Abstract
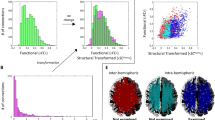
The corpus callosum (CC) is the largest white matter structure of the brain and offers the structural basis for an intense interaction between both cerebral hemispheres. Especially with respect to the interaction of both motor cortices it shows a differentiated somatotopic organization. Neuropathological processes are often reflected in structural alterations of the CC and a spatially precise description of structures for the healthy brain is essential for further differentiation of structural damage in patients. We performed a fine-grained parcellation of the CC on 1065 diffusion-weighted data sets of the Human Connectome Project. Interhemispheric tractograms between interhemispherically corresponding functional subdivisions of the primary motor cortex (M1; Brainnetome Atlas) were calculated, transformed into a common space, averaged and thresholded, to be assessed for localization, fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD). Spatially distinct CC regions for each functional M1 subdivision (lower and upper limbs, head/face, tongue/larynx) were identified and will be available as anatomical masks. Non-parametrical statistics for the average FA and MD values showed significant differences between all callosal regions. The newly proposed callosal regions allow for a precise differentiation of M1–M1 motor connectivity and the structural integrity of these tracts. Availability of masked regions in a common space will help to better understand inter-hemispherical callosal connectivity in patients or healthy volunteers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboitiz F, Scheibel AB, Fisher RS, Zaidel E (1992) Fiber composition of the human corpus callosum. Brain Res 598:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(92)90178-C
Andersson JLR, Sotiropoulos SN (2016) An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage 125:1063–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.019
Andersson JL, Xu J, Yacoub E et al (2012) A comprehensive Gaussian process framework for correcting distortions and movements in diffusion images. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 20:2426
Behrens TEJ, Woolrich MW, Jenkinson M et al (2003) Characterization and propagation of uncertainty in diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 50:1077–1088. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.10609
Behrens TEJ, Berg HJ, Jbabdi S et al (2007) Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: what can we gain? Neuroimage 34:144–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.09.018
Brambilla P, Cerini R, Gasparini A et al (2005) Investigation of corpus callosum in schizophrenia with diffusion imaging. Schizophr Res 79:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2005.04.012
Chao YP, Cho KH, Yeh CH et al (2009) Probabilistic topography of human corpus callosum using cytoarchitectural parcellation and high angular resolution diffusion imaging tractography. Hum Brain Map 30:3172–3187. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20739
Clarke JM, Zaidel E (1994) Anatomical-behavioral relationships: corpus callosum morphometry and hemispheric specialization. Behav Brain Res 64:185–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(94)90131-7
Cook PA, Zhang H, Avants BB et al (2005) An automated approach to connectivity-based partitioning of brain structures. 164–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/11566465_21
Cover G, Pereira M, Bento M et al (2017) Data-driven corpus callosum parcellation method through diffusion tensor imaging. IEEE Access 5:22421–22432. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2761701
de Reus MA, van den Heuvel MP (2013) The parcellation-based connectome: limitations and extensions. Neuroimage 80:397–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.03.053
Fan L, Li H, Zhuo J et al (2016) The human brainnetome atlas: a new brain atlas based on connectional architecture. Cereb Cortex 26:3508–3526. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw157
Glasser MF, Sotiropoulos SN, Wilson JA et al (2013) The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the human connectome project. Neuroimage 80:105–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.127
Grefkes C, Eickhoff SB, Nowak DA et al (2008) Dynamic intra- and interhemispheric interactions during unilateral and bilateral hand movements assessed with fMRI and DCM. Neuroimage 41:1382–1394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.048
Hofer S, Frahm J (2006) Topography of the human corpus callosum revisited-comprehensive fiber tractography using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 32:989–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.05.044
Horn U, Roschka S, Eyme K et al (2016) Increased ventral premotor cortex recruitment after arm training in an fMRI study with subacute stroke patients. Behav Brain Res 308:152–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.04.040
Huang H, Zhang J, Jiang H et al (2005) DTI tractography based parcellation of white matter: application to the mid-sagittal morphology of corpus callosum. Neuroimage 26:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.01.019
Hynd GW, Hall J, Novey ES et al (1995) Dyslexia and corpus callosum morphometry. Arch Neurol 52:32–38
Jbabdi S, Sotiropoulos SN, Savio AM et al (2012) Model-based analysis of multishell diffusion MR data for tractography: how to get over fitting problems. Magn Reson Med 68:1846–1855. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24204
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TEJ et al (2012) FSL Neuroimage 62:782–790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015
Kochunov P, Glahn DC, Lancaster JL et al (2010) Genetics of microstructure of cerebral white matter using diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroimage 53:1109–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.078
Lebel C, Caverhill-Godkewitsch S, Beaulieu C (2010) Age-related regional variations of the corpus callosum identified by diffusion tensor tractography. Neuroimage 52:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.03.072
Lee SJ, Steiner RJ, Luo S et al (2015) Quantitative tract-based white matter heritability in twin neonates. Neuroimage 111:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.021
Li Y, Wu P, Liang F, Huang W (2015) The microstructural status of the corpus callosum is associated with the degree of motor function and neurological deficit in stroke patients. PLoS One 10:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122615
Lindow J, Domin M, Grothe M et al (2016) Connectivity-based predictions of hand motor outcome for patients at the subacute stage after stroke. Front Hum Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00101
Lotze M, Ladda AM, Roschka S et al (2017) Priming hand motor training with repetitive stimulation of the fingertips; Performance gain and functional imaging of training effects. Brain Stimul 10:139–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2016.10.004
Mihai PG, Otto M, Domin M et al (2016) Brain imaging correlates of recovered swallowing after dysphagic stroke: a fMRI and DWI study. NeuroImage Clin 12:1013–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2016.05.006
Mori S, Wakana S, Van Zijl PCM, Poetscher L (2005) MRI atlas of human white matter. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Park H-J, Kim JJ, Lee S-K et al (2008) Corpus callosal connection mapping using cortical gray matter parcellation and DT-MRI. Hum Brain Map 29:503–516. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20314
Rittner L, Freitas PF, Appenzeller S, Lotufo R de A (2014) Automatic DTI-based parcellation of the corpus callosum through the watershed transform. Rev Bras Eng Biomed 30:132–143. https://doi.org/10.1590/rbeb.2014.012
Schulz R, Koch P, Zimerman M et al (2015) Parietofrontal motor pathways and their association with motor function after stroke. Brain 138:1949–1960. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awv100
Skranes J, Vangberg TR, Kulseng S et al (2007) Clinical findings and white matter abnormalities seen on diffusion tensor imaging in adolescents with very low birth weight. Brain 130:654–666. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm001
Sotiropoulos SN, Jbabdi S, Xu J et al (2013) Advances in diffusion MRI acquisition and processing in the human connectome project. Neuroimage 80:125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.057
Wahl M, Hübers A, Lauterbach-Soon B et al (2011) Motor callosal disconnection in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Hum Brain Map 32:846–855. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21071
Wassermann EM, Fuhr P, Cohen LG, Hallett M (1991) Effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation on ipsilateral muscles. Neurology 41:1795–1795. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.41.11.1795
Witelson SF (1989) Hand and sex differences in the isthmus and genus of the human corpus callosum: a postmortem morphological study. Brain 112:779–835
Acknowledgements
Diffusion-weighted images were generously provided by the courtesy of the Human Connectome Project. MD and ML were funded by the University Medicine Greifswald.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domin, M., Lotze, M. Parcellation of motor cortex-associated regions in the human corpus callosum on the basis of Human Connectome Project data. Brain Struct Funct 224, 1447–1455 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01849-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01849-1