syndrome. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.008342
Yu EW, Gao L, Stastka P, Cheney MC, Mahabamunuge J, Torres Soto M, Ford CB, Bryant JA, Henn MR, Hohmann EL (2020) Fecal microbiota transplantation for the improvement of metabolism in obesity: the FMT-TRIM double-blind placebo-controlled pilot trial. PLoS Med 17(3):e1003051. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003051
Craven L, Rahman A, Nair Parvathy S, Beaton M, Silverman J, Qumosani K, Hramiak I, Hegele R, Joy T, Meddings J, Urquhart B, Harvie R, McKenzie C, Summers K, Reid G, Burton JP, Silverman M (2020) Allogenic fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease improves abnormal small intestinal permeability: a randomized control trial. Am J Gastroenterol 115(7):1055–1065. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000000661
Whang A, Nagpal R, Yadav H (2019) Bi-directional drug-microbiome interactions of anti-diabetics. EBioMedicine 39:591–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.11.046
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghorbani, Y., Schwenger, K.J.P. & Allard, J.P. Manipulation of intestinal microbiome as potential treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Eur J Nutr 60, 2361–2379 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-021-02520-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-021-02520-4