Abstract
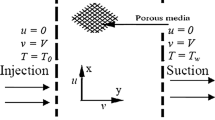
In this study we investigated unsteady mixed convection flow and heat transfer of radiating and reacting nanofluid with variable transport properties in a microchannel filed with a saturated porous medium by taking into account the convective boundary conditions. The Buongiorno’s nanofluid flow model is used to study the effects of the Brownian motion and the thermophoresis. The governing highly nonlinear partial differential equations corresponding to the momentum, energy and concentration profiles have been formulated and solved numerically by utilizing the semi-discretization finite difference method. The effect of each governing thermophysical parameters on the microchannel hydrodynamic and thermal behaviors is discussed with the usage of graphs. The numerical results indicate that the velocity and temperature profiles show an increasing behavior with the variable viscosity parameter, Eckert number, thermal Grashof number, solutal Grashof number, Prandtl number and chemical reaction parameter, whereas the concentration profile increases with increasing values of variable thermal conductivity parameter, porous medium shape parameter, Forchheimer number, Brownian motion parameter, Schmidt number, Biot number and radiation parameter. Moreover, the result reveals that the skin friction coefficient increases with suction/injection Reynolds number, porous medium shape parameter, thermal Grashof number, Schmidt number and Brownian motion parameter but decreases with Eckert number, thermophoresis parameter, Biot number and radiation parameter. Both the heat transfer and the mass transfer rates at both sides of the microchannel walls are higher for large values of suction/injection Reynolds number, porous medium shape parameter and variable viscosity parameter, while both are lower for large values of Eckert number, variable thermal conductivity parameter and radiation parameter. Besides, Grashof number, Schmidt number and Biot number indicate an increasing effect on both the heat transfer and mass transfer rates at the cold wall of the microchannel. The numerical simulation also reveals that Brownian motion parameter and thermophoresis parameter show an opposite effect on both heat transfer and mass transfer rates at both sides of the microchannel walls.


























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Microchannel width
- \(\sigma ^{*}\) :
-
Stefan Boltzmann constant
- \(D_\mathrm{b}\) :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- \(k^{*}\) :
-
Rosseland mean absorption coefficient
- \(D_\mathrm{T}\) :
-
Thermal diffusion coefficient
- \(q_\mathrm{r}\) :
-
Thermal radiative heat flux
- u :
-
Axial nanofluid velocity
- \({ Ec}\) :
-
Eckert number
- V :
-
Constant wall suction/injection velocity
- A :
-
Dimensionless nanofluid pressure
- g :
-
Acceleration due to gravity
- Re :
-
Suction/injection Reynolds number
- \(\mu \)(T):
-
Temperature-dependent nanofluid dynamic viscosity
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Dimensionless variable viscosity parameter
- \(\mu _{0}\) :
-
Initial nanofluid dynamic viscosity
- \(\lambda \) :
-
Dimensionless variable thermal conductivity parameter
- \(\gamma _{1}\) :
-
Viscosity variation parameter
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- \(\rho \) :
-
Density of nanofluid
- Gt:
-
Thermal Grashof number
- C :
-
Nanoparticles concentration
- \({ Gt}\) :
-
Solutal Grashof number
- \(C_{p}\) :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure
- S :
-
Porous medium shape parameter
- K :
-
Permeability parameter
- F :
-
Forchheimer number
- k(T):
-
Temperature-dependent thermal conductivity of nanofluid
- Nb :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- \(k_{0}\) :
-
Initial nanofluid thermal conductivity
- Nt :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- \(\gamma _{2}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity variation parameter
- R :
-
Radiation parameter
- \(h_{f}\) :
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient
- \(\alpha \) :
-
Chemical reaction parameter
- \(\Gamma \) :
-
Heat capacity ratio
- \({ Sc}\) :
-
Schmidt number
- \(T_{0}\) :
-
Initial temperature
- Bi :
-
Biot number
- \(T_\mathrm{w}\) :
-
Right wall temperature
- \(C_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Coefficient of skin friction
- \(T_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Nanofluid temperature heating microchannel surface
- \({ Nu}\) :
-
Nusselt number/heat transfer rate
- T :
-
Temperature of nanofluid
- \(\eta \) :
-
Dimensionless microchannel width
- P :
-
Pressure of nanofluid
- W :
-
Dimensionless axial nanofluid velocity
- t :
-
Time
- \(\tau \) :
-
Dimensionless time
- b :
-
Porous inertial resistance coefficient
- \(\theta \) :
-
Dimensionless nanofluid temperature
- Da :
-
Darcy number
- \(\phi \) :
-
Dimensionless nanoparticles concentration
- \(\varepsilon \) :
-
Rate of reaction
- Sh :
-
Sherwood number/mass transfer rate
References
Rai, S.K., Sharma, R., Saifi, M., Tyagi, R., Singh, D., Gupta, H.: Review of recent applications of microchannel in MEMS devices. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 13(9), 64–69 (2018)
Jahangiri,M., Farsani,R.Y., Shamsabadi,A.A.: Numerical investigation of the water/alumina nanofluid within a microchannel with baffeles. J. Mech. Eng. Tech. 10(2) (2018)
Saleel, C.A., Algahtani, A., Badruddin, I.A., Khan, T.M.Y., Kamangar, S., Abdelmohimen, M.A.H.: Pressure-driven electro-osmotic flow and mass transport in constricted mixing microchannels. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 13(2) 429–441 (2019). https://doi.org/10.29252/jafm.13.02.30146
Reddy, K.V., Makinde, O.D., Reddy, M.G.: Thermal analysis of MHD electro-osmotic peristaltic pumping of Casson fluid through a rotating asymmetric microchannel. Indian J. Phys. 92(11), 1439–1448 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-018-1209-1
Kmiotek,M., Kucab-Pietal,A.: Influence of slim obstacle geometry on the flow and heat transfer in microchannels. Bull. Polish Acad. Technol. Sci. 66(2) (2018). https://doi.org/10.24425/119064
Ahadi, A., Antoun, S., Saghir, M.Z., Swift, J.: Computational fluid dynamic evaluation of heat transfer enhancement in microchannel solar collectors sustained by alumina nanofluid. Energy Storage, 1(e37) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/est2.37
Venkateswarlu, M., Prameela, M., Makinde, O.D.: Influence of heat generation and viscous dissipation on hydromagnetic fully developed natural convection flow in a vertical microchannel. J. Nanofluids 8(7), 1506–1516 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1166/jon.2019.1692
Moon, J., Pacheco, J.R., Pacheco-Vega, A.: Heat transfer enhancement in wavy microchannels: effect of block material. In: Proceedings of the 4th World Congress on Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer (MHMT’19), Rome Italy, ENFHT120 1–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.11159/enfht19.120
Dewan, A., Srivastava, P.: A review of heat transfer enhancement through flow disruption in a microchannel. J. Therm. Sci. 24(3), 203–214 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-015-0775-1
Choi, S.U.S.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Fluids Eng. Div. 231, 99–105 (1995)
Jedi, A. Shamsudeen, A., Razali, N., Othman, H., Zainuri, N.A., Zulkarnain, N., Abu Bakar, N.A., Pati, K.D., Thanoon, T.Y.: Statistical modeling for nanofluid flow: a stretching sheet with thermophysical property data. Colloids Interfaces, 4(3) (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4010003
Subramanian, K.R.V., Rao, T.N., Balakrishnan, A.: Nanofluids and Their Engineering Applications. Taylor & Francis Group. CRC Press (2020)
Xu, H., Huang, H., Xu, X.H., Sun, Q.: Modeling heat transfer of nanofluid flow in microchannels with electrokinetic and slippery effects using Buongiorno’s model. Int. J. Numer. Methods for Heat Fluid Flow. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-09-2018-0506
Patel, A.K., Bhuvad, S., Rajput, S.P.S.: Effects of nanofluid flow in microchannel heat sink for forced convection cooling of electronics device: a numerical simulation. Int. J. Innovative Tech. Exploring Eng., 9(2) 5230–5243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.35940/ijitee.A4122.129219
Niazi, M.D.K., Xu, H.: Modelling two-layer nanofluid flow in a microchannel with electro-osmotic effects by means of the Buongiorno’s model. Appl. Math. Mech. 41(1) 83–104 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2558-7
Shahrestani, M.I., Maleki, A., Shadloo, M.S., Tlili, I.: Numerical investigation of forced convective heat transfer and performance evaluation criterion of \(Al_{2}O_{3}\)/water nanofluid flow inside an axisymmetric microchannel. Symmetry 12(120), 1–17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12010120
Muhammad, H., Muhammad, U., Rizwan, U.H., Zhenfu, T.: A Galerkin approach to analyze MHD flow of nanofluid along converging/diverging channels. Arch. Appl. Mech. 91, 1907–1924 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01861-6
Feroz, A.S., Rizwan, U.H., Muhammad, H.: Brownian motion and thermophoretic effects on non-Newtonian nanofluid flow via Crank–Nicolson scheme. Arch. App. Mech. 91, 3303–3313 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-01966-6
Mahmoudi, Y., Hooman, K., Vafai, K.: Convective Heat Transfer in Porous Media. Taylor & Francis Group. CRC Press (2020)
Al-Rashed, A.A.A.A., Sheikhzadeh, G.A., Aghaei, A., Monfared, F., Shahsavar, A., Afrand, M.: Effect of a porous medium on flow and mixed convection heat transfer of nanofluids with variable properties in a trapezoidal enclosure. J. Therm. Anal. Calorimetry (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08404-4
Muthamilselvan, M., Ureshkumar, S.S.: A tilted Lorentz force effect on porous media filled with nanofluid. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. Sofia 48(2), 50–71 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2478/jtam-2018-0010
Shashikumar, N.S., Prasannakumara, B.C., Gireesha, B.J., Makinde, O.D.: Thermodynamics analysis of mhd casson fluid slip flow in a porous microchannel with thermal radiation. In: Diffusion Foundations, Switzerland. Trans Tech Publications 16, 120–139 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/DF.16.120
Gireesha,B.J., Srinivasa,C.T., Shashikumar,N.S., Macha,M., Singh,J.K., Mahanthesh,B.: Entropy generation and heat transport analysis of Casson fluid flow with viscous and Joule heating in an inclined porous micro-channel. Proc. I Mech. Eng. Part E: J. Process Mech. Eng. 0(0) 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408919849987
Aina, B., Malgwi, P.B.: MHD convection fluid and heat transfer in an inclined micro-porous-channel. Nonlinear Eng. 8, 755–763 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1515/nleng-2018-0081
Muhammad,M.,B., Chaudry,M.K., Lehlohonolo,P.: Heat transfer effects on electro-magnetohydrodynamic Carreau fluid flow between two micro-parallel plates with Darcy-Brinkman-Forchheimer medium. Arch. Appl. Mech. 91 1683–1695 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-020-01847-4
Suresh Babu,R., Kumar,R.B., Makinde, O.D.: (2018). Chemical reaction and thermal radiation effects on MHD mixed convection over a vertical plate with variable fluid properties. Defect Diffusion Forum, 387 332–342 (2018)
Nayak, M.K., Sachin, S., Makinde, O.D.: Chemically reacting and radiating nanofluid flow past an exponentially stretching sheet in a porous medium. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 56, 773–786 (2018)
Sharma, R.P., Makinde, O.D., Animasaun, I.L.: Buoyancy effects on MHD Unsteady convection of a radiating chemically reacting fluid past a moving porous vertical plate in a binary mixture. Defect Diffusion Forum 387, 308–318 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/DDF.387.308
Makinde, O.D., Mbood, F., Ibrahim, M.S.: Chemically reacting on MHD boundary-layer flow of nanofluids over a non-linear stretching sheet with heat source/sink and thermal radiation. Therm. Sci. 22, 495–506 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2298/TSCI151003284M
Reddy, B.P.: Radiation and chemical reaction effects on unsteady MHD free convection parabolic flow past an infinite isothermal vertical plate with viscous dissipation. Int. J. Appl. Mech. Eng. 24(2), 343–358 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2478/ijame-2019-0022
Matao, P.M., Reddy, B.P., Sunzu, J.M., Makinde, O.D.: Finite element numerical investigation into unsteady MHD radiating and reacting mixed convection past an impulsively started oscillating plate. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Tech. 12(1), 38–53 (2020). https://doi.org/10.4314/ijest.v12i1.4
Zigta, B.: Mixed convection on MHD flow with thermal radiation, chemical reaction and viscous dissipation embedded in a porous medium. Int. J. Appl. Mech. Eng. 25(1), 219–235 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2478/ijame-2020-0014
Hamid, M., Usman, M., Khan, Z. H., Haq, R. U., Wang, W.: Numerical study of unsteady MHD flow of Williamson nanofluid in a permeable channel with heat source/sink and thermal radiation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 133(527), 1–12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12322-5
Buongiorno, J.: Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 128, 240–250 (2006)
Rundora, L., Makinde, O.D.: Buoyancy effects on unsteady reactive variable properties fluid flow in a channel filled with a porous medium. J. Porous Media 21(8), 721–737 (2018)
Hindebu, B., Makinde, O. D., Guta, L.: Unsteady mixed convection flow of nanofluid in a micro-channel filled with a porous medium. Indian J. Phys. 1–18 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-021-02116-y
Hamid, M., Zubair, T., Usman, M., Haq, R.U.: Numerical investigation of fractional-order unsteady natural convective radiating flow of nanofluid in a vertical channel. AIMS Math. 4(5), 1416–1429 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3934/math.2019.5.1416
Makinde, O.D., Khan, Z.H., Ahmad, R., Haq, R.U., Khan, W.A.: Unsteady MHD flow in a porous channel with thermal radiation and heat source/sink. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 559, 1–21 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-019-0644-9
Monaledi, R.L., Makinde, O.D.: Entropy analysis of a radiating variable viscosity EG/Ag nanofluid flow in microchannels with buoyancy force and convective cooling. Defect Diffusion Forum 387, 273–285 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/DDF.387.273
Bhandari, A.: Radiation and chemical reaction effects on nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. FDMP 155, 557–582 (2019)
Venkateswarlu, M., Makinde, O.D., Lakshmi, D.V.: Influence of thermal radiation and heat generation on steady hydromagnetic flow in a vertical micro-porous-channel in presence of suction/injection. J. Nanofluids 8(5), 1010–1019 (2019)
Rundora, L., Makinde, O.D.: Unsteady MHD flow of non-Newtonian fluid in a channel filled with a saturated porous medium with asymmetric navier slip and convective heating. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 12(3) 483–493 (2018). https://doi.org/10.18576/amis/120302
Sujatha, T., Reddy, K.J., Kumar, J.G.: Chemical reaction effect on nonlinear radiative MHD nanofluid flow over cone and wedge. Defect Diffusion Forum 393, 83–102 (2019)
Ramzan, M., Rafiq, A., Chung, J.D., Kadry, S., Chu, Y.M.: Nanofluid flow with autocatalytic chemical reaction over a curved surface with nonlinear thermal radiation and slip condition. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73142-9
Acknowledgements
The authors are very much thankful for the constructive comments and suggestions of the editor as well as the anonymous reviewers, which led to improvement of the paper. The corresponding author is very grateful to the financial support of Adama Science and Technology University (Grant No. ASTU/SP-R/073/20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing interests that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rikitu, B.H., Makinde, O.D. & Enyadene, L.G. Unsteady mixed convection of a radiating and reacting nanofluid with variable properties in a porous medium microchannel. Arch Appl Mech 92, 99–119 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-02043-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-021-02043-8