Abstract
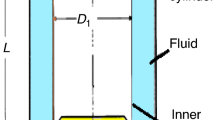
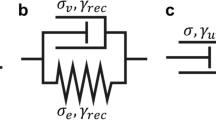
It is well known that particles in initially well-mixed suspensions subjected to inhomogeneous shear flows can migrate and establish particle concentration gradients and non-Newtonian velocity profiles. In this study we introduce a modified version of the shear-induced migration model to predict transient torque reductions in torsional startup flows and transient pressure drop reductions in capillary developing flows. Special attention is devoted to the relationship between the evolution of the driving forces and various mechanisms that contribute to the shear-induced migration of the suspended particles. This analysis reveals that suspension rheometry can complement other techniques, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging, in qualitatively and quantitatively evaluating the model parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 May 1997 Accepted: 21 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graham, A., Mammoli, A. & Busch, M. Effects of demixing on suspension rheometry. Rheol. Acta 37, 139–150 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003970050100
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003970050100