Abstract
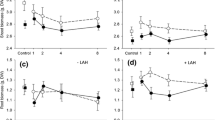
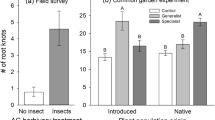
Separate and combined effects of root and leaf herbivores on plant growth, flower visitation and seed set were tested in a factorial experiment using potted mustard, Sinapis arvensis, at an old fallow field. A 50% leaf removal by cabbageworms (Pieris rapae) when the seedlings had their first four leaves reduced plant height and shoot mass, and delayed the onset of flowering. Root herbivory by two wireworms (Agriotes sp.) over the whole experiment changed flower visitation; the number of flower visitors per plant was higher in plants with root herbivores than in plants without root herbivores. Combined leaf and root herbivory affected flowering period, number of fruits per plant and number of seeds per fruit. Plants attacked by leaf and root herbivores had a shorter flowering period and produced fewer fruits per plant than plants with root herbivores only. Although the experimental plants faced major herbivore-induced growth changes, plant reproduction (seed set and weight per plant) was similar in all treatments, documenting their ability to effectively compensate for leaf and root herbivory.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen DC (1987) Below-ground herbivory in natural communities: a review emphasizing fossorial animals. Q Rev Biol 62:261–286
Bonkowski M, Geoghegann I, Nicholas A, Birch E, Griffiths B (2001) Effects of soil decomposer invertebrates (protozoa and earthworms) on above-ground phytophagous insect (cereal aphid) mediated through changes in the host plant. Oikos 95:441–450
Bonkowski M, Cheng W, Griffiths B, Alphei J, Scheu S (2000) Microbial-faunal interactions in the rhizosphere and effects on plant growth. Eur J Soil Biol 36:135–147
Brown VK, Gange AC (1989) Herbivory by soil-dwelling insects depresses plant species richness. Funct Ecol 3:667–671
Brown VK, Gange AC (1990) Insect herbivory below ground. In: Begon M, Fitter AH, Macfadyen A (eds) Adv Ecol Res 20:1–58
Brown VK, Gange AC (2002) Tritrophic below-and above-ground interactions in succession. In: Tscharntke T, Hawkins B (eds) Multitrophic level interactions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 197–222
Brown VK, Gange AC, Evans IM, Storr L (1987) The effect of insect herbivory on the growth and reproduction of two annual Vicia species at different stages in plant succession. J Ecol 75:1173–1189
Conner JK, Rush S (1996) Effects of flower size and number on pollinator visitation to wild radish, Raphanus raphanistrum. Oecologia 105:509–516
Crawley M (1983) Herbivory: the dynamics of animal-plant interactions. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 40–70
Davidson RL, Wensler RJ, Wolfe VJ (1970) Damage to ryegrass plants of different size by various densities of the pruinose scarab (Sericesthis geminata (Coleoptera)). Aust J Exp Agric Anim Husb 10:166–171
Gange AC, Brown VK (1989) Effects of root herbivory by an insect on a foliar feeding species, mediated through changes in the host plant. Oecologia 81:38–42
Hambäck PA (2001) Direct and indirect effects of herbivory: feeding by spittlebugs affects pollinator visitation rates and seed set of Rudbeckia hirta. Ecoscience 8:45–50
Karban R, Strauss S (1993) Effects of herbivores on growth and reproduction of their perennial host, Erigeron glaucus. Ecology 74:39–46
Kinsmann S, Platt WJ (1984) The impact of a herbivore upon Mirabilis hirsuta, a fugitive prairie plant. Oecologia 65:2–6
Lehtila K, Strauss S (1997) Leaf damage by herbivores affects attractiveness to pollinators in wild radish, Raphanus raphanistrum. Oecologia 111:396–403
Lehtila K, Strauss S (1999) Effects of foliar herbivory on male and female reproductive traits of wild radish, Raphanus raphanistrum. Ecology 80:116–124
Maron JL (1998) Insect herbivory above- and belowground: individual and joint effects on plant fitness. Ecology 79:1281–1293
Marquis R (1984) Leaf herbivores decrease fitness of a tropical plant. Science 226:537–539
Masters GJ, Brown VK (1992) Plant mediated interactions between two spatially separated insects. Funct Ecol 6:175–179
Masters GJ, Brown VK, Gange AC (1993) Plant mediated interactions between above- and below- ground insect herbivores. Oikos 66:148–151
Masters GJ, Jones H, Rogers M (2001) Host-plant mediated effects of root herbivory on insect seed predators and their parasitoids. Oecologia 127:246–250
McNaughton SJ (1983) Compensatory plant growth as a response to herbivory. Oikos 40:329–336
Moran N, Whitham T (1990) Interspecific competition between root-feeding and leaf-galling aphids mediated by host-plant resistance. Ecology 71:1050–1058
Mothershead K, Marquis R (2000) Fitness impacts of herbivory through indirect effects on plant-pollinator interactions in Oenothera macrocarpa. Ecology 81:30–40
Nötzold R, Blossey B, Newton E (1998) The influence of below ground herbivory and plant competition on growth and biomass allocation of purple loosestrife. Oecologia 113:82–93
Powell RD, Myers JH (1988) The effect of Sphenoptera jugoslavica Obenb. (Col., Buprestidae) on its host plant Centaurea diffusa Lam. (Compositae). J Appl Entomol 160:25–45
Ridsdill Smith TJ (1977) Effects of root-feeding by scarabaeid larvae on growth of perennial ryegrass plants. J Appl Ecol 14:73–80
Riedell W (1989) Western corn rootworm damage in maize: greenhouse technique and plant response. Crop Sci 29:412–415
Scheu S, Parkinson D (1994) Effects of invasion of an aspen forest (Canada) by Dendrobaena octaedra (Lumbricidae) on plant growth. Ecology 75:2348–2361
Scheu S, Setälä H (2002) Multitrophic interactions in decomposer food-webs. In: Tscharntke T, Hawkins B (eds) Multitrophic level interactions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 223–264
Scheu S, Theenhaus A, Jones TH (1999) Links between the detritivore and the herbivore system: effects of earthworms and Collembola on plant growth and aphid development. Oecologia 119:541–551
Simberloff D, Brown BJ, Lowrie S (1978) Isopod and insect root borers may benefit Florida mangroves. Science 201:630–632
StatSoft (1995) Statistica version 5 for Windows. Statsoft, Tulsa, Okla.
Stephenson AG (1981) Flower and fruit abortion: proximate causes and ultimate functions. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 12:253–279
Stirling KJ, Clark RJ, Brown PH, Wilson SJ (2002) Effect of photoperiod on flower bud initiation and development in myoga (Zingiber mioga Roscoe.). Sci Hortic 95:261–268
Strauss S (1991) Direct, indirect, and cumulative effects of three native herbivores on a shared host plant. Ecology 72:543–558
Strauss S (1997) Floral characters link herbivores, pollinators, and plant fitness. Ecology 78:1640–1645
Strauss S, Conner J, Rush S (1996) Foliar herbivory affects floral characters and plant attractiveness to pollinators: implications for male and female plant fitness. Am Nat 147:1098–1107
Van der Putten W, Vet L, Harvey J, Wäckers F (2001) Linking above- and belowground multitrophic interactions of plants, herbivores, pathogens, and their antagonists. Trends Ecol Evol 16:547–554
Wardle D (1999) How soil food webs make plants grow. Trends Ecol Evol 14:418–420
Acknowledgements
We thank Jorge Jácome for his invaluable help with field work, and Martijn Bezemer, David Wardle, Gregory Masters, Oscar Murillo, Gilbert Barrantes and two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments on drafts of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poveda, K., Steffan-Dewenter, I., Scheu, S. et al. Effects of below- and above-ground herbivores on plant growth, flower visitation and seed set. Oecologia 135, 601–605 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-003-1228-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-003-1228-1