Abstract
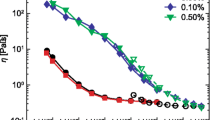
Semi-dilute (\(c^\ast < c < c_{\rm e}\)) as well as concentrated, entangled (c > c e) solutions of PEO yield uniformly thinning, cylindrical filaments in capillary breakup extensional rheometry (CaBER) experiments. Up to c ≈ c e thinning can be characterized by a single elongational relaxation time λ E. Comparison with the longest shear relaxation time, λ S reveals that λ E/λ S decreases with increasing concentration or molecular weight according to (c[η]) − 4/3. This is attributed to the large deformation the solutions experience during filament thinning. A factorable integral model including a single relaxation time and a Soskey or Wagner damping function accounting for the large deformation in CaBER experiments is used to calculate λ E/λ S and provides good agreement with experimental results. Irrespective of concentration or molecular weight a beads-on-a-string structure occurs prior to filament breakup at a diameter ratio D/D 0 ≈ 0.01. This instability is supposed to be closely related to a flow-induced phase separation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anna SL, McKinley GH et al (2001) Elasto-capillary thinning and breakup of model elastic liquids. J Rheol 45:115–138
Bailey FE, Kucera JL, Imhof LG (1958) Molecular weight relations of poly(ethylene) oxide. J Polym Sci 32:517–518
Bazilevsky AV, Entov VM, Rozhkov AN (1990) Liquid filament microrheometer and some of its applications. In: Oliver DR (ed) Third European rheology conference. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 41–43
Bazilevskii AV, Entov VM et al (1997) Failure of polymer solution filaments. Polym Sci A 39:316–324
Böhme G (2000) Strömungsmechanik nichtnewtonischer Fluide. Teuber, Stuttgart
Chang HC, Demekhin EA, Kalaidin E (1999) Iterated stretching of viscoelastic Jets. Phys Fluids 11:1717
Christanti Y, Walker LM (2001a) Surface tension driven jet break up on strain-hardening solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 100:9–26
Christanti Y, Walker LM (2001b) Effect of fluid relaxation time of dilute polymer solutions on jet breakup due to a forced disturbance. J Rheol 46:733–748
Clasen C, Eggers J, Fontelos MA, Li J, McKinley GH (2006a) The beads on-string structure of viscoelastic threads. J Fluid Mech 556:283–308
Clasen C, Plog JP et al (2006b) How dilute are dilute solutions in extensional flows? J Rheol 50:849–881
Crassous JJ, Régisser R, Ballauff M, Willenbacher N (2005) Characterization of the viscoelastic behaviour of complex fluids using the piezoelastic axial vibrator. J Rheol 49:851–863
Goldin M, Yerushalmi J, Pfeffer R, Shinnar R (1969) Breakup of laminar capillary jet of a viscoelastic fluid. J Fluid Mech 38:689–711
James DF, Walters K (1993) A critical appraisal of available methods for the measurement of extensional properties of mobile systems. Techniques in Rheological Measurements. Elsevier, London, pp 33–53
Kheirandish S, Gubaydullin I, Willenbacher N (2008) Shear and elongational flow behaviour of acrylic thickener solutions, Part I: effect of intermolecular aggregation. Rheol Acta 49:397–407
Kheirandish S, Guybaidullin I et al (2009) Shear and elongational flow behavior of acrylic thickener solutions, Part II: effect of gel content. Rheol Acta 48:397–407
Liang RF, Mackley MR (1994) Rheological characterization of the time and strain dependence for polyisobutylene solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 52:387–405
Matta J, Tytus RP (1990) Liquid stretching using a falling cylinder. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 35:215–229
McKinley G, Tripathi A (2000) How to extract the Newtonian viscosity from capillary breakup measurements in a filament rheometer. J Rheol 44(3):653–670
Miller E, Cooper-White J (2009) The effects of chain conformation in the microfluidic entry flow of polymer-surfactant systems. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 160:22–30
Niedzwiedz K, Arnolds O, Willenbacher N, Brummer R (2009) How to characterize yield stress fluids with Capillary Breakup Extensional Rheometry (CaBER)? Appl Rheol 19:41969–1–41969–10
Oliveira MSN, McKinley GH (2005) Iterated stretching and multiple beads-on-string phenomena in dilute solutions of highly extensible flexible polymers. Phys Fluids 17:071704
Oliveira MSN, Yeh R, McKinley GH (2006) Iterated stretching, extensional rheology and formation of beads-on-string structures in polymer solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 137:137–148
Rodd LE, Scott JJ et al (2005) Capillary break-up rheometry of low-viscosity elastic fluids. Appl Rheol 15:12–27
Rothstein JP (2009) Strong flows of viscoelastic wormlike micelle solutions. In: Binding DM, Walters K (eds) Rheology review. The British Society of Rheology, Aberystwyth, pp 1–42
Rubinstein M, Colby RH (2003) Polymer physics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Sattler R, Wagner C, Eggers J (2008) Blistering pattern and formation of nanofibers in capillary thinning of polymer solutions. Phys Rev Lett 100:164502
Solomon MJ, Muller SJ (1996) The transient extensional behaviour of polystyrene-based Boger fluids of varying solvent quality and molecular weight. J Rheol 40(5):837–856
Soskey PR, Winter HH (1984) Large step shear strain experiments with parallel-disk rotational rheometers. J Rheol 29:625–645
Sostarcez MC, Belmonte A (2004) Beads-on-string phenomena in wormlike micellar fluids. Phys Fluids 16:67
Stelter M, Brenn G, Yarin AL, Singh RP, Durst F (2000) Validation and application of a novel elongational device for polymer solutions. J Rheol 44:595–616
Tirtaatmadja V, Sridhar T (1993) A filament stretching device for measurement of extensional viscosity. J Rheol 37:1081–1102
Tirtaatmadja V, McKinley GH, Cooper-White JJ (2006) Drop formation and breakup of low viscosity elastic fluids: effects of molecular weight and concentration. Phys Fluids 18:043101
Tiwari MK, Bazilevsky AV, Yarin AL, Megaridis CM (2009) Elongational and shear Rheology of carbon nanotube suspensions. Rheol Acta 48:597–609
Trouton FT (1906) On the coefficient of viscous and its relation to that of viscosity. Proc R Soc Lond, A 77(Iss 519):426–440
Wagner MH, Demarmels A (1990) A constitutive analysis of extensional flows of polyisobutylene. J Rheol 34:943–958
Willenbacher N, Matter Y, Gubaydullin I (2008) Effect of aggregation on shear and elongational flow properties of acrylic thickeners. K-A Rheol J 20:109–116
Yesilata B, Clasen C, McKinley GH (2006) Nonlinear shear and extensional flow dynamics of wormlike surfactant solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 133:73–90
Acknowledgements
We thank F. Bossler for his help in sample preparation and performing shear and CaBER experiments. S. Pfeiffer and C. Woodson are thanked for programming the analysis software. We appreciate valuable discussions with Prof. M. Wagner, Dr. K. Niedzwiedz and Dr. B. Hochstein. Prof. Wagner drew our attention to the appropriate determination of the damping function parameters from the shear viscosity function.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arnolds, O., Buggisch, H., Sachsenheimer, D. et al. Capillary breakup extensional rheometry (CaBER) on semi-dilute and concentrated polyethyleneoxide (PEO) solutions. Rheol Acta 49, 1207–1217 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-010-0500-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-010-0500-7