Abstract
Main conclusion
Role of terpenes and isoprenoids has been pivotal in the survival and evolution of higher plants in various ecoregions. These products find application in the pharmaceutical, flavor fragrance, and biofuel industries.
Fitness of plants in a wide range of environmental conditions entailed (i) evolution of secondary metabolic pathways enabling utilization of photosynthate for the synthesis of a variety of biomolecules, thereby facilitating diverse eco-interactive functions, and (ii) evolution of structural features for the sequestration of such compounds away from the mainstream primary metabolism to prevent autotoxicity. This review summarizes features and applications of terpene and isoprenoid compounds, comprising the largest class of secondary metabolites. Many of these terpene and isoprenoid biomolecules happen to be high-value bioproducts. They are essential components of all living organisms that are chemically highly variant. They are constituents of primary (quinones, chlorophylls, carotenoids, steroids) as well as secondary metabolism compounds with roles in signal transduction, reproduction, communication, climatic acclimation, defense mechanisms and more. They comprise single to several hundreds of repetitive five-carbon units of isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and its isomer dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). In plants, there are two pathways that lead to the synthesis of terpene and isoprenoid precursors, the cytosolic mevalonic acid (MVA) pathway and the plastidic methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway. The diversity of terpenoids can be attributed to differential enzyme and substrate specificities and to secondary modifications acquired by terpene synthases. The biological role of secondary metabolites has been recognized as pivotal in the survival and evolution of higher plants. Terpenes and isoprenoids find application in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, synthetic chemistry, flavor fragrance, and possibly biofuel industries.

The cross-sectional view of a mitochondrion shown in this figure is modified from Google images (please see supplementary materials)

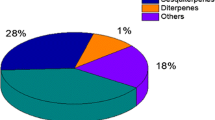
Images used in the preparation of this figure, left and right panels, were modified from Google images, clip art and creative commons and these sites are listed in the supplementary materials
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas F, Ke Y, Yu R et al (2017) Volatile terpenoids: multiple functions, biosynthesis, modulation and manipulation by genetic engineering. Planta 246:803–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2749-x
Betterle N, Melis A (2018) Heterologous leader sequences in fusion constructs enhance expression of geranyl diphosphate synthase and yield of β-phellandrene production in cyanobacteria (Synechocystis). ACS Synth Biol 7(3):912–921. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.7b00431
Bohlmann J, Keeling CI (2008) Terpenoid biomaterials. Plant J 54:656–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313x.2008.03449.x
Bracha-Drori K, Shichrur K, Lubetzky TC, Yalovsky S (2008) Functional analysis of Arabidopsis postprenylation CaaX processing enzymes and their function in subcellular protein targeting. Plant Physiol 148:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.120477
Chaves JE, Melis A (2018a) Engineering isoprene synthesis in cyanobacteria. FEBS Lett 592:2059–2069. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.13052
Chaves JE, Melis A (2018b) Biotechnology of cyanobacterial isoprene production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:6451–6458
Cho KS, Lim YR, Lee K et al (2017) Terpenes from forests and human health. Toxicol Res 33:97–106. https://doi.org/10.5487/tr.2017.33.2.097
Croteau R, Kutcahn TM, Lewis NG (2000) Natural products. In: Buchanan B, Gruissem W, Jones R (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville, pp 1250–1318
Englund E, Shabestary K, Hudson EP et al (2018) Cyanobacterial production of plant essential oils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 248:2791–2800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.07.004
Formighieri C, Melis A (2016) Sustainable heterologous production of terpene hydrocarbons in cyanobacteria. Photosynth Res 130:123–135
Formighieri C, Melis A (2017) Heterologous synthesis of geranyllinalool, a diterpenol plant product, in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:2791–2800
Formighieri C, Melis A (2018) Cyanobacterial production of plant essential oils. Planta 248:933–946
Gao Y, Honzatko RB, Peters RJ (2012) Terpenoid synthase structures: a so far incomplete view of complex catalysis. Nat Prod Rep 29:1153–1175. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2np20059g
Gershenzon J, Dudareva N (2007) The function of terpene natural products in the natural world. Nat Chem Biol 3:408–414. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2007.5
Hausch BJ, Lorjaroenphon Y, Cadwallader KR (2015) Flavor chemistry of lemon-lime carbonated beverages. J Agric Food Chem 63:112–119
Holstein SA, Hohl RJ (2004) Isoprenoids: remarkable diversity of form and function. Lipids 39:293–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-004-1233-3
Kokkiripati PK, Bhakshu LM, Marri S et al (2011) Gum resin of Boswellia serrata inhibited human monocytic (THP-1) cell activation and platelet aggregation. J Ethnopharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.07.004
Kokkiripati PK, Kamsala RV, Bashyam L et al (2013) Stem-bark of Terminalia arjuna attenuates human monocytic (THP-1) and aortic endothelial cell activation. J Ethnopharmacol 146:456–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.12.050
Kutyna DR, Borneman AR (2018) Heterologous production of flavour and aroma compounds in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes (Basel) 9:326–341. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9070326
Lauersen KJ, Wichmann J, Baier T et al (2018) Phototrophic production of heterologous diterpenoids and a hydroxy- functionalized derivative from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metab Eng 49:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.07.005
Laule O, Furholz A, Chang H-S et al (2003) Crosstalk between cytosolic and plastidial pathways of isoprenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:6866–6871. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1031755100
Laurent M (2018) Vitamin E biosynthesis and its regulation in plants. Antiioxidants. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7010002
Lee C (2016) Fifty years of research and development of cosmeceuticals: a contemporary review. J Cosmet Dermatol 15:527–539. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12261
Li L, Ma X, Zhan R et al (2017) Profiling of volatile fragrant components in a mini-core collection of mango germplasms from seven countries. PLoS One 12:1–14
Lohr M, Schwender J, Polle JEW (2012) Isoprenoid biosynthesis in eukaryotic phototrophs: a spotlight on algae. Plant Sci 185–186:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.07.018
Lombard J, Moreira D (2011) Origins and early evolution of the mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in the three domains of life. Mol Biol Evol 28:87–99. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msq177
Melis A (2017) Terpene hydrocarbons production in cyanobacteria. In: Los DA (ed) Cyanobacteria: omics and manipulation. Caister Academic Press, UK, pp 187–198
Moniodis J, Jones CG, Barbour EL et al (2015) The transcriptome of sesquiterpenoid biosynthesis in heartwood xylem of Western Australian sandalwood (Santalum spicatum). Phytochemistry 113:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.12.009
Moses T, Pollier J, Thevelein JM, Goossens A (2013) Bioengineering of plant (tri) terpenoids: from metabolic engineering of plants to synthetic biology in vivo and in vitro. New Phytol 200:27–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12325
Niebler J, Buettner A (2015) Identification of odorants in frankincense (Boswellia sacra Flueck.) by aroma extract dilution analysis and two-dimensional gas chromatography–mass spectrometry/olfactometry. Phytochemistry 109:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.10.030
Nolan KA, Marmur ES (2012) Over-the-counter topical skincare products: a review of the literature. J Drugs Dermatol 11:220–224
Nuutinen T (2018) Medicinal properties of terpenes found in Cannabis sativa and Humulus lupulus. Eur J Med Chem 157:198–228
Paddon CJ, Westfall PJ, Pitera DJ et al (2013) High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin. Nature 496:528–536. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12051
Pateraki I, Kanellis A (2010) Stress and developmental responses of terpenoid biosynthetic genes in Cistus creticus subsp. creticus. Plant Cell Rep 29:629–641
Pérez-Sánchez A, Barrajón-Catalán E, Herranz-López M, Micol V (2018) Nutraceuticals for skin care: a comprehensive review of human clinical studies. Nutrients 10:1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040403
Phulara SC, Chaturvedi P, Gupta P (2016) Isoprenoid-based biofuels: homologous expression and heterologous expression in prokaryotes. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:5730–5740. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01192-16
Pragadheesh VS, Chanotiya CS, Rastogi S, Shasany AK (2017) Scent from Jasminum grandiflorum flowers: investigation of the change in linalool enantiomers at various developmental stages using chemical and molecular methods. Phytochemistry 140:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.04.018
Pulido P, Perello C, Rodriguez-Concepcion M (2012) New insights into plant isoprenoid metabolism. Mol Plant 5:964–967. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sss088
Raguso RA (2016) More lessons from linalool: insights gained from a ubiquitous floral volatile. Curr Opin Plant Biol 32:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2016.05.007
Rodríguez-Concepción M (2014) Plant isoprenoids: a general overview. In: Rodríguez-Concepción M (ed) Plant isoprenoids: methods and protocols, methods in molecular biology. Springer, New York, pp 1–5
Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Avalos J, Bonet ML et al (2018) A global perspective on carotenoids: metabolism, biotechnology, and benefits for nutrition and health. Prog Lipid Res 70:62–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2018.04.004
Sathasivam R, Ki J-S (2018) A Review of the biological activities of microalgal carotenoids and their potential use in healthcare and cosmetic industries. Mar Drugs 16:26–37. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010026
Schwieterman ML, Colquhoun TA, Jaworski EA et al (2014) Strawberry flavor: diverse chemical compositions, a seasonal influence, and effects on sensory perception. PLoS One 9:e88446. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088446
Shahidi F, de Camargo AC (2016) Tocopherols and tocotrienols in common and emerging dietary sources: occurrence, applications, and health benefits. Int J Mol Sci 17:1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101745
Sugawara Y, Hara C, Aoki T et al (2000) Odor distinctiveness between enantiomers of linalool: difference in perception and responses elicited by sensory test and forehead surface potential wave measurement. Chem Senses 25:77–84
Sun P, Schuurink RC, Caissard J et al (2016) My way: noncanonical biosynthesis pathways for plant volatiles. Trends Plant Sci 10:884–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2016.07.007
Tholl D (2015) Biosynthesis and biological functions of terpenoids in plants. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 148:63–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/10_2014_295
Tippmann S, Chen Y, Siewers V, Nielsen J (2013) From flavors and pharmaceuticals to advanced biofuels: production of isoprenoids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol J 8:1435–1444. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201300028
Vickers CE, Williams TC, Peng B, Cherry J (2017) Recent advances in synthetic biology for engineering isoprenoid production in yeast. Curr Opin Chem Biol 40:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.05.017
Wagner K-H, Elmadfa I (2003) Biological relevance of terpenoids. Overview focusing on mono-, di- and tetraterpenes. Ann Nutr Metab Nutr Metab 47:95–106
Wang G, Tang W, Bidigare RR (2005) Terpenoids as therapeutic drugs and pharmaceutical agents. In: Z L (ed) Natural Products. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 197–227
Wichmann J, Baier T, Wentnagel E et al (2018) Tailored carbon partitioning for phototrophic production of (E)-α-bisabolene from the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metab Eng 45:211–222
Wojtunik-kulesza KA, Targowska-duda K, Klimek K (2017) Volatile terpenoids as potential drug leads in Alzheimer’ s disease. Open Chem 15:332–343
Zhao DD, Jiang LL, Li HY et al (2016) Chemical components and pharmacological activities of terpene natural products from the genus Paeonia. Molecules 21:E1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101362
Acknowledgements
The author thanks the Indian Government funding agencies, DBT (BT/PR/10972/GBD/27/123/2008), UGC (37/532/2010 SR), CSIR (38(1334)/12/EMR-II/2013) and ICMR (59/48/2010/BMS/TRM) for support to her laboratory and for enabling work with medicinal and aromatic plants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tetali, S.D. Terpenes and isoprenoids: a wealth of compounds for global use. Planta 249, 1–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-3056-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-3056-x