Abstract.
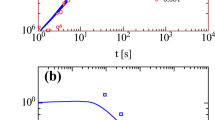
Several linear (LLDPE, HDPE, PS) and long-chain-branched (LDPE, PP) polymer melts were investigated by an elongational rheometer (RME Rheometrics) and by Rheotens (Göttfert). The Molecular Stress Function (MSF) theory is briefly reviewed and used to extrapolate the steady-state elongational viscosity. To evaluate Rheotens experiments, a new process model is introduced which assumes that the elongational viscosity in the Rheotens test is a function of the draw ratio only. The apparent elongational viscosities extracted from Rheotens curves are found to lie in between the steady-state elongational viscosity and three times the shear viscosity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, M.H., Bastian, H., Bernnat, A. et al. Determination of elongational viscosity of polymer melts by RME and Rheotens experiments. Rheol Acta 41, 316–325 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-002-0228-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-002-0228-0