Abstract
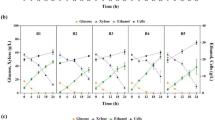
Recombinant Escherichia coli whole cells harboring Bacillus licheniformis l-arabinose isomerase (BLAI) were immobilized with alginate. The operational conditions for immobilization were optimized with response surface methodology. Optimal alginate concentration, Ca2+ concentration, and cell mass loading were 1.8% (w/v), 0.1 M, and 44.5 g L−1, respectively. The interactions between Ca2+ concentration, alginate concentration, and initial cell mass were significant. After immobilization of BLAI, cross-linking with 0.1% glutaraldehyde significantly reduced cell leakage. The half-life of immobilized whole cells was 150 days, which was 50-fold longer than that of free cells. In seven repeated batches for l-ribulose production, the productivity was as high as 56.7 g L−1 h−1 at 400 g L−1 substrate concentration. The immobilized cells retained 89% of the initial yield after 33 days of reaction. Immobilization of whole cells harboring BLAI, therefore, makes a suitable biocatalyst for the production of l-ribulose, particularly because of its high stability and low cost.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan LW, Heng PW (2002) Effects of aldehydes and methods of cross-linking on properties of calcium alginate microspheres prepared by emulsification. Biomaterials 23:1319–1326
Chan L, Jin Y, Heng P (2002) Cross-linking mechanisms of calcium and zinc in production of alginate microspheres. Int J Pharm 242:255–258
Roy I, Sharma S, Gupta MN (2004) Smart biocatalysts: design and applications. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 86:159–189
Akagi M, Omae D, Tamura Y, Ueda T, Kumashiro T, Urata H (2002) A practical synthesis of l-ribose. Chem Pharm Bull 50:866–868
Yun M, Moon HR, Kim HO, Choi WJ, Kim YC, Park CS, Jeong LS (2005) A highly efficient synthesis of unnatural l-sugars from d-ribose. Tetrahedron Lett 46:5903–5905
Takahashi H, Iwai Y, Hitomi Y, Ikegami S (2002) Novel synthesis of l-ribose from d-mannono-1, 4-lactone. Org Lett 4:2401–2403
Helanto M, Kiviharju K, Leisola M, Nyyssola A (2007) Metabolic engineering of Lactobacillus plantarum for production of l-ribulose. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:7083–7091
Roh HJ, Kim P, Park YC, Choi JH (2000) Bioconversion of d-galactose into d-tagatose by expression of l-arabinose isomerase. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 31:1–4
Jorgensen F, Hansen OC, Stougaard P (2004) Enzymatic conversion of d-galactose to d-tagatose: heterologous expression and characterisation of a thermostable l-arabinose isomerase from Thermoanaerobacter mathranii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:816–822
Kim BC, Lee YH, Lee HS, Lee DW, Choe EA, Pyun YR (2002) Cloning, expression and characterization of l-arabinose isomerase from Thermotoga neapolitana: bioconversion of d-galactose to d-tagatose using the enzyme. FEMS Microbiol Lett 212:121–126
Lee DW, Jang HJ, Choe EA, Kim BC, Lee SJ, Kim SB, Hong YH, Pyun YR (2004) Characterization of a thermostable l-arabinose (d-galactose) isomerase from the hyperthermophilic eubacterium Thermotoga maritima. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1397–1404
Lee SJ, Lee DW, Choe EA, Hong YH, Kim SB, Kim BC, Pyun YR (2005) Characterization of a thermoacidophilic l-arabinose isomerase from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius: role of Lys-269 in pH optimum. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7888–7896
Prabhu P, Tiwari MK, Jeya M, Gunasekaran P, Kim IW, Lee JK (2008) Cloning and characterization of a novel l-arabinose isomerase from Bacillus licheniformis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:283–290
Dische Z, Borenfreund E (1951) A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J Biol Chem 192:583–587
Potumarthi R, Subhakar C, Pavani A, Jetty A (2008) Evaluation of various parameters of calcium-alginate immobilization method for enhanced alkaline protease production by Bacillus licheniformis NCIM-2042 using statistical methods. Bioresour Technol 99:1776–1786
Li W, Du W, Liu D (2007) Optimization of whole cell-catalyzed methanolysis of soybean oil for biodiesel production using response surface methodology. J Mol Catal B Enzym 45:122–127
Anisha GS, Prema P (2008) Cell immobilization technique for the enhanced production of α-galactosidase by Streptomyces griseoloalbus. Bioresour Technol 99:3325–3330
Orive G, Hernández RM, Gascón AR, Pedraz JL (2006) Encapsulation of cells in alginate gels. Method Biotechnol 22:345–355
Jamuna R, Sai ST, Vora S, Ramakrishna SV (1992) Optimization of critical parameters for immobilization of yeast cells to alginate gel matrix. J Ferment Bioeng 73:319–322
Alloue W, Destain J, El Medjoub T, Ghalfi H, Kabran P, Thonart P (2008) Comparison of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase immobilization yield of entrapment, adsorption, and covalent bond techniques. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 150:51–63
Hung CP, Lo HF, Hsu WH, Chen SC, Lin LL (2008) Immobilization of Escherichia coli novablue γ-glutamyltranspeptidase in Ca-alginate- k -carrageenan beads. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 150:157–170
Oh DK, Kim HJ, Ryu SA, Rho HJ, Kim P (2001) Development of an immobilization method of l-arabinose isomerase for industrial production of tagatose. Biotechnol Lett 23:1859–1862
Novick SJ, Rozzell JD (2005) Immobilization of enzymes by covalent attachment. Method Biotechnol 17:247–271
Li S, Hu J, Liu B (2004) Use of chemically modified PMMA microspheres for enzyme immobilization. Biosystems 77:25–32
Leon J, Galvan F, Vega JM (1990) Effect of immobilization on the catalytic properties of ferredoxin-nitrite reductase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Mol Catal 58:393–403
Mohapatra BR (2008) Effect of immobilization on kinetic and thermodynamic characteristics of sulfide oxidase from Arthrobacter species. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 38:61–73
Klibanov AM (1979) Enzyme stabilization by immobilization. Anal Biochem 93:1–25
Kennedy JF, Melo EHM, Jumel K (1990) Immobilized enzymes and cells. Chem Eng Prog 86:81–89
Munjal N, Sawhney SK (2002) Stability and properties of mushroom tyrosinase entrapped in alginate, polyacrylamide and gelatin gels. Enzyme Microb Technol 30:613–619
Sahin F, Demirel G, Tumturk H (2005) A novel matrix for the immobilization of acetylcholinesterase. Int J Biol Macromol 37:148–153
Heath EC, Horecker BL, Smyrniotis PZ, Takagi Y (1958) Pentose fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum. II. l-Arabinose isomerase. J Biol Chem 231:1031–1037
Yeom SJ, Ji JH, Yoon RY, Oh DK (2008) l-Ribulose production from l-arabinose by an l-arabinose isomerase mutant from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans. Biotechnol Lett 30:1789–1793
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 21C Frontier Microbial Genomics and Applications Center Program, Ministry of Education, Science & Technology, Republic of Korea. This research was supported by a grant from the Korea Research Foundation (KRF-2007-314-D00073). This research was also supported by the 2009 KU Brain Pool of Konkuk University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YW., Prabhu, P. & Lee, JK. Alginate immobilization of recombinant Escherichia coli whole cells harboring l-arabinose isomerase for l-ribulose production. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 33, 741–748 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-009-0397-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-009-0397-7