Abstract
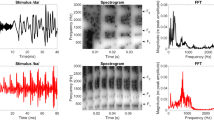
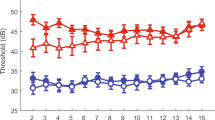
This study aimed at evaluating the feasibility of an implanted microphone for cochlear implants (CI) by comparison of hearing outcomes, sound quality and patient satisfaction of a subcutaneous microphone to a standard external microphone of a behind-the-ear sound processor. In this prospective feasibility study with a within-subject repeated measures design comparing the microphone modalities, ten experienced adult unilateral CI users received an implantable contralateral subcutaneous microphone attached to a percutaneous plug. The signal was pre-processed and fed into their CI sound processor. Subjects compared listening modes at home for a period of up to 4 months. At the end of the study the microphone was explanted. Aided audiometric thresholds, speech understanding in quiet, and sound quality questionnaires were assessed. On average thresholds (250, 500, 750, 1k, 2k, 3k, 4k and 6 kHz) with the subcutaneous microphone were 44.9 dB, compared to 36.4 dB for the external mode. Speech understanding on sentences in quiet was high, within approximately 90% of performance levels compared to hearing with an external microphone. Body sounds were audible but not annoying to almost all subjects. This feasibility study with a research device shows significantly better results than previous studies with implanted microphones. This is attributed to technology enhancements and careful fitting. Listening effort was somewhat increased with an implanted microphone. Under good sound conditions, speech performance is nearly similar to that of external microphones demonstrating that an implanted microphone is feasible in a range of normal listening conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pulcherio JO, Bittencourt AG, Burke PR et al (2014) Carina and Esteem: a systematic review of fully implantable hearing devices. PLoS ONE 9(10):e110636
Briggs RJS, Eder HC, Seligman PM et al (2008) Initial clinical experience with a totally implantable cochlear implant research device. Otol Neurotol 29(2):114–119
Briggs RJS, Eder HC, Seligman PM et al (2012) Six years of experience with a totally implantable cochlear implant. In: CI conference, Baltimore
Jenkins HA, Uhler K (2012) Speech perception comparisons of the otologics implanted Carina™ and the Freedom™ microphones in cochlear implant patients. Otol Neurotol 33(1):13–19
van den Honert C, Kelsall DC (2007) Focused intracochlear electric stimulation with phased array channels. J Acoust Soc Am 121(6):3703–3716
Cox RM (1997) Administration and application of the APHAB. Hear J 50(4):32–48
Sang J, Hu H, Zheng C et al (2015) Speech quality evaluation of a sparse coding shrinkage noise reduction algorithm with normal hearing and hearing impaired listeners. Hear Res 327:175–185
Mauger SJ, Arora K, Dawson PW (2012) Cochlear implant optimized noise reduction. J Neural Eng 9(6):e065007
Perrault M (2011) Matrix test: Une harmonisation européenne des procédures de mesures audiologiques chez les implantés cochléaires. Mémoire II Université de Montpellier, pp 9–20
Vaerenberg B, De Ceulaer G, Szlávik Z et al (2014) Setting and reaching targets with computer-assisted cochlear implant fitting. Sci World J 16:64659
Martin C, Deveze A, Richard C et al (2009) European results with totally implantable Carina placed on the round window: 2-year follow-up. Otol Neurotol 30(8):1196–1203
Jenkins HA, Uhler K (2014) Otologics active middle ear implants. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 47(6):967–978
Acknowledgements
Funding for this study has been received from Cochlear Ltd., Sydney, Australia. The authors sincerely thank the clinical team at CHU Liège, Ms. Madeleine Flas, Ms. Véronique Pacolet and at audio-phonology center team at UCL Brussels for their contributions to this study. The authors also express their gratitude to the technical team, Brian Conn, David Basinger, Jason Leavens, Florent Hubert-Brierre and Thomas Leroux for their efforts to design, produce and enhance the investigational devices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Filiep Vanpoucke, Joris Walraevens and Anke Plasmans are employed by Cochlear Technology Centre, Belgium. The remaining authors have no conflict of interest.
Funding
Funding for this study has been received from Cochlear Ltd., Sydney, Australia.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval for the original protocol, and the subsequent amendments supporting the hardware and software changes, was obtained for the study under registration number B403201214375 from the Belgian Ministry of Health. This research involved human participants.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gérard, JM., Demanez, L., Salmon, C. et al. Feasibility of an implanted microphone for cochlear implant listening. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 1383–1390 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4410-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4410-x