Abstract
Background
Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer (PC) by using sensitive and specific biomarkers is considered necessary. MiRNAs are master regulators of gene expression and several biological processes, and they are dysregulated in various cancers, where they play a vital role in either cancer progression or suppression. So, this study was designed to investigate the role of plasma miR-22-3p, miR-642b-3p and miR-885-5p expression as possible diagnostic markers in PC patients as compared to serum CA19-9. In addition, the correlation of those miRNAs and CA19-9 with clinical characteristics of PC patients was analyzed.
Methods
The expression levels of selected miRNAs and serum CA19-9 concentration were determined for 35 patients with PDAC and 15 healthy controls by quantitative real-time RT-PCR and electro-chemiluminescence immune assay, respectively. The sensitivities of miRNAs as biomarkers of PC were evaluated and compared with CA19-9 using a receiver operating characteristic analysis.
Results
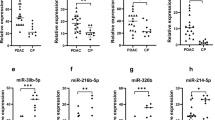
The levels of three miRNAs (miR-22-3p, miR-642b-3p and miR-885-5p) and CA19-9 were significantly higher in PC patients, even those with early-stage disease (IB and IIB), than in healthy control. Both miRNAs and CA19-9 were associated with tumor stage. The high sensitivities of the three selected miRNAs and CA19-9 were observed.
Conclusion
The measurement of miR-22-3p, miR-642b-3p and miR-885-5p may prove to have clinical utility in diagnosis of PC. Those miRNAs are ideal early biomarkers for PC diagnosis. So, they can effectively be used with serum CA19-9 for PC screening in early tumor stage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abue M, Yokoyama M, Shibuya R, Tamai K, Yamaguchi K, Sato I (2015) Circulating miR-483-3p and miR-21 is highly expressed in plasma of pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol 46:539–547
Afanasyeva EA, Mestdagh P, Kumps C, Vandesompele J, Ehemann V, Theissen J et al (2011) MicroRNA miR-885-5p targets CDK2 and MCM5, activates p53 and inhibits proliferation and survival. Cell Death Differ 18:974–984
Amirkande SY, Assmar M, Faribors MG, Noor AM (2015) The frequency of CA15-3, CA125, CA19-9 in Patients with Hepatitis B and C. Zahedan J Res Med Sci 17:29–33
Bae S, Lim KM, Cha HJ, An IS, Lee JP, Lee KS et al (2014) Arctiin blocks hydrogen peroxide-induced senescence and cell death though microRNA expression changes in human dermal papilla cells. Biol Res 47:50–60
Becker AE, Hernandez YG, Frucht H, Lucas AL (2014) Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: risk factors, screening, and early detection. World J Gastroenterol 20:11182–11198
Bertino G, Ardiri AM, Calvagno GS, Malaguarnera G, Interlandi D, Vacante M et al (2013) Carbohydrate 19.9 antigen serum levels in liver disease. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–6
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S et al (2004) Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2999–3004
Chitkara D, Mittal A, Mahato RI (2015) MiRNAs in pancreatic cancer: therapeutic potential, delivery challenges and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 81:34–52
Ganepola GAP, Rutledge JR, Suman P, Yiengpruksawan A, Chang DH (2014) Novel blood-based microRNA biomarker panel for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 6:22–33
Garzon R, Volina S, Liu CG, Cymering CF, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F et al (2008) MicroRNA signatures associated with cytogenetic and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 111:3183–3189
Gayral M, Jo S, Hanoun N, Vidoni AV, Lulka H, Delpu Y et al (2014) MicroRNAs as emerging biomarkers and therapeutic targets for pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 20:11199–11209
Guan X, Liu Z, Liu H, Yu H, Wang LE, Sturgis EM et al (2013) A functional variant at the miR-885-5p binding site of CASP3 confers risk of both index and second primary malignancies in patients with head and neck cancer. FASEB J 27:1404–1412
Gui J, Tian Y, Wen X, Zhang W, Zhang P, Gao J (2011) Serum microRNA characterization identifies miR-885-5p as a potential marker for detecting liver pathologies. Clin Sci 120:183–193
Gurha P, Abreu-Goodger C, Wang T, Ramirez MO, Drumond AL, Van Dongen S et al (2012) Targeted deletion of microRNA-22 promotes stress-induced cardiac dilation and contractile dysfunction. Circulation 125:2751–2761
Halkova T, Cuperkova R, Minarik M, Benesova L (2015) MicroRNAs in pancreatic cancer: involvement in carcinogenesis and potential use for diagnosis and prognosis. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2015:1–11
Hawa Z, Haque I, Ghosh A, Banerjee S, Harris LC, Banerjee SK (2016) The miRacle in Pancreatic Cancer by miRNAs: tiny Angels or Devils in Disease Progression. Int J Mol Sci 17:809–831
Hekele MS, Muller C (2006) The combined elevation of tumor markers CA 19-9 and CA 125 in liver disease patients is highly specific for severe liver fibrosis. Dig Dis Sci 51:338–345
Kim JE, Kim SJ, Lee BH, Park RW, Kim KS, Kim IS (2000) Identification of motifs for cell adhesion within the repeated domains of transforming growth factor-beta-induced gene, betaig-h3. J Biol Chem 275:30907–30915
Ko AH (2015) Progress in the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer and the search for next opportunities. J Clin Oncol 33:1779–1786
Kojima M, Sudo H, Kawauchi J, Takizawa S, Kondou S, Nobumasa H et al (2015) MicroRNA markers for the diagnosis of pancreatic and biliary-tract cancers. PLoS ONE 10:1–22
Kumar S, Kumar A, Shah PP, Rai SN, Panguluri SK, Kakar SS (2011) MicroRNA signature of cisplatin resistant vs. cisplatin sensitive ovarian cancer cell lines. J Ovarian Res 4:17–27
Li A, Yu J, Kim H, Wolfgang CL, Canto MI, Hruban RH et al (2013) MicroRNA array analysis finds elevated serum miR-1290 accurately distinguishes patients with low-stage pancreatic cancer from healthy and disease controls. Clin Cancer Res 19:3600–3610
Lin MS, Huang JX, Yu H (2014) Elevated serum level of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in benign biliary stricture diseases can reduce its value as tumor marker. Int J Clin Exp Med 7:744–750
Ling B, Wang GX, Long G, Qiu JH, Hu ZL (2012) Tumor suppressor miR-22 suppresses lung cancer cell progression through post-transcriptional regulation of ErbB3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138:1355–1361
Liu J, Gao J, Du Y, Li Z, Ren Y, Gu J et al (2012) Combination of plasma microRNAs with serum CA19-9 for early detection of pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 131:683–691
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL et al (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10513–10518
Negrini M, Ferracin M, Sabbioni S, Croce CM (2007) MicroRNAs in human cancer: from research to therapy. J Cell Sci 120:1833–1840
Nelson KM, Weiss GJ (2008) MicroRNAs and cancer: past, present, and potential future. Mol Cancer Ther 7:3655–3660
Park JY, Helm J, Coppola D, Kim D, Mokenge M, Kim SJ (2011) MiroRNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 17(7):817–827
Patel JB, Appaiah HN, Burnett RM, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Wang G, Mehta R et al (2011) Control of EVI-1 oncogene expression in metastatic breast cancer cells through microRNA miR-22. Oncogene 30:1290–1301
Polioudakis D, Bhinge AA, Killion PJ, Lee BK, Abell NS, Iyer VR (2013) A Myc-microRNA network promotes exit from quiescence by suppressing the interferon response and cell-cycle arrest genes. Nucleic Acids Res 41:2239–2254
Price C, Chen J (2014) MicroRNAs in cancer biology and therapy: current status and perspectives. Genes Dis 1:53–63
Qureshi KM, Raman AK, Tan D, Fakih MG (2006) Leukemoid reaction in pancreatic cancer: a case report and review of the literature. JOP J Pancreas 7:631–634
Rachagania S, Machaa MA, Heimanna N, Seshacharyulua P, Haridasa D, Chugha S et al (2015) Clinical implications of miRNAs in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 81:16–33
Schwarzenbach H, Nishida N, Calin GA, Pantel K (2014) Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 11:145–156
Su SB, Qin SY, Chen W, Luo W, Jiang HX (2015) Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 for differential diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 14(21):4323–4333
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylo C (2008) MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 110:13–21
Tian Y, Gui J, Run W, Wen X, Zhang W, Zhang P (2012) Hepatic diseases related peripheral blood RNAs variation and their clinical significance. J Mol Biomark Diagn 3:39
Ting Y, Medina DJ, Strair RK, Schaar DG (2010) Differentiation-associated miR-22 represses Max expression and inhibits cell cycle progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394:606–611
Vestergaard EM, Hein HO, Meyer H, Grunnet N, Jørgensen J, Wolf H et al (1999) Reference values and biological variation for tumor marker CA 19-9 in serum for different Lewis and secretor genotypes and evaluation of secretor and Lewis genotyping in a Caucasian population. Clin Chem 45:54–61
Vietsch EE, Eijck CHJ, Wellstein A (2015) Circulating DNA and micro-RNA in patients with pancreatic cancer. Pancreat Disord Ther 5:1–11
Wang W, Li F, Zhang Y, Tu Y, Yang Q, Gao X (2013a) Reduced expression of miR-22 in gastric cancer is related to clinicopathologic characteristics or patient prognosis. Diagn Pathol 8:102–107
Wang WS, Liu LX, Li GP, Chen Y, Li CY, Jin DY et al (2013b) Combined serum CA19-9 and miR-27a-3p in peripheral blood mononuclear cells to diagnose pancreatic cancer. Cancer Prev Res 6:331–338
Winter JM, Yeo CJ, Brody JR (2013) Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol 107:15–22
Xiong J, Yu D, Wei N, Fu H, Cai T, Huang Y et al (2010) An estrogen receptor alpha suppressor, microRNA-22, is downregulated in estrogen receptor alpha-positive human breast cancer cell lines and clinical samples. FEBS J 277:1684–1694
Yamakuchi M, Yagi S, Ito T, Lowenstein CJ (2011) MicroRNA-22 regulates hypoxia signaling in colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 6:e20291
Yan W, Zhang W, Sun L, Liu Y, You G, Wang Y et al (2011) Identification of MMP-9 specific microRNA expression profile as potential targets of anti-invasion therapy in glioblastoma multiforme. Brain Res 1411:108–115
Yu DC, Li QG, Ding XW, Ding YT (2011) Circulating microRNAs: potential biomarkers for cancer. Int J Mol Sci 12:2055–2063
Zaragosi LE, Wdziekonski B, Brigand KL, Villageois P, Mari B, Waldmann R et al (2011) Small RNA sequencing reveals miR-642a-3p as a novel adipocyte-specific microRNA and miR-30 as a key regulator of human adipogenesis. Genome Biol 12:1–13
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2007) MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol 302:1–12
Zhang L, Jamaluddin MS, Weakley SM, Yao Q, Chen C (2011) Roles and mechanisms of microRNAs in pancreatic cancer. World J Surg 35:1725–1731
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the Local Ethical Committee of the Medical Research Institute, Alexandria University.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussein, N.A.E.M., Kholy, Z.A.E., Anwar, M.M. et al. Plasma miR-22-3p, miR-642b-3p and miR-885-5p as diagnostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143, 83–93 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2248-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2248-7